mirror of
https://github.com/outbackdingo/firezone.git
synced 2026-01-27 10:18:54 +00:00
Refactor docs for REST API and consistency (#1404)
Also will include the following: - [x] Fixes #1281 - [x] Fixes #1218
This commit is contained in:
@@ -2,6 +2,8 @@ defmodule FzHttpWeb.JSON.ConfigurationController do
|
||||
@moduledoc api_doc: [title: "Configurations", group: "Configuration"]
|
||||
@moduledoc """
|
||||
This endpoint allows an administrator to manage Configurations.
|
||||
|
||||
Updates here can be applied at runtime with little to no downtime of affected services.
|
||||
"""
|
||||
use FzHttpWeb, :controller
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -12,7 +12,7 @@ your private network and internal applications from an intuitive web UI.
|
||||
|
||||
These docs explain how to deploy, configure, and use Firezone.
|
||||
|
||||
## Quick Start
|
||||
## Quick start
|
||||
|
||||
1. [Deploy](deploy): A step-by-step walk-through setting up Firezone.
|
||||
Start here if you are new.
|
||||
@@ -25,7 +25,7 @@ These docs explain how to deploy, configure, and use Firezone.
|
||||
Firezone and troubleshoot common issues. Consult this section
|
||||
after you successfully deploy the Firezone server.
|
||||
|
||||
## Common Configuration Guides
|
||||
## Common configuration guides
|
||||
|
||||
1. [Split Tunneling](./user-guides/use-cases/split-tunnel):
|
||||
Only route traffic to certain IP ranges through the VPN.
|
||||
@@ -38,7 +38,7 @@ These docs explain how to deploy, configure, and use Firezone.
|
||||
import SupportOptions from '@site/src/partials/_support_options.mdx';
|
||||
<SupportOptions />
|
||||
|
||||
## Contribute to Firezone
|
||||
## Contribute to firezone
|
||||
|
||||
We deeply appreciate any and all contributions to the project and do our best to
|
||||
ensure your contribution is included. To get started, see [CONTRIBUTING.md
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -2,8 +2,8 @@
|
||||
title: Debug Logs
|
||||
sidebar_position: 8
|
||||
description:
|
||||
Docker deployments of Firezone generate and store debug logs to a JSON
|
||||
file on the host machine.
|
||||
Docker deployments of Firezone generate and store debug logs to a JSON
|
||||
file on the host machine.
|
||||
---
|
||||
|
||||
:::note
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -6,33 +6,48 @@ sidebar_position: 2
|
||||
# Migrate from Omnibus to Docker
|
||||
|
||||
Chef Infra Client, the configuration system Chef Omnibus relies on, has been
|
||||
[scheduled for End-of-Life in 2024](https://docs.chef.io/versions/#supported-commercial-distributions).
|
||||
As such, Omnibus-based deployments
|
||||
will be deprecated in a future version of Firezone.
|
||||
[scheduled for End-of-Life in 2024](https://docs.chef.io/versions/).
|
||||
Firezone 0.7 will be the last version to offer Omnibus-based deployments.
|
||||
Users are encouraged to migrate to a Docker-based deployment of Firezone using
|
||||
this guide.
|
||||
|
||||
Existing Omnibus-based deployments of Firezone will continue to function as-is,
|
||||
but no officially supported RedHat or Debian packages will be published for
|
||||
Firezone 0.8 and above.
|
||||
|
||||
See this [GitHub issue tracking discussion
|
||||
](https://github.com/firezone/firezone/issues/1304) for more details.
|
||||
|
||||
Follow this guide to migrate from an Omnibus-based deployment to a Docker-based
|
||||
deployment. In most cases this can be done with minimal downtime and without
|
||||
requiring you to regenerate WireGuard configurations for each device.
|
||||
|
||||
Heavily customized deployments (such as those using an external database or
|
||||
custom reverse proxy) will likely need extra troubleshooting and manual
|
||||
steps taken to perform a successful migration.
|
||||
|
||||
Take a look at the [migration script source
|
||||
](https://github.com/firezone/firezone/blob/master/scripts/docker_migrate.sh)
|
||||
to get a detailed idea of the steps involved.
|
||||
|
||||
Estimated time to complete: **2 hours**.
|
||||
|
||||
## Steps to Migrate
|
||||
## Steps to migrate
|
||||
|
||||
1. **Back up** your server. This ensures you have a working state to roll back to
|
||||
in case anything goes wrong. At a _bare minimum_ you'll want to back up the
|
||||
in case anything goes terribly wrong. At a _bare minimum_ you'll want to back up the
|
||||
[file and directories Firezone uses
|
||||
](/reference/file-and-directory-locations/), but we recommend taking a full
|
||||
snapshot if possible.
|
||||
snapshot of your VPS if possible.
|
||||
1. Ensure you're running the latest version of Firezone. See our [upgrade guide
|
||||
](/administer/upgrade/) if not.
|
||||
1. Install the latest version of [**Docker**
|
||||
](https://docs.docker.com/engine/install/) and [Docker Compose
|
||||
](https://docs.docker.com/compose/install/linux/#install-compose)
|
||||
for your OS. **Docker Compose version 2 or higher is required**.
|
||||
We recommend using Docker Server for Linux. Docker
|
||||
Desktop will work too, but is not preferred for production use cases at this time
|
||||
because it rewrites packets under some conditions and may cause unexpected
|
||||
issues with Firezone.
|
||||
We recommend using Docker Server for Linux. Docker Desktop will work too, but is not
|
||||
preferred for production use cases at this time because it rewrites packets under
|
||||
some conditions and may cause unexpected issues with Firezone.
|
||||
1. Download and run the migration script:
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
bash <(curl -fsSL https://github.com/firezone/firezone/raw/master/scripts/docker_migrate.sh)
|
||||
@@ -40,7 +55,7 @@ bash <(curl -fsSL https://github.com/firezone/firezone/raw/master/scripts/docker
|
||||
This will ask you a few questions, then attempt to migrate your installation to
|
||||
Docker. If all goes well, your Firezone instance should be running with Docker, data intact.
|
||||
|
||||
## Rolling Back
|
||||
## Rolling back
|
||||
|
||||
If anything goes wrong, you can abort the migration by simply bringing the Docker
|
||||
services down and the Omnibus ones back up:
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -20,14 +20,14 @@ starting with an empty database. You have been warned.
|
||||
|
||||
:::caution
|
||||
Replacing `GUARDIAN_SECRET_KEY`, `SECRET_KEY_BASE`, `LIVE_VIEW_SIGNING_SALT`,
|
||||
`COOKIE_SIGNING_SALT`, or `COOKIE_ENCRYPTION_SALT`
|
||||
will render all browser sessions and JWTs useless.
|
||||
`COOKIE_SIGNING_SALT`, and `COOKIE_ENCRYPTION_SALT` will reset all browser
|
||||
sessions and REST API tokens.
|
||||
:::
|
||||
|
||||
Use the procedure below to regenerate secrets:
|
||||
|
||||
<Tabs>
|
||||
<TabItem value="docker" label="Docker" default>
|
||||
<TabItem value="docker" label="Docker" default>
|
||||
|
||||
Navigate to the Firezone installation directory, then:
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -36,22 +36,25 @@ mv .env .env.bak
|
||||
docker run firezone/firezone bin/gen-env > .env
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
</TabItem>
|
||||
<TabItem value="omnibus" label="Omnibus">
|
||||
Now, move desired env vars from `.env.bak` back to `.env`, keeping
|
||||
the new secrets intact.
|
||||
|
||||
</TabItem>
|
||||
<TabItem value="omnibus" label="Omnibus">
|
||||
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
mv /etc/firezone/secrets.json /etc/firezone/secrets.bak.json
|
||||
sudo firezone-ctl reconfigure
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
</TabItem>
|
||||
</TabItem>
|
||||
</Tabs>
|
||||
|
||||
## Regenerate WireGuard private key
|
||||
|
||||
:::warning
|
||||
Replacing the WireGuard private key will render all existing device configs
|
||||
useless. Only do so if you're prepared to also regenerate device configs
|
||||
invalid. Only do so if you're prepared to also regenerate device configs
|
||||
after regenerating the WireGuard private key.
|
||||
:::
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -59,16 +62,17 @@ To regenerate WireGuard private key, simply move or rename the private key file.
|
||||
Firezone will generate a new one on next start.
|
||||
|
||||
<Tabs>
|
||||
<TabItem value="docker" label="Docker" default>
|
||||
<TabItem value="docker" label="Docker" default>
|
||||
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
cd $HOME/.firezone
|
||||
docker-compose stop firezone
|
||||
sudo mv $HOME/.firezone/firezone/private_key $HOME/.firezone/firezone/private_key.bak
|
||||
sudo mv firezone/private_key firezone/private_key.bak
|
||||
docker-compose start firezone
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
</TabItem>
|
||||
<TabItem value="omnibus" label="Omnibus">
|
||||
</TabItem>
|
||||
<TabItem value="omnibus" label="Omnibus">
|
||||
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
sudo firezone-ctl stop phoenix
|
||||
@@ -76,5 +80,5 @@ sudo mv /var/opt/firezone/cache/wg_private_key /var/opt/firezone/cache/wg_privat
|
||||
sudo firezone-ctl start phoenix
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
</TabItem>
|
||||
</TabItem>
|
||||
</Tabs>
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -61,13 +61,9 @@ Similarly, to clear SAML configs:
|
||||
</TabItem>
|
||||
</Tabs>
|
||||
|
||||
## Debugging portal WebSocket connectivity issues
|
||||
|
||||
The portal UI requires a secure websocket connection to function. To facilitate
|
||||
this, the Firezone phoenix service checks the `Host` header for inbound
|
||||
websocket connections and only permits the connection if it matches the host
|
||||
portion of your `default['firezone']['external_url']` variable.
|
||||
## Debugging WebSocket connectivity issues
|
||||
|
||||
The Web UI requires a secure websocket connection to function.
|
||||
If a secure websocket connection can't be established, you'll see a red dot
|
||||
indicator in the upper-right portion of the Firezone web UI and a corresponding
|
||||
message when you hover over it:
|
||||
@@ -77,8 +73,10 @@ Secure websocket not connected! ...
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
If you're accessing Firezone using the same URL defined in your
|
||||
`default['firezone']['external_url']` variable from above, the issue is likely
|
||||
to be in your reverse proxy configuration.
|
||||
`EXTERNAL_URL` variable from above, the issue is likely to be in your reverse
|
||||
proxy configuration. Ensure your reverse proxy has WebSocket support enabled
|
||||
for Firezone. If you're using the default Caddy reverse proxy, WebSocket
|
||||
is enabled and configured automatically.
|
||||
|
||||
In most cases, you'll find clues in one or more of the following locations:
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -153,12 +151,14 @@ To Action From
|
||||
|
||||
## Admin login isn't working
|
||||
|
||||
If the password for the account with email `ADMIN_EMAIL` isn't working, you can reset it using the process below.
|
||||
If the password for the account with email `ADMIN_EMAIL` isn't working, you can
|
||||
reset it using the process below.
|
||||
|
||||
<Tabs>
|
||||
<TabItem value="docker" label="Docker">
|
||||
<TabItem value="docker" label="Docker" default>
|
||||
|
||||
First change directory to your Firezone root, then run the `bin/create-or-reset-admin` script
|
||||
First change directory to your Firezone installation directory
|
||||
(`$HOME/.firezone` by default), then run the `bin/create-or-reset-admin` script
|
||||
to reset the admin user's password. The password for the user specified by
|
||||
`ADMIN_EMAIL`
|
||||
in `$HOME/.firezone/.env` will be reset to the `DEFAULT_ADMIN_PASSWORD` variable.
|
||||
@@ -172,7 +172,6 @@ docker compose exec firezone bin/create-or-reset-admin
|
||||
password will not re-enable it.
|
||||
|
||||
</TabItem>
|
||||
|
||||
<TabItem value="omnibus" label="Omnibus">
|
||||
|
||||
Run the following command to reset the password on the default admin user.
|
||||
@@ -186,15 +185,16 @@ sudo firezone-ctl create-or-reset-admin
|
||||
|
||||
## Re-enable local authentication via CLI
|
||||
|
||||
When using the local authentication method we recommend adding a
|
||||
[TOTP-based second factor](/authenticate/multi-factor/) to admin accounts.
|
||||
If you've configured an [OIDC](/authenticate/oidc/) or [SAML](/authenticate/saml/)
|
||||
provider, you can consider disabling local authentication for additional security.
|
||||
|
||||
If issues arise with your identity provider integration, it's possible you
|
||||
If, however, issues arise with your identity provider integration, it's possible you
|
||||
could be locked out of the admin portal. To re-enable local authentication so
|
||||
you can log in and resolve the issue, run the following query on the host of
|
||||
your Firezone instance:
|
||||
you can log in and resolve the issue, you can temporarily re-enable local authentication
|
||||
via the [REST API](/reference/rest-api/configurations).
|
||||
|
||||
If that's not an option, you can re-enable local authentication by
|
||||
running the following commands on the host of your Firezone instance:
|
||||
|
||||
```shell
|
||||
cd $HOME/.firezone
|
||||
@@ -202,5 +202,4 @@ docker compose exec postgres psql -U postgres -h 127.0.0.1 -d firezone -c "UPDAT
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
import SupportOptions from '@site/src/partials/_support_options.mdx';
|
||||
|
||||
<SupportOptions />
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -83,8 +83,8 @@ variables to the DB.
|
||||
### `AUTH_OIDC_JSON` config
|
||||
|
||||
Similar to the `WIREGUARD_*` env vars above, the `AUTH_OIDC_JSON` env var has similarly
|
||||
been moved to the database and can be configured at `/settings/site`. <!--In Firezone 0.7 this
|
||||
is now configurable via the REST API.-->
|
||||
been moved to the database and can be configured at `/settings/site`. In Firezone 0.7 this
|
||||
is now configurable via the [REST API](/reference/rest-api/configurations) as well.
|
||||
|
||||
### Fix IPv6
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -37,33 +37,23 @@ Open a [Github issue](https://github.com/firezone/firezone/issues)
|
||||
to request documentation or submit a pull request to add documentation for your
|
||||
provider.
|
||||
|
||||
### The OIDC Redirect URL
|
||||
### The OIDC redirect URI
|
||||
|
||||
For each OIDC provider a corresponding URL is created for redirecting to
|
||||
the configured provider's sign-in URL. The URL format is `https://firezone.example.com/auth/oidc/PROVIDER`
|
||||
where `PROVIDER` is the OIDC key for that particular provider.
|
||||
the configured provider's sign-in URL. The URL format is `https://firezone.example.com/auth/oidc/CONFIG_ID`
|
||||
where `CONFIG_ID` is the OIDC Config ID for that particular provider.
|
||||
|
||||
For example, the OIDC config below
|
||||
For example, the OIDC config below:
|
||||
|
||||
```json
|
||||
{
|
||||
"google": {
|
||||
"client_id": "...",
|
||||
"...": "..."
|
||||
},
|
||||
"okta": {
|
||||
"client_id": "...",
|
||||
"...": "..."
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
<center>
|
||||
<img width="509" alt="config-oidc" src="https://user-images.githubusercontent.com/167144/216438674-a2b64b3b-2ed6-43dc-b554-de9c055dc741.png"/>
|
||||
</center>
|
||||
|
||||
would generate the following URLs:
|
||||
would generate the following OIDC login URL:
|
||||
|
||||
* `https://firezone.example.com/auth/oidc/google`
|
||||
* `https://firezone.example.com/auth/oidc/okta`
|
||||
|
||||
These URLs could then be distributed to end users for direct navigation to
|
||||
This URL could then be distributed to end users for direct navigation to
|
||||
the identity provider's login portal for authentication to Firezone.
|
||||
|
||||
## Enforce periodic re-authentication
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -3,25 +3,27 @@ title: Local Authentication
|
||||
sidebar_position: 1
|
||||
---
|
||||
|
||||
# Local authentication (username & password)
|
||||
# Local authentication (email & password)
|
||||
|
||||
By default, Firezone will use local email / password for authenticating users to
|
||||
the Firezone portal. Administrators can add users and assign their passwords on
|
||||
the `/users` page. See [Add users](/user-guides/add-users/) for more details.
|
||||
|
||||
:::note
|
||||
:::caution
|
||||
Although local authentication is quick and easy to get started with, you can
|
||||
limit attack surface by [disabling local authentication](#disabling-local-authentication)
|
||||
altogether. See our [OIDC](/authenticate/oidc/) or [SAML](/authenticate/saml/) guides
|
||||
for details.
|
||||
for details. For production deployments it's usually a good idea to **disable
|
||||
local authentication** and enforce MFA through your identity provider.
|
||||
:::
|
||||
|
||||
We recommend [enabling TOTP-based MFA](/authenticate/multi-factor/) for any
|
||||
accounts that use the local authentication method.
|
||||
If you choose to keep Local authentication enabled, we recommend [enabling TOTP-based MFA
|
||||
](/authenticate/multi-factor/) for any accounts that use the local authentication method.
|
||||
|
||||
## Disabling local authentication
|
||||
|
||||
Local authentication can be enabled or disabled from the `/settings/security` page.
|
||||
Local authentication can be enabled or disabled from the `/settings/security` page
|
||||
or via the [REST API](/reference/rest-api/configurations).
|
||||
If you've disabled local authentication and can no longer authenticate to the portal
|
||||
to re-enable it, see our [troubleshooting guide
|
||||
](/administer/troubleshoot#re-enable-local-authentication-via-cli) for re-enabling
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -2,8 +2,8 @@
|
||||
title: Multi-Factor Authentication
|
||||
sidebar_position: 2
|
||||
description:
|
||||
Enforce multi-factor authentication with Firezone's WireGuard®-based
|
||||
secure access platform.
|
||||
Enforce multi-factor authentication with Firezone's WireGuard®-based
|
||||
secure access platform.
|
||||
---
|
||||
|
||||
# Multi-factor authentication (MFA)
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -2,9 +2,9 @@
|
||||
title: OpenID Connect
|
||||
sidebar_position: 10
|
||||
description:
|
||||
Enforce single sign-on with your identity provider. Integrate
|
||||
providers like Okta, Google, Azure, and JumpCloud using Firezone's
|
||||
OIDC connector.
|
||||
Setup single sign-on with your identity provider. Integrate
|
||||
providers like Okta, Google, Azure, and JumpCloud using Firezone's
|
||||
OpenID Connect (OIDC) connector.
|
||||
---
|
||||
|
||||
# Integrate your identity provider using OIDC
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -2,9 +2,9 @@
|
||||
title: Auth0
|
||||
sidebar_position: 1
|
||||
description:
|
||||
Enforce 2FA/MFA for users of Firezone's WireGuard®-based
|
||||
secure access platform. This guide walks through integrating Auth0
|
||||
for single sign-on using OpenID Connect (OIDC).
|
||||
Enforce 2FA/MFA for users of Firezone's WireGuard®-based
|
||||
secure access platform. This guide walks through integrating Auth0
|
||||
for single sign-on using OpenID Connect (OIDC).
|
||||
---
|
||||
|
||||
# Enable SSO with Auth0 (OIDC)
|
||||
@@ -26,9 +26,7 @@ to provide Firezone with the user's email in the returned claims.
|
||||
which returns a JSON document used to construct subsequent requests to this OIDC
|
||||
provider.
|
||||
|
||||
## Obtain Config Settings
|
||||
|
||||
### Step 1 - Create and set up an application
|
||||
## Step 1: Obtain OIDC configuration parameters
|
||||
|
||||
In the Auth0 dashboard, create an application.
|
||||
Select **Regular Web Application** as the application type.
|
||||
@@ -40,8 +38,7 @@ modify the following parameters:
|
||||
|
||||
1. **Name**: `Firezone`
|
||||
1. **Domain**: The domain will be used to construct
|
||||
the url to retrieve the OIDC discovery document -
|
||||
`https://<AUTH0_DOMAIN>/.well-known/openid-configuration`
|
||||
the url to retrieve the OIDC discovery document - `https://<AUTH0_DOMAIN>/.well-known/openid-configuration`
|
||||
1. **Icon**:
|
||||
[Firezone icon](https://user-images.githubusercontent.com/52545545/156854754-da66a9e1-33d5-47f5-877f-eff8b330ab2b.png)
|
||||
(save link as).
|
||||
@@ -52,7 +49,7 @@ the url to retrieve the OIDC discovery document -
|
||||

|
||||
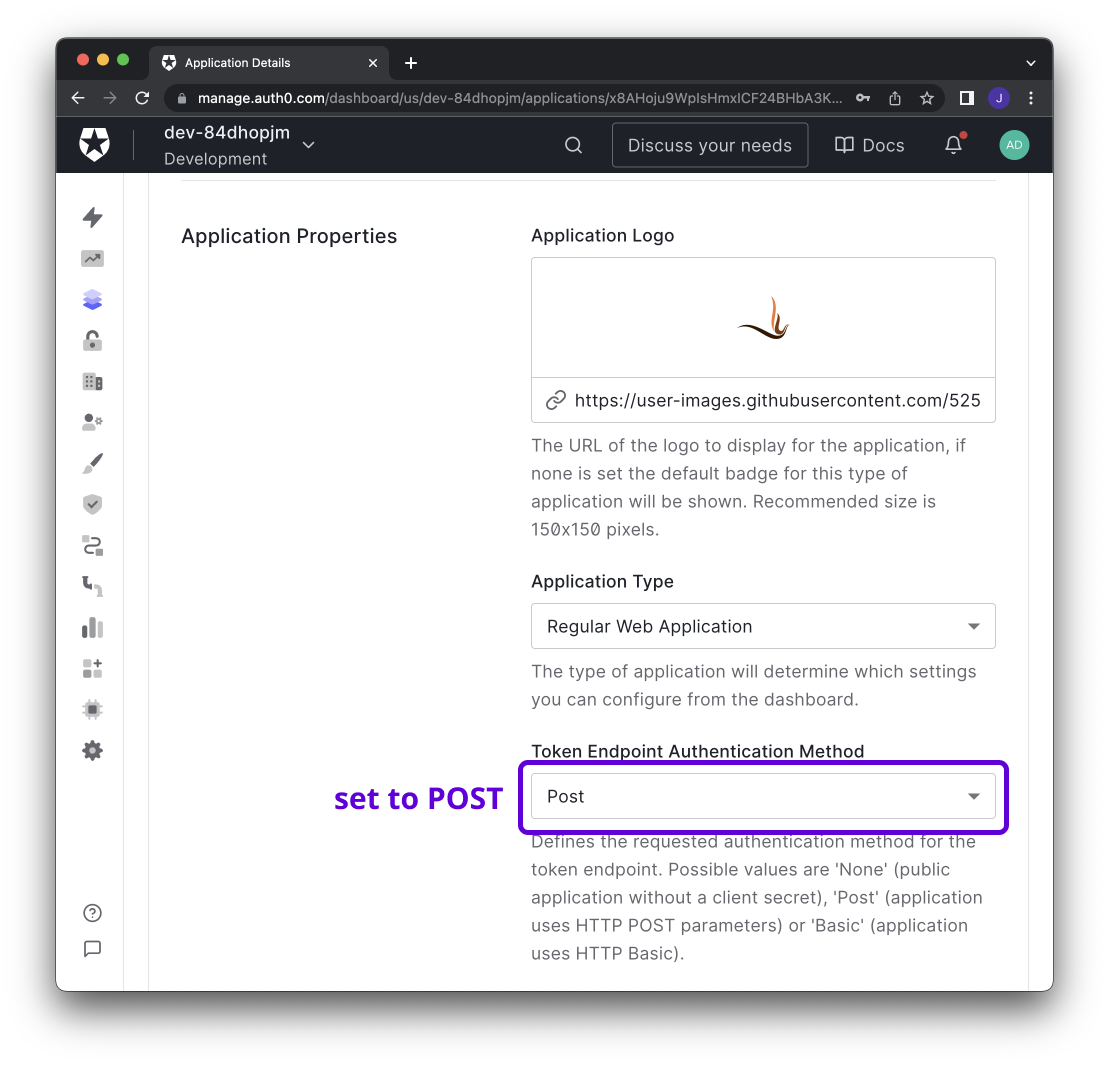
|
||||
|
||||
## Integrate With Firezone
|
||||
## Step 2: Integrate with Firezone
|
||||
|
||||
Navigate to the `/settings/security` page in the admin portal, click
|
||||
"Add OpenID Connect Provider" and enter the details you obtained in the steps
|
||||
@@ -64,7 +61,7 @@ an unprivileged user when signing in via this authentication mechanism.
|
||||
And that's it! The configuration should be updated immediately.
|
||||
You should now see a `Sign in with Auth0` button on the sign in page.
|
||||
|
||||
## Restricting Access to Certain Users
|
||||
## Step 3 (optional): Restrict access to specific users
|
||||
|
||||
Auth0 supports setting access policies to control which users
|
||||
can access the Firezone application. See Auth0's
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -2,9 +2,9 @@
|
||||
title: Azure Active Directory
|
||||
sidebar_position: 2
|
||||
description:
|
||||
Enforce 2FA/MFA for users of Firezone's WireGuard®-based
|
||||
secure access platform. This guide walks through integrating Azure AD
|
||||
for single sign-on using OpenID Connect (OIDC).
|
||||
Enforce 2FA/MFA for users of Firezone's WireGuard®-based
|
||||
secure access platform. This guide walks through integrating Azure AD
|
||||
for single sign-on using OpenID Connect (OIDC).
|
||||
---
|
||||
|
||||
# Enable SSO with Azure Active Directory (OIDC)
|
||||
@@ -28,7 +28,7 @@ OIDC provider.
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
## Obtain Config Settings
|
||||
## Step 1: Obtain configuration parameters
|
||||
|
||||
_This guide is adapted from the [Azure Active Directory documentation](https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/azure/active-directory/fundamentals/auth-oidc)._
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -64,7 +64,7 @@ click `Add a permission`, and select `Microsoft Graph`. Add `email`, `openid`,
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
## Integrate With Firezone
|
||||
## Step 2: Integrate with Firezone
|
||||
|
||||
Navigate to the `/settings/security` page in the admin portal, click
|
||||
"Add OpenID Connect Provider" and enter the details you obtained in the steps
|
||||
@@ -76,7 +76,7 @@ an unprivileged user when signing in via this authentication mechanism.
|
||||
And that's it! The configuration should be updated immediately.
|
||||
You should now see a `Sign in with Azure` button on the sign in page.
|
||||
|
||||
## Restricting Access to Certain Users
|
||||
## Step 3 (optional): Restrict access to specific users
|
||||
|
||||
Azure AD allows admins to restrict OAuth application access to a subset of users
|
||||
within your organization. See Microsoft's
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -2,9 +2,9 @@
|
||||
title: Google Workspace
|
||||
sidebar_position: 3
|
||||
description:
|
||||
Enforce 2FA/MFA for users of Firezone's WireGuard®-based
|
||||
secure access platform. This guide walks through integrating Google Workspace
|
||||
for single sign-on using OpenID Connect (OIDC).
|
||||
Enforce 2FA/MFA for users of Firezone's WireGuard®-based
|
||||
secure access platform. This guide walks through integrating Google Workspace
|
||||
for single sign-on using OpenID Connect (OIDC).
|
||||
---
|
||||
|
||||
# Enable SSO with Google Workspace (OIDC)
|
||||
@@ -28,9 +28,7 @@ OIDC provider.
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
## Obtain Config Settings
|
||||
|
||||
### Step 1 - OAuth Config Screen
|
||||
## Step 1: Configure OAuth consent screen
|
||||
|
||||
If this is the first time you are creating a new OAuth client ID, you will
|
||||
be asked to configure a consent screen.
|
||||
@@ -56,7 +54,7 @@ On the next step add the following scopes:
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
### Step 2 - Create OAuth Client IDs
|
||||
## Step 2: Create OAuth client
|
||||
|
||||
_This section is based off Google's own documentation on
|
||||
[setting up OAuth 2.0](https://support.google.com/cloud/answer/6158849)._
|
||||
@@ -81,7 +79,7 @@ These will be used together with the redirect URI in the next step.
|
||||
|
||||
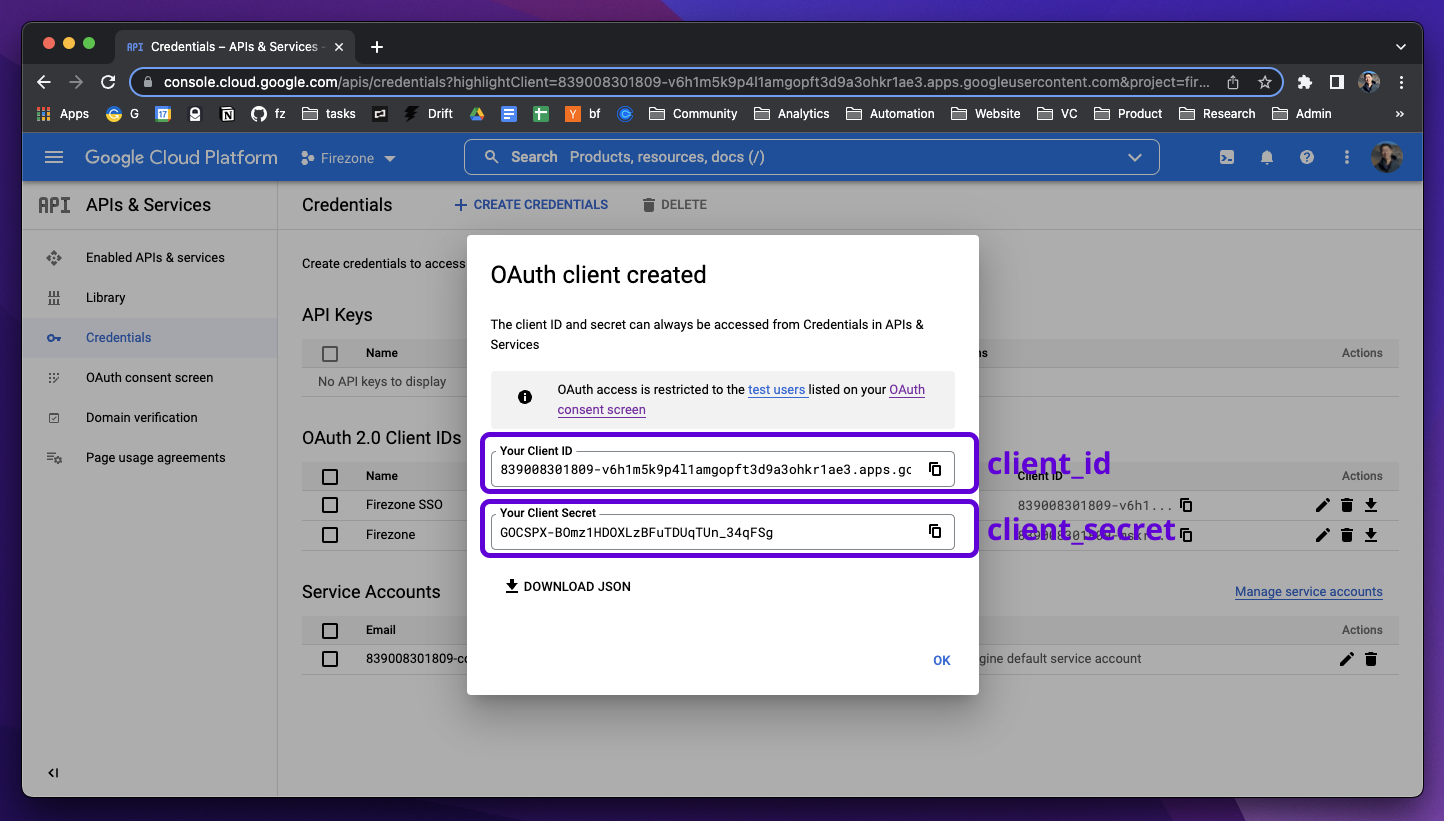
|
||||
|
||||
## Integrate with Firezone
|
||||
## Step 3: Integrate with Firezone
|
||||
|
||||
Navigate to the `/settings/security` page in the admin portal, click
|
||||
"Add OpenID Connect Provider" and enter the details you obtained in the steps
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -2,9 +2,9 @@
|
||||
title: Keycloak
|
||||
sidebar_position: 4
|
||||
description:
|
||||
Enforce 2FA/MFA for users of Firezone's WireGuard®-based
|
||||
secure access platform. This guide walks through integrating Keycloak
|
||||
for single sign-on using OpenID Connect (OIDC).
|
||||
Enforce 2FA/MFA for users of Firezone's WireGuard®-based
|
||||
secure access platform. This guide walks through integrating Keycloak
|
||||
for single sign-on using OpenID Connect (OIDC).
|
||||
---
|
||||
|
||||
# Enable SSO with Keycloak (OIDC)
|
||||
@@ -26,14 +26,14 @@ to provide Firezone with the user's email in the returned claims.
|
||||
which returns a JSON document used to construct subsequent requests to this
|
||||
OIDC provider.
|
||||
|
||||
## Obtain Config Settings
|
||||
## Step 1: Obtain configuration parameters
|
||||
|
||||
In the Keycloak Admin Console, make sure the realm you want to use with Firezone
|
||||
is selected.
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
### Create Firezone Client
|
||||
### Create Firezone OAuth client
|
||||
|
||||
Create a new Client for Firezone by navigating to **Clients > Create Client** and
|
||||
configure the following:
|
||||
@@ -67,7 +67,7 @@ copying the **OpenID Endpoint Configuration** link at the bottom of the page.
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
## Integrate With Firezone
|
||||
## Step 2: Integrate with Firezone
|
||||
|
||||
Navigate to the `/settings/security` page in the admin portal, click
|
||||
"Add OpenID Connect Provider" and enter the details you obtained in the steps
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -2,9 +2,9 @@
|
||||
title: Okta
|
||||
sidebar_position: 5
|
||||
description:
|
||||
Enforce 2FA/MFA for users of Firezone's WireGuard®-based
|
||||
secure access platform. This guide walks through integrating Okta
|
||||
for single sign-on using OpenID Connect (OIDC).
|
||||
Enforce 2FA/MFA for users of Firezone's WireGuard®-based
|
||||
secure access platform. This guide walks through integrating Okta
|
||||
for single sign-on using OpenID Connect (OIDC).
|
||||
---
|
||||
|
||||
# Enable SSO with Okta (OIDC)
|
||||
@@ -28,7 +28,7 @@ OIDC provider.
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
## Step 1 - Create Okta App Integration
|
||||
## Step 1: Create Okta app integration
|
||||
|
||||
_This section of the guide is based on
|
||||
[Okta's documentation](https://help.okta.com/en/prod/Content/Topics/Apps/Apps_App_Integration_Wizard_OIDC.htm)._
|
||||
@@ -62,7 +62,7 @@ and **Okta Domain**. These 3 values will be used in Step 2 to configure Firezone
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
## Integrate With Firezone
|
||||
## Step 2: Integrate with Firezone
|
||||
|
||||
Navigate to the `/settings/security` page in the admin portal, click
|
||||
"Add OpenID Connect Provider" and enter the details you obtained in the steps
|
||||
@@ -74,7 +74,7 @@ an unprivileged user when signing in via this authentication mechanism.
|
||||
And that's it! The configuration should be updated immediately.
|
||||
You should now see a `Sign in with Okta` button on the sign in page.
|
||||
|
||||
## Restricting Access to Certain Users in Okta
|
||||
## Step 3 (optional): Restrict Access to specific users
|
||||
|
||||
Okta can limit the users with access to the Firezone app. To do this,
|
||||
go to the Assignments tab of the Firezone App Integration in your Okta
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -2,9 +2,9 @@
|
||||
title: OneLogin
|
||||
sidebar_position: 6
|
||||
description:
|
||||
Enforce 2FA/MFA for users of Firezone's WireGuard®-based
|
||||
secure access platform. This guide walks through integrating OneLogin
|
||||
for single sign-on using OpenID Connect (OIDC).
|
||||
Enforce 2FA/MFA for users of Firezone's WireGuard®-based
|
||||
secure access platform. This guide walks through integrating OneLogin
|
||||
for single sign-on using OpenID Connect (OIDC).
|
||||
---
|
||||
|
||||
# Enable SSO with OneLogin (OIDC)
|
||||
@@ -26,9 +26,7 @@ to provide Firezone with the user's email in the returned claims.
|
||||
which returns a JSON document used to construct subsequent requests to this
|
||||
OIDC provider.
|
||||
|
||||
## Obtain Config Settings
|
||||
|
||||
### Step 1 - Configure Custom Connector
|
||||
## Step 1: Create custom connector
|
||||
|
||||
Create a new OIDC connector by visiting **Appliances > Custom Connectors**.
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -43,7 +41,7 @@ or
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
### Step 2 - Configure the OIDC Application
|
||||
## Step 2: Obtain configuration parameters
|
||||
|
||||
Next, click **Add App to Connector** to create an OIDC application.
|
||||
Visit the **SSO** tab, then change the token endpoint authentication method
|
||||
@@ -54,7 +52,7 @@ on this page as well.
|
||||
|
||||
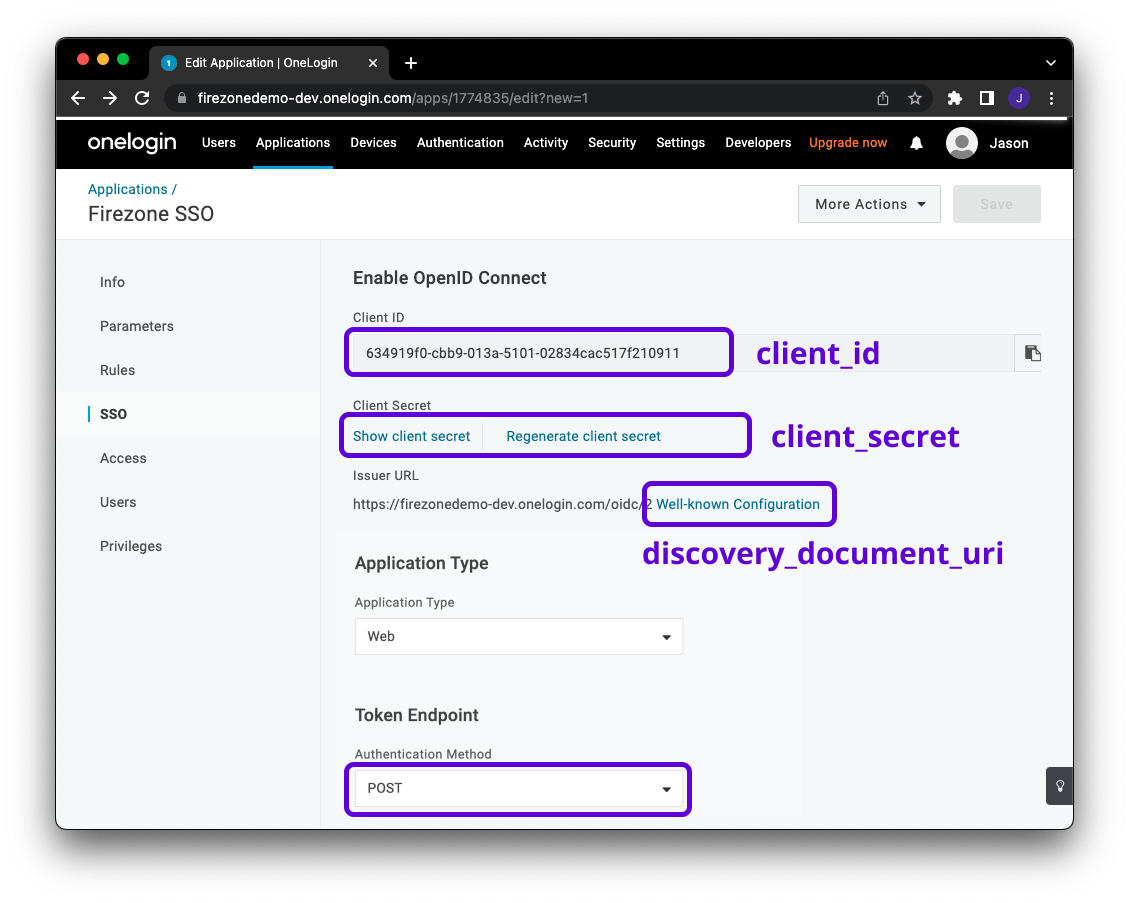
|
||||
|
||||
## Integrate With Firezone
|
||||
## Step 3: Integrate with Firezone
|
||||
|
||||
Navigate to the `/settings/security` page in the admin portal, click
|
||||
"Add OpenID Connect Provider" and enter the details you obtained in the steps
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -2,9 +2,9 @@
|
||||
title: Zitadel
|
||||
sidebar_position: 7
|
||||
description:
|
||||
Enforce 2FA/MFA for users of Firezone's WireGuard®-based
|
||||
secure access platform. This guide walks through integrating Zitadel
|
||||
for single sign-on using OpenID Connect (OIDC).
|
||||
Enforce 2FA/MFA for users of Firezone's WireGuard®-based
|
||||
secure access platform. This guide walks through integrating Zitadel
|
||||
for single sign-on using OpenID Connect (OIDC).
|
||||
---
|
||||
|
||||
# Enable SSO with Zitadel (OIDC)
|
||||
@@ -93,7 +93,7 @@ an unprivileged user when signing in via this authentication mechanism.
|
||||
And that's it! The configuration should be updated immediately.
|
||||
You should now see a `Sign in with Zitadel` button on the sign in page.
|
||||
|
||||
## Restricting Access to Certain Users in Zitadel
|
||||
## Step 3 (optional): Restrict access to specific users
|
||||
|
||||
Zitadel can limit which users have access to Firezone. To do this,
|
||||
go to the project where your created your application. In **General** you can
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -2,9 +2,9 @@
|
||||
title: SAML 2.0
|
||||
sidebar_position: 11
|
||||
description:
|
||||
Enforce single sign-on with your identity provider. Integrate
|
||||
providers like Okta, Google, OneLogin, and JumpCloud using Firezone's
|
||||
SAML 2.0 connector.
|
||||
Enforce single sign-on with your identity provider. Integrate
|
||||
providers like Okta, Google, OneLogin, and JumpCloud using Firezone's
|
||||
SAML 2.0 connector.
|
||||
---
|
||||
|
||||
# Integrate your identity provider using SAML 2.0
|
||||
@@ -27,36 +27,37 @@ Occasionally, providers that don't implement the full SAML 2.0 standard or use
|
||||
uncommon configurations may be problematic. If this is the case, [contact us](
|
||||
https://www.firezone.dev/contact/sales?utm_source=docs.firezone.dev) about a custom integration.
|
||||
|
||||
## Prerequisites
|
||||
## Custom SAML cert and keyfile
|
||||
|
||||
Before using SAML 2.0 in Firezone, you'll first need to generate a set of
|
||||
private and public keys using the RSA or DSA algorithms along with an X.509
|
||||
certificate that contains the public key. This can be generated with `openssl`
|
||||
using the following one-liner:
|
||||
SAML 2.0 requires a set of private and public keys using the RSA or
|
||||
DSA algorithms along with an X.509 certificate that contains the public key.
|
||||
|
||||
```text
|
||||
Firezone automatically generates these for on both Docker and Omnibus-based
|
||||
deployments. If you'd like to use your own cert and key, however, you can generate
|
||||
them with `openssl`:
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
openssl req -x509 -sha256 -nodes -days 365 -newkey rsa:2048 -keyout saml.key -out saml.crt
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Now, configure your Firezone portal to use these:
|
||||
Then use them with your Firezone installation:
|
||||
|
||||
<Tabs>
|
||||
<TabItem value="docker" label="Docker" default>
|
||||
<TabItem value="docker" label="Docker" default>
|
||||
|
||||
Set the `SAML_KEY_PATH` and `SAML_CERT_PATH` environment variables to
|
||||
Set the `SAML_KEYFILE_PATH` and `SAML_CERTFILE_PATH` environment variables to
|
||||
the path containing your `saml.key` and `saml.crt` above. If using our [example
|
||||
docker compose file](https://github.com/firezone/firezone/blob/master/docker-compose.prod.yml),
|
||||
which includes a volume for mapping configuration,
|
||||
save these files to `$HOME/.firezone/firezone` on the Docker host and set the
|
||||
`SAML_KEY_PATH=/var/firezone/saml.key` and
|
||||
`SAML_CERT_PATH=/var/firezone/saml.crt` environment variables for the Firezone
|
||||
`SAML_KEYFILE_PATH=/var/firezone/saml.key` and
|
||||
`SAML_CERTFILE_PATH=/var/firezone/saml.crt` environment variables for the Firezone
|
||||
container.
|
||||
|
||||
</TabItem>
|
||||
<TabItem value="omnibus" label="Omnibus">
|
||||
</TabItem>
|
||||
<TabItem value="omnibus" label="Omnibus">
|
||||
|
||||
Set the following attributes in your `/etc/firezone/firezone.rb`
|
||||
configuration file:
|
||||
Set the following attributes in your `/etc/firezone/firezone.rb` configuration file:
|
||||
|
||||
```ruby
|
||||
default['firezone']['authentication']['saml']['key'] = '/path/to/your/saml.key'
|
||||
@@ -65,7 +66,7 @@ default['firezone']['authentication']['saml']['cert'] = '/path/to/your/saml.crt'
|
||||
|
||||
and run `firezone-ctl reconfigure` to pick up the changes.
|
||||
|
||||
</TabItem>
|
||||
</TabItem>
|
||||
</Tabs>
|
||||
|
||||
## General setup instructions
|
||||
@@ -74,9 +75,6 @@ Once you've configured Firezone with an X.509 certificate and corresponding
|
||||
private key as shown above, you'll need a few more things to set up a generic
|
||||
SAML integration.
|
||||
|
||||
Use these general instructions to configure a SAML connector for a provider not listed
|
||||
above.
|
||||
|
||||
### IdP metadata document
|
||||
|
||||
You'll need to get the SAML Metadata XML document from your identity provider. In most
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -2,22 +2,17 @@
|
||||
title: Google Workspace
|
||||
sidebar_position: 2
|
||||
description:
|
||||
Enforce 2FA/MFA using Google Workspace for users of Firezone's WireGuard®-based
|
||||
secure access platform. This guide walks through integrating Google Workspace
|
||||
for single sign-on using the SAML 2.0 connector.
|
||||
Enforce 2FA/MFA using Google Workspace for users of Firezone's WireGuard®-based
|
||||
secure access platform. This guide walks through integrating Google Workspace
|
||||
for single sign-on using the SAML 2.0 connector.
|
||||
---
|
||||
|
||||
# Enable SSO with Google Workspace (SAML 2.0)
|
||||
|
||||
:::note
|
||||
This guide assumes you have completed the prerequisite steps
|
||||
(e.g. generate self-signed X.509 certificates) outlined [here](/authenticate/saml#prerequisites).
|
||||
:::
|
||||
|
||||
Firezone supports Single Sign-On (SSO) using Google through the generic SAML 2.0
|
||||
connector. This guide will walk you through how to configure the integration.
|
||||
|
||||
## Create a SAML connector
|
||||
## Step 1: Create a SAML connector
|
||||
|
||||
In the Google Workspace admin portal, create a new SAML app under
|
||||
the Application > Web and mobile apps tab. Use the following config values during setup:
|
||||
@@ -37,7 +32,7 @@ the Application > Web and mobile apps tab. Use the following config values durin
|
||||
Once complete, save the changes and download the SAML metadata document. You'll need
|
||||
to copy-paste the contents of this document into the Firezone portal in the next step.
|
||||
|
||||
## Add SAML identity provider to Firezone
|
||||
## Step 2: Add SAML identity provider to Firezone
|
||||
|
||||
In the Firezone portal, add a SAML identity provider under the Security tab
|
||||
by filling out the following information:
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -2,9 +2,9 @@
|
||||
title: JumpCloud
|
||||
sidebar_position: 4
|
||||
description:
|
||||
Enforce 2FA/MFA using JumpCloud for users of Firezone's WireGuard®-based
|
||||
secure access platform. This guide walks through integrating JumpCloud
|
||||
for single sign-on using the SAML 2.0 connector.
|
||||
Enforce 2FA/MFA using JumpCloud for users of Firezone's WireGuard®-based
|
||||
secure access platform. This guide walks through integrating JumpCloud
|
||||
for single sign-on using the SAML 2.0 connector.
|
||||
---
|
||||
|
||||
# Enable SSO with JumpCloud (SAML 2.0)
|
||||
@@ -17,7 +17,7 @@ This guide assumes you have completed the prerequisite steps
|
||||
Firezone supports Single Sign-On (SSO) using JumpCloud through the generic SAML 2.0 connector.
|
||||
This guide will walk you through how to configure the integration.
|
||||
|
||||
## Create a SAML connector
|
||||
## Step 1: Create a SAML connector
|
||||
|
||||
In the JumpCloud admin portal, create a new App under
|
||||
the SSO tab. At the bottom of the popup window, click `Custom SAML App`.
|
||||
@@ -46,7 +46,7 @@ Now, download the IdP Metadata document by selecting the App you just created
|
||||
and then clicking the `export metadata` button in the upper-right. You'll need
|
||||
to copy-paste the contents of this document into the Firezone portal in the next step.
|
||||
|
||||
## Add SAML identity provider to Firezone
|
||||
## Step 2: Add SAML identity provider to Firezone
|
||||
|
||||
In the Firezone portal, add a SAML identity provider under the Security tab
|
||||
by filling out the following information:
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -2,9 +2,9 @@
|
||||
title: Okta
|
||||
sidebar_position: 1
|
||||
description:
|
||||
Enforce 2FA/MFA using Okta for users of Firezone's WireGuard®-based
|
||||
secure access platform. This guide walks through integrating Okta
|
||||
for single sign-on using the SAML 2.0 connector.
|
||||
Enforce 2FA/MFA using Okta for users of Firezone's WireGuard®-based
|
||||
secure access platform. This guide walks through integrating Okta
|
||||
for single sign-on using the SAML 2.0 connector.
|
||||
---
|
||||
|
||||
# Enable SSO with Okta (SAML 2.0)
|
||||
@@ -16,7 +16,7 @@ This guide assumes you have completed the prerequisite steps
|
||||
|
||||
Firezone supports Single Sign-On (SSO) using Okta through the generic SAML 2.0 connector. This guide will walk you through how to configure the integration.
|
||||
|
||||
## Create a SAML connector
|
||||
## Step 1: Create a SAML connector
|
||||
|
||||
In the Okta admin portal, create a new app integration under
|
||||
the Application tab. Select `SAML 2.0` as the authentication method.
|
||||
@@ -41,7 +41,7 @@ After creating the SAML connector, visit the `View SAML setup instructions` link
|
||||
the Sign On tab to download the metadata document. You'll need
|
||||
to copy-paste the contents of this document into the Firezone portal in the next step.
|
||||
|
||||
## Add SAML identity provider to Firezone
|
||||
## Step 2: Add SAML identity provider to Firezone
|
||||
|
||||
In the Firezone portal, add a SAML identity provider under the Security tab
|
||||
by filling out the following information:
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -2,9 +2,9 @@
|
||||
title: OneLogin
|
||||
sidebar_position: 3
|
||||
description:
|
||||
Enforce 2FA/MFA using Onelogin for users of Firezone's WireGuard®-based
|
||||
secure access platform. This guide walks through integrating OneLogin
|
||||
for single sign-on using the SAML 2.0 connector.
|
||||
Enforce 2FA/MFA using Onelogin for users of Firezone's WireGuard®-based
|
||||
secure access platform. This guide walks through integrating OneLogin
|
||||
for single sign-on using the SAML 2.0 connector.
|
||||
---
|
||||
|
||||
# Enable SSO with OneLogin (SAML 2.0)
|
||||
@@ -17,7 +17,7 @@ This guide assumes you have completed the prerequisite steps
|
||||
Firezone supports Single Sign-On (SSO) using OneLogin through the generic SAML 2.0 connector.
|
||||
This guide will walk you through how to configure the integration.
|
||||
|
||||
## Create a SAML connector
|
||||
## Step 1: Create a SAML connector
|
||||
|
||||
In the OneLogin admin portal, add an app under the application tab.
|
||||
Select `SAML Custom Connector (Advanced)` and provide the appropriate
|
||||
@@ -45,7 +45,7 @@ Once complete, save the changes and download the SAML metadata document
|
||||
found unde the `More Actions` dropdown. You'll need
|
||||
to copy-paste the contents of this document into the Firezone portal in the next step.
|
||||
|
||||
## Add SAML identity provider to Firezone
|
||||
## Step 2: Add SAML identity provider to Firezone
|
||||
|
||||
In the Firezone portal, add a SAML identity provider under the Security tab
|
||||
by filling out the following information:
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -8,28 +8,10 @@ description:
|
||||
|
||||
# Deploy Firezone
|
||||
|
||||
Firezone can be deployed on most Docker-supported platforms in about a minute.
|
||||
Firezone can be deployed on most Docker-supported platforms in a couple of minutes.
|
||||
Read more below to get started.
|
||||
|
||||
## Deployment methods
|
||||
|
||||
You have two options for deploying Firezone:
|
||||
|
||||
1. [Docker](docker) (recommended)
|
||||
1. [Omnibus](omnibus)
|
||||
|
||||
Docker is the easiest way to install, manage, and upgrade Firezone and is the
|
||||
preferred method of deployment.
|
||||
|
||||
:::note
|
||||
Chef Infra Client, the configuration system Chef Omnibus relies on, has been
|
||||
[scheduled for End-of-Life in 2024](https://docs.chef.io/versions/). As such,
|
||||
support for Omnibus-based deployments will be removed in a future version of
|
||||
Firezone. To transition to Docker from Omnibus today, follow our [migration guide
|
||||
](../administer/migrate).
|
||||
:::
|
||||
|
||||
## Prepare to deploy
|
||||
## Step 1: Prepare to deploy
|
||||
|
||||
Regardless of which deployment method you choose, you'll need to follow the
|
||||
preparation steps below before deploying Firezone to production.
|
||||
@@ -105,3 +87,21 @@ debug and results in strange, unpredictable failure modes.
|
||||
For the VPN tunnels themselves, Firezone uses in-kernel WireGuard, so its
|
||||
performance should be very good. 1 vCPU should be more than enough to saturate
|
||||
a 1 Gbps link.
|
||||
|
||||
## Step 2: Deploy
|
||||
|
||||
You have two options for deploying Firezone:
|
||||
|
||||
1. [Docker](docker) (recommended)
|
||||
1. [Omnibus](omnibus)
|
||||
|
||||
Docker is the easiest way to install, manage, and upgrade Firezone and is the
|
||||
preferred method of deployment.
|
||||
|
||||
:::warning
|
||||
Chef Infra Client, the configuration system Chef Omnibus relies on, has been
|
||||
[scheduled for End-of-Life in 2024](https://docs.chef.io/versions/). As such,
|
||||
support for Omnibus-based deployments will be removed starting with Firezone 0.8.
|
||||
Firezone. To transition to Docker from Omnibus today, follow our [migration guide
|
||||
](../administer/migrate).
|
||||
:::
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -12,9 +12,10 @@ There are two types of configuration in Firezone:
|
||||
* [Deployment configuration](#deployment-configuration): Deployment or
|
||||
infrastructure-related configuration relevant to running Firezone on-prem.
|
||||
|
||||
## Runtime Configuration
|
||||
## Runtime configuration
|
||||
|
||||
Most day-to-day configuration of Firezone can be done via the Web UI.
|
||||
Most day-to-day configuration of Firezone can be done via the Web UI or
|
||||
[REST API](/reference/rest-api/configurations).
|
||||
This type of configuration can be expected to be changed **with no downtime**
|
||||
in a production deployment.
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -22,7 +23,7 @@ We're actively working to move more configuration variables to
|
||||
this type of configuration, so expect more ENV vars to transition to runtime
|
||||
configuration in the future.
|
||||
|
||||
## Deployment Configuration
|
||||
## Deployment configuration
|
||||
|
||||
Deployment-related and infrastructure configuration require restarting Firezone
|
||||
services after change.
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -41,11 +41,11 @@ pointing to this instance. See [Prepare to Deploy](../#prepare-to-deploy)
|
||||
if you haven't done this already.
|
||||
:::
|
||||
|
||||
## Step 2: Install Server
|
||||
## Step 2: Install server
|
||||
|
||||
After prerequisites are satisfied, you're ready to install the Firezone Server.
|
||||
|
||||
### Option 1: Automatic Install
|
||||
### Option 1: Automatic install
|
||||
|
||||
The easiest way to deploy Firezone with Docker is the automatic install script:
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -57,40 +57,40 @@ and then print instructions for accessing the Web UI.
|
||||
|
||||
Firezone files will be installed in `$HOME/.firezone` by default.
|
||||
|
||||
### Option 2: Manual Install
|
||||
### Option 2: Manual install
|
||||
|
||||
If the automatic install fails, or you'd just like more control over the
|
||||
installation process, follow the steps below to install manually.
|
||||
|
||||
1. Download the docker compose template to a local working directory:
|
||||
**For Linux**:
|
||||
```shell
|
||||
curl -fsSL https://raw.githubusercontent.com/firezone/firezone/master/docker-compose.prod.yml -o docker-compose.yml
|
||||
```
|
||||
**For macOS, Windows (non-production only)**:
|
||||
```shell
|
||||
curl -fsSL https://raw.githubusercontent.com/firezone/firezone/master/docker-compose.desktop.yml -o docker-compose.yml
|
||||
```
|
||||
**For Linux**:
|
||||
```
|
||||
curl -fsSL https://raw.githubusercontent.com/firezone/firezone/master/docker-compose.prod.yml -o docker-compose.yml
|
||||
```
|
||||
**For macOS, Windows (non-production only)**:
|
||||
```
|
||||
curl -fsSL https://raw.githubusercontent.com/firezone/firezone/master/docker-compose.desktop.yml -o docker-compose.yml
|
||||
```
|
||||
1. Generate required secrets:
|
||||
```shell
|
||||
docker run --rm firezone/firezone bin/gen-env > .env
|
||||
```
|
||||
```
|
||||
docker run --rm firezone/firezone bin/gen-env > .env
|
||||
```
|
||||
1. At a minimum, change the `ADMIN_EMAIL` and `EXTERNAL_URL` variables.
|
||||
Optionally modify other secrets as needed.
|
||||
Optionally modify other secrets as needed.
|
||||
1. Migrate the database:
|
||||
```shell
|
||||
docker compose run --rm firezone bin/migrate
|
||||
```
|
||||
```
|
||||
docker compose run --rm firezone bin/migrate
|
||||
```
|
||||
1. Create the first admin:
|
||||
```shell
|
||||
docker compose run --rm firezone bin/create-or-reset-admin
|
||||
```
|
||||
```
|
||||
docker compose run --rm firezone bin/create-or-reset-admin
|
||||
```
|
||||
1. Bring the services up: `docker compose up -d`
|
||||
|
||||
You should now be able to access the Firezone web portal at the `EXTERNAL_URL`
|
||||
variable you defined above.
|
||||
|
||||
## Step 3: Enable on Boot (optional)
|
||||
## Step 3 (optional): Enable on boot
|
||||
|
||||
If you'd like Firezone to start automatically on boot, first ensure Docker is enabled at startup:
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -102,26 +102,26 @@ Then, make sure your Firezone services have the `restart: always` or `restart: u
|
||||
specified in the `docker-compose.yml` file. This is the default used in the docker-compose.prod.yml
|
||||
production template file.
|
||||
|
||||
## Step 4: Enable IPv6 (optional)
|
||||
## Step 4 (optional): Enable IPv6
|
||||
|
||||
By default, Firezone ships with IPv6 connectivity enabled inside the tunnel but not routable
|
||||
to the public internet. To enable IPv6 support in Docker-deployed Firezone, follow the steps below.
|
||||
|
||||
1. Enable IPv6 support within Docker by adding the following to `/etc/docker/daemon.json`:
|
||||
```json
|
||||
{
|
||||
"ipv6": true,
|
||||
"ip6tables": true,
|
||||
"experimental": true,
|
||||
“fixed-cidr-v6”: “2001:db8:1::/64”
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
```json
|
||||
{
|
||||
"ipv6": true,
|
||||
"ip6tables": true,
|
||||
"experimental": true,
|
||||
"fixed-cidr-v6": "2001:db8:1::/64"
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
This enables IPv6 NAT and configures IPv6 forwarding for Docker containers.
|
||||
1. Enable router advertisements on boot for your default egress interface:
|
||||
```
|
||||
egress=`ip route show default 0.0.0.0/0 | grep -oP '(?<=dev ).*' | cut -f1 -d' ' | tr -d '\n'`
|
||||
sudo bash -c "echo net.ipv6.conf.${egress}.accept_ra=2 >> /etc/sysctl.conf"
|
||||
```
|
||||
```
|
||||
egress=`ip route show default 0.0.0.0/0 | grep -oP '(?<=dev ).*' | cut -f1 -d' ' | tr -d '\n'`
|
||||
sudo bash -c "echo net.ipv6.conf.${egress}.accept_ra=2 >> /etc/sysctl.conf"
|
||||
```
|
||||
1. Reboot
|
||||
|
||||
You should now be able to ping google from within a docker container:
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -13,7 +13,7 @@ deployments.
|
||||
| macOS | `amd64` `arm64` | Docker Desktop | Works. but unsupported. | Not recommended for production deployments. See [caveats](#non-linux-platform-caveats). |
|
||||
| Windows | `amd64` `arm64` | Docker Desktop | **Untested** | Not recommended for production deployments. See [caveats](#non-linux-platform-caveats). |
|
||||
|
||||
## Docker Desktop Caveats
|
||||
## Docker Desktop caveats
|
||||
|
||||
Docker Desktop [rewrites the source address
|
||||
](https://www.docker.com/blog/how-docker-desktop-networking-works-under-the-hood/)
|
||||
@@ -21,7 +21,7 @@ for packets flowing out of container networks under some conditions. This can
|
||||
cause routing loops and other hard to debug connectivity issues with Firezone.
|
||||
We recommend **only** using Docker Server for Linux for production deployments.
|
||||
|
||||
## Non-Linux Platform Caveats
|
||||
## Non-Linux platform caveats
|
||||
|
||||
Only Docker for Linux supports the host networking mode, so macOS and Windows
|
||||
platforms will be able unable to properly attribute client source address
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -37,7 +37,7 @@ Note that we only support RPM and DEB based packaging systems. Others, like Arch
|
||||
Linux are currently being investigated [
|
||||
in this issue](https://github.com/firezone/firezone/issues/378).
|
||||
|
||||
## AmazonLinux 2 Notes
|
||||
## AmazonLinux 2 notes
|
||||
|
||||
Kernel upgrade required:
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -45,7 +45,7 @@ Kernel upgrade required:
|
||||
sudo amazon-linux-extras install -y kernel-5.10
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
## CentOS 7 Notes
|
||||
## CentOS 7 notes
|
||||
|
||||
Kernel upgrade to 5.6+ required. To upgrade to the latest mainline kernel and
|
||||
select it as the default boot kernel:
|
||||
@@ -60,7 +60,7 @@ sudo grub2-mkconfig -o /boot/grub2/grub.cfg
|
||||
sudo reboot
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
## CentOS 8 Notes
|
||||
## CentOS 8 notes
|
||||
|
||||
The WireGuard kernel module needs to be installed:
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -69,25 +69,25 @@ yum install elrepo-release epel-release
|
||||
yum install kmod-wireguard
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
## RHEL 7 Notes
|
||||
## RHEL 7 notes
|
||||
|
||||
Red Hat Enterprise Linux is binary compatible with CentOS, so the Firezone
|
||||
package for CentOS 7 should work just fine for RHEL 7. You'll still need to
|
||||
upgrade your kernel to 5.6+ however. To do so, follow the steps for
|
||||
[CentOS 7 Notes](#centos-7-notes) above.
|
||||
|
||||
## RHEL 8 Notes
|
||||
## RHEL 8 notes
|
||||
|
||||
Red Hat Enterprise Linux is binary compatible with CentOS, so the Firezone
|
||||
package for CentOS 8 should work just fine for RHEL 8. You'll still need to
|
||||
install the WireGuard kernel module, however. See [CentOS 8 Notes
|
||||
](#centos-8-notes) above.
|
||||
|
||||
## RHEL 9 Notes
|
||||
## RHEL 9 notes
|
||||
|
||||
Use the package for CentOS 9.
|
||||
|
||||
## Fedora Notes
|
||||
## Fedora notes
|
||||
|
||||
On fresh Fedora installations you'll probably need to install a cron
|
||||
implementation to support the logrotate functionality, otherwise
|
||||
@@ -97,7 +97,7 @@ you may receive errors about a missing `/etc/cron.hourly` directory.
|
||||
yum install cronie-anacron
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
## Ubuntu 18.04 Notes
|
||||
## Ubuntu 18.04 notes
|
||||
|
||||
Kernel upgrade to 5.4+ required:
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -105,13 +105,13 @@ Kernel upgrade to 5.4+ required:
|
||||
sudo apt install linux-image-generic-hwe-18.04
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
## Debian 10 Notes
|
||||
## Debian 10 notes
|
||||
|
||||
Kernel upgrade to 5.6+ required. See [this guide
|
||||
](https://jensd.be/968/linux/install-a-newer-kernel-in-debian-10-buster-stable)
|
||||
for an example.
|
||||
|
||||
## openSUSE Notes
|
||||
## openSUSE notes
|
||||
|
||||
Firezone requires the `setcap` utility, but some recent openSUSE releases may
|
||||
not have it installed by default. To fix, ensure `libcap-progs` is installed:
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -51,7 +51,7 @@ Ensure you've set up a working [OIDC](/authenticate/oidc/) or [SAML](/authentica
|
||||
authentication provider before disabling the local authentication method.
|
||||
:::
|
||||
|
||||
## Reporting Security Issues
|
||||
## Reporting security issues
|
||||
|
||||
To report any security-related bugs, see [our security bug reporting policy
|
||||
](https://github.com/firezone/firezone/blob/master/SECURITY.md).
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -7,9 +7,7 @@ sidebar_position: 2
|
||||
|
||||
:::warning
|
||||
This reference is written for Omnibus-based deployments of Firezone. For
|
||||
Docker-based deployments visit the
|
||||
[Environment Variables](../env-vars)
|
||||
page.
|
||||
Docker-based deployments visit the [Environment Variables](../env-vars) page.
|
||||
:::
|
||||
|
||||
To configure Omnibus-based deployments of Firezone:
|
||||
@@ -19,7 +17,7 @@ To configure Omnibus-based deployments of Firezone:
|
||||
|
||||
Read more about configuring Firezone in the [configure guide](/deploy/configure).
|
||||
|
||||
## Configuration File Reference
|
||||
## Configuration file reference
|
||||
|
||||
Shown below is a complete listing of the configuration options available in
|
||||
`/etc/firezone/firezone.rb`.
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -10,13 +10,13 @@ your installation.
|
||||
<Tabs>
|
||||
<TabItem label="Docker" value="docker" default>
|
||||
|
||||
| Default path | Description |
|
||||
| --- | --- |
|
||||
| `$HOME/.firezone/.env` | Firezone secrets used for encryption, cookies, and sessions. **Losing this file will result in irrecoverable data loss**. |
|
||||
| `$HOME/.firezone/docker-compose.yml` | Docker Compose file used to manage Firezone services. |
|
||||
| `$HOME/.firezone/firezone` | Top-level directory containing Firezone-related persisted data |
|
||||
| `$HOME/.firezone/caddy` | Caddy persisted files. |
|
||||
| Default Docker volume location. | Postgres DB files. |
|
||||
| Default path | Description |
|
||||
| --- | --- |
|
||||
| `$HOME/.firezone/.env` | Firezone secrets used for encryption, cookies, and sessions. **Losing this file will result in irrecoverable data loss**. |
|
||||
| `$HOME/.firezone/docker-compose.yml` | Docker Compose file used to manage Firezone services. |
|
||||
| `$HOME/.firezone/firezone` | Top-level directory containing Firezone-related persisted data |
|
||||
| `$HOME/.firezone/caddy` | Caddy persisted files. |
|
||||
| Default Docker volume location, typically `/var/lib/docker/volumes/firezone_postgres-data`. | Postgres DB files. |
|
||||
|
||||
</TabItem>
|
||||
<TabItem label="Omnibus" value="omnibus">
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -3,8 +3,8 @@ title: Firewall Templates
|
||||
sidebar_position: 9
|
||||
---
|
||||
|
||||
Firewall templates to secure the Firezone server are available from here. If
|
||||
the server is not running any services other than Firezone, the firewall
|
||||
Firewall templates to secure the Firezone server itself are available from here.
|
||||
If the server is not running any services other than Firezone, the firewall
|
||||
template should work as-is.
|
||||
|
||||
```mdx-code-block
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -5,7 +5,7 @@ sidebar_position: 1
|
||||
|
||||
The following nftables firewall template can be used to secure the server
|
||||
running Firezone. The template does make some assumptions; you may need to
|
||||
adjust the rules to suite your use case:
|
||||
adjust the rules to suit your use case:
|
||||
|
||||
* The WireGuard interface is named `wg-firezone`. If this is not correct,
|
||||
change the `DEV_WIREGUARD` variable to match the
|
||||
@@ -30,7 +30,7 @@ default port change the `WIREGUARD_PORT` variable.
|
||||
from the rules to drop traffic and are rate limited. Removing the relevant
|
||||
logging rules will not affect traffic.
|
||||
|
||||
#### Firezone Managed Rules
|
||||
## Firezone-managed rules
|
||||
|
||||
Firezone configures its own nftables rules to permit/reject traffic to destinations
|
||||
configured in the web interface and to handle outbound NAT for client traffic.
|
||||
@@ -44,7 +44,7 @@ To work around this restart the `phoenix` service:
|
||||
firezone-ctl restart phoenix
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
#### Base Firewall Template
|
||||
## Base firewall template
|
||||
|
||||
```shell
|
||||
#!/usr/sbin/nft -f
|
||||
@@ -316,7 +316,7 @@ table inet nat {
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
#### Usage
|
||||
## Usage
|
||||
|
||||
The firewall should be stored in the relevant location for the Linux distribution
|
||||
that is running. For Debian/Ubuntu this is `/etc/nftables.conf` and for RHEL this
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -3,7 +3,7 @@ title: REST API
|
||||
sidebar_position: 10
|
||||
---
|
||||
|
||||
Welcome to Firezone REST API v0 documentation.
|
||||
Welcome to Firezone's REST API v0 documentation.
|
||||
|
||||
## Getting started
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -23,7 +23,8 @@ docker compose -f $HOME/.firezone/docker-compose.yml exec firezone bin/create-ap
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
:::caution
|
||||
API tokens generated from the CLI are owned by the primary administrator.
|
||||
API tokens generated from the CLI are owned by the primary administrator specified by
|
||||
the `ADMIN_EMAIL` environment variable.
|
||||
:::
|
||||
|
||||
```mdx-code-block
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -17,7 +17,7 @@ Below is a table of cryptography used and to which contexts they apply.
|
||||
| TLSv1.2/TLSv1.3 | Data in transit | Used by the Caddy server to encrypt HTTP connections to the portal. Read more at https://caddyserver.com/docs/caddyfile/directives/tls. SSL certificates are provisioned automatically with the ACME protocol by Let's Encrypt by default. |
|
||||
| ChaCha20, Poly1305, Curve25519, BLAKE2s, SipHash24, HKDF | Data in transit | Used by WireGuard® for VPN tunnels. Read more at https://wireguard.com/protocol. Firezone uses Linux kernel WireGuard without modification. |
|
||||
|
||||
## Security Policy
|
||||
## Security policy
|
||||
|
||||
We take security issues very seriously and strive to fix all security issues
|
||||
as soon as they're reported.
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -33,8 +33,7 @@ to answer the questions in the section above.
|
||||
Admin emails are collected **only if** you explicitly opt-in to product updates.
|
||||
Otherwise, personally-identifiable information is ***never*** collected.
|
||||
|
||||
We store telemetry in a self-hosted instance of [PostHog](https://posthog.com)
|
||||
running in a private Kubernetes cluster, only accessible by the Firezone team.
|
||||
We store telemetry in [PostHog](https://posthog.com) only accessible by the Firezone team.
|
||||
Here is an example of a telemetry event that is sent from your instance of
|
||||
Firezone to our telemetry server:
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -14,7 +14,7 @@ WireGuard private key is not exposed.** Users can follow instructions
|
||||
on the [Client Instructions](/user-guides/client-instructions/) page to
|
||||
generate their own WireGuard configs.
|
||||
|
||||
## Admin Device Config Generation
|
||||
## Admin device config generation
|
||||
|
||||
Firezone admins can generate device configs for all users. This can be done by
|
||||
clicking the "Add Device" button on the user profile page found in `/users`.
|
||||
@@ -27,6 +27,6 @@ WireGuard configuration file to the user over a secure channel.
|
||||
See [Add Users](/user-guides/add-users/) for more information on how to add a
|
||||
user.
|
||||
|
||||
### Related Guides
|
||||
## Related guides
|
||||
|
||||
* [Client Instructions](/user-guides/client-instructions/)
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -6,7 +6,8 @@ sidebar_position: 1
|
||||
# Add or remove users
|
||||
|
||||
Once you have successfully installed Firezone you'll need to add users to grant
|
||||
them access to your network. This is done through the Web UI.
|
||||
them access to your network. This can be done through the Web UI or the
|
||||
[REST API](/reference/rest-api/users).
|
||||
|
||||
## Web UI
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -18,6 +19,6 @@ information.
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
### Related Guides
|
||||
## Related guides
|
||||
|
||||
* [Authenticate](/authenticate/)
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -2,10 +2,10 @@
|
||||
title: Client Instructions
|
||||
sidebar_position: 4
|
||||
description:
|
||||
Set up your client app to connect to your organization's private
|
||||
networks and resources. Download the open-source WireGuard® app
|
||||
for your operating system (Windows, MacOS, iOS, Android, Linux) to
|
||||
get started.
|
||||
Set up your client app to connect to your organization's private
|
||||
networks and resources. Download the open-source WireGuard® app
|
||||
for your operating system (Windows, MacOS, iOS, Android, Linux) to
|
||||
get started.
|
||||
---
|
||||
|
||||
# End-user client instructions
|
||||
@@ -40,7 +40,7 @@ administrator. This URL will be specific to your company
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
### Step 3: Enable on boot (optional)
|
||||
### Step 3 (optional): Enable on boot
|
||||
|
||||
Open the WireGuard client and import the `.conf` file.
|
||||
Activate the VPN session by toggling the `Activate` switch.
|
||||
@@ -73,7 +73,7 @@ click the `Reauthenticate` button, then sign in again.
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
## Linux - Network Manager
|
||||
## Linux: Network Manager
|
||||
|
||||
The following steps can be used on Linux devices to import the WireGuard
|
||||
configuration profile using Network Manager CLI (`nmcli`).
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -2,8 +2,8 @@
|
||||
title: Egress Rules
|
||||
sidebar_position: 3
|
||||
description:
|
||||
Define access policies with egress filtering rules using
|
||||
Firezone's WireGuard®-based secure access platform.
|
||||
Define access policies with egress filtering rules using
|
||||
Firezone's WireGuard®-based secure access platform.
|
||||
---
|
||||
|
||||
# Network access control
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -25,7 +25,7 @@ access list grows and team members' IP addresses change.
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
## AWS Example
|
||||
## AWS example
|
||||
|
||||
Our goal is to configure VPN traffic to the restricted resource to be routed
|
||||
through a Firezone server on an EC2 instance. In this case Firezone is acting as
|
||||
@@ -49,7 +49,7 @@ In this case, the IP is `52.202.88.54`.
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
### Step 2 - Restrict access to the protected resource
|
||||
### Step 2: Restrict access to the protected resource
|
||||
|
||||
In this example, the protected resource is a self-hosted web app. Access to the
|
||||
web app is restricted to only requests from `52.202.88.54`.
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -1,7 +1,8 @@
|
||||
---
|
||||
title: Reverse Tunnel
|
||||
sidebar_position: 2
|
||||
description: Configure Firezone as a relay to connect two or more devices.
|
||||
description:
|
||||
Configure Firezone as a relay to connect two or more devices.
|
||||
---
|
||||
|
||||
This guide will walk through using Firezone as a relay to connect
|
||||
@@ -9,7 +10,7 @@ two devices. A typical use case for this configuration is to enable an
|
||||
administrator to access a server, container, or machine that is normally
|
||||
behind a NAT or firewall.
|
||||
|
||||
## General Case - Node to Node
|
||||
## General case: node to node
|
||||
|
||||
This example demonstrates a simple scenario where a tunnel is established
|
||||
between Device A and Device B.
|
||||
@@ -38,7 +39,7 @@ Device B
|
||||
- `AllowedIPs = 10.3.2.2/32`: This is the IP or range of IPs of Device A
|
||||
- `PersistentKeepalive = 25`
|
||||
|
||||
## Admin Case - One to Many Nodes
|
||||
## Admin case: one to many nodes
|
||||
|
||||
This example demonstrates a scenario where Device A can communicate
|
||||
bi-directionally with Devices B through D. This configuration could represent an
|
||||
@@ -78,6 +79,6 @@ Device D
|
||||
- `AllowedIPs = 10.3.2.2/32`: This is the IP or range of IPs of Device A
|
||||
- `PersistentKeepalive = 25`
|
||||
|
||||
### Related Guides
|
||||
## Related guides
|
||||
|
||||
- [NAT Gateway](/user-guides/use-cases/nat-gateway/)
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -2,8 +2,8 @@
|
||||
title: Split Tunnel VPN
|
||||
sidebar_position: 1
|
||||
description:
|
||||
Configure Firezone for split tunneling. Route some network traffic
|
||||
from end users through the encrypted WireGuard® tunnel.
|
||||
Configure Firezone for split tunneling. Route some network traffic
|
||||
from end users through the encrypted WireGuard® tunnel.
|
||||
---
|
||||
|
||||
# Set up IP-based split tunneling with Firezone
|
||||
@@ -37,7 +37,7 @@ When deciding where to route a packet, Firezone chooses the egress
|
||||
interface corresponding to the most specific route first.
|
||||
:::
|
||||
|
||||
## Step 2: Set the DNS server(s) (optional)
|
||||
## Step 2 (optional): Set the DNS server(s)
|
||||
|
||||
You can define the DNS server(s) used by devices when the WireGuard tunnel
|
||||
is active. By default, it uses Cloudflare's DNS servers (`1.1.1.1, 1.0.0.1`).
|
||||
|
||||
851
docs/yarn.lock
851
docs/yarn.lock
File diff suppressed because it is too large
Load Diff
Reference in New Issue
Block a user