mirror of
https://github.com/outbackdingo/firezone.git
synced 2026-01-27 10:18:54 +00:00
jamilbk%feat/stub website in cloud (#1675)
* Remove `www/` * Stub empty `website/` to silence Vercel. This shouldn't cause conflicts when we merge `cloud` to `master`. Perhaps we want to start working off `master` soon, and move the current tip of master to `legacy`?
This commit is contained in:
10
.github/workflows/codespell.yml
vendored
10
.github/workflows/codespell.yml
vendored
@@ -10,12 +10,6 @@ jobs:
|
||||
GITHUB_TOKEN: ${{ secrets.GITHUB_TOKEN }}
|
||||
steps:
|
||||
- uses: actions/checkout@v3
|
||||
- uses: actions/setup-node@v3
|
||||
with:
|
||||
node-version: "16"
|
||||
cache: "yarn"
|
||||
cache-dependency-path: |
|
||||
www/yarn.lock
|
||||
- uses: actions/setup-python@v2
|
||||
with:
|
||||
python-version: "3.9"
|
||||
@@ -29,10 +23,6 @@ jobs:
|
||||
- name: Install Python Dependencies
|
||||
run: |
|
||||
pip install -r requirements.txt
|
||||
- name: Install node modules
|
||||
run: |
|
||||
cd www/
|
||||
yarn install --frozen-lockfile
|
||||
- name: Run pre-commit
|
||||
run: |
|
||||
pre-commit install
|
||||
|
||||
23
www/.gitignore
vendored
23
www/.gitignore
vendored
@@ -1,23 +0,0 @@
|
||||
# Dependencies
|
||||
/node_modules
|
||||
|
||||
# Generated OpenAPI docs
|
||||
/docs/reference/REST\ API/
|
||||
|
||||
# Production
|
||||
/build
|
||||
|
||||
# Generated files
|
||||
.docusaurus
|
||||
.cache-loader
|
||||
|
||||
# Misc
|
||||
.DS_Store
|
||||
.env.local
|
||||
.env.development.local
|
||||
.env.test.local
|
||||
.env.production.local
|
||||
|
||||
npm-debug.log*
|
||||
yarn-debug.log*
|
||||
yarn-error.log*
|
||||
@@ -1,33 +0,0 @@
|
||||
# Website
|
||||
|
||||
This website is built using [Docusaurus 2](https://docusaurus.io/), a modern
|
||||
static website generator.
|
||||
|
||||
## Installation
|
||||
|
||||
```shell
|
||||
yarn
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
## Local Development
|
||||
|
||||
```shell
|
||||
yarn run start
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
This command starts a local development server and opens up a browser window.
|
||||
Most changes are reflected live without having to restart the server.
|
||||
|
||||
## Build
|
||||
|
||||
```shell
|
||||
yarn run build
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
This command generates static content into the `build` directory and can be
|
||||
served using any static contents hosting service.
|
||||
|
||||
## Deployment
|
||||
|
||||
Deployment happens automatically when a new version is published. See the
|
||||
`publish_www` CI workflow.
|
||||
@@ -1,3 +0,0 @@
|
||||
module.exports = {
|
||||
presets: [require.resolve('@docusaurus/core/lib/babel/preset')],
|
||||
};
|
||||
@@ -1,115 +0,0 @@
|
||||
---
|
||||
slug: release-0-5-0
|
||||
title: Release 0.5.0
|
||||
authors: [jamil]
|
||||
tags: [release, beta, acme, reverse proxy, docs]
|
||||
---
|
||||
|
||||
## Firezone 0.5 Released!
|
||||
|
||||
As the first post on our new blog, we thought it'd be fitting to kick things
|
||||
off with a release announcement. So without further ado, we're excited to
|
||||
announce: Firezone [0.5.0 is
|
||||
here](https://github.com/firezone/firezone/releases)! It's packed with new
|
||||
features, bug fixes, and other improvements — more on that below.
|
||||
|
||||
### User-scoped egress rules
|
||||
|
||||
Rules can now optionally receive a user scope, limiting the rule's application
|
||||
only to devices owned by that user. This allows you to selectively allow or
|
||||
deny traffic from a particular user to an IP, set of IPs, or CIDR range.
|
||||
|
||||
### Auto-renewed, ECDSA-backed, ACME-powered SSL certificates
|
||||
|
||||
One of our most-requested features is now available — Firezone 0.5.0 supports
|
||||
ACME SSL certificate renewal backed by Let's Encrypt's new ECDSA key type.
|
||||
Other providers and key types are available too. See all ACME configuration
|
||||
options in our [configuration file
|
||||
reference](/docs/reference/configuration-file/).
|
||||
|
||||
**Note**: ACME is disabled by default to remain compatible with existing
|
||||
Firezone installations. To enable, set the following in your config file:
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
default['firezone']['ssl']['acme']['enabled'] = true
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
### BYORP: Bring Your Own Reverse Proxy
|
||||
|
||||
Want to disable Nginx and deploy Firezone under your own reverse proxy or HTTP
|
||||
load balancer? Well, now you can! We've documented the required headers and
|
||||
other configuration necessary to make this happen. [Check the
|
||||
docs](/docs/deploy/advanced/reverse-proxy) for some configuration
|
||||
examples for popular proxies. In short:
|
||||
|
||||
Set the
|
||||
`default['firezone']['phoenix']['external_trusted_proxies']`
|
||||
configuration variable to a comma-separated list containing the proxies
|
||||
you'd like to receive forwarded requests from. If your proxy uses an
|
||||
[RFC1918 address](https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Private_network), add its
|
||||
IP to `default['firezone']['phoenix']['private_clients']` instead of
|
||||
`default['firezone']['phoenix']['external_trusted_proxies']`.
|
||||
Update your proxy's configuration to point to Firezone, making sure to set
|
||||
the `X-Forwarded-For` header and enable WebSocket connection upgrades.
|
||||
|
||||
**Note:** ACME support is tied to Nginx. If you disable the bundled
|
||||
Firezone Nginx service, you'll need to provide your own SSL certificates
|
||||
(or configure ACME renewal manually).
|
||||
|
||||
**Additional note:** If you go this route, you'll need to terminate SSL
|
||||
yourself — Firezone sets the secure attribute on all cookies and thus
|
||||
requires the downstream proxy to terminate SSL.
|
||||
|
||||
### Runtime configuration available in the UI
|
||||
|
||||
Some Firezone configuration settings are now configurable in the product UI
|
||||
under the Security settings. This will override anything you have set in the
|
||||
config file. Moving runtime configuration into the application itself brings us
|
||||
a step closer to Docker-based deployments (coming Soon™).
|
||||
|
||||
### New and improved documentation
|
||||
|
||||
Our docs have been migrated from Jekyll to [Docusaurus](https://docusaurus.io).
|
||||
Aside from all the Formatting is improved, user guides are updated and many
|
||||
pages have been edited for clarify and further detail. As an added bonus, our
|
||||
docs are feature improved search thanks to the powerful search functionality
|
||||
provided by [DocSearch by Algolia](https://docsearch.algolia.com/).
|
||||
Contributions welcome!
|
||||
|
||||
### Red Hat and Debian package repositories
|
||||
|
||||
If you're on one of our [supported
|
||||
distros](/docs/deploy/omnibus/supported-platforms/) (or its
|
||||
derivatives), the one-line install script will automatically install Firezone
|
||||
from our package repository and track further updates from there. This means
|
||||
your Firezone installation can be managed like any other package on your system
|
||||
and will be marked for upgrades by the same apt and yum tools you're already
|
||||
familiar with. Be sure to check the [upgrade
|
||||
notes](/docs/administer/upgrade/) prior to each
|
||||
upgrade in case there are any backwards-incompatible changes or manual steps
|
||||
involved.
|
||||
|
||||
If you've got an existing installation and still want to add our package
|
||||
repository for easier package management, just follow the [relevant
|
||||
section](/docs/deploy/omnibus) in the manual
|
||||
install guide.
|
||||
|
||||
### Smaller package sizes
|
||||
|
||||
Speaking of packages, we've done a bit of work reducing the size of our Omnibus
|
||||
release package. The Nodejs, Python, Erlang, and Elixir runtimes have all been
|
||||
removed, reducing the package size by 50% and total installed size by even
|
||||
more. There's still lots of work to be done to be done here — we expect
|
||||
package sizes to be reduced even further moving forward.
|
||||
|
||||
### Custom landing page logo
|
||||
|
||||
In the first round of what we hope to be the start of a full-featured
|
||||
customization experience, it's now possible to change the landing page logo.
|
||||
Upload an image up to 1 MB or specify a URL to an image your end users will see
|
||||
when landing at your Firezone portal.
|
||||
|
||||
## Conclusion
|
||||
|
||||
That's all we've got for now. If you'd like to spin up Firezone to try it out,
|
||||
head to the [deploy guide](/docs/deploy) in our docs.
|
||||
@@ -1,126 +0,0 @@
|
||||
---
|
||||
slug: release-0-6-0
|
||||
title: Release 0.6.0
|
||||
authors: [jamil]
|
||||
tags: [release, docker, saml]
|
||||
---
|
||||
|
||||
## Firezone 0.6 Released!
|
||||
|
||||
Today, I'm excited to announce we've closed the [first public issue
|
||||
](https://github.com/firezone/firezone/issues/260) on our GitHub repository,
|
||||
more than a year after it was originally opened: Containerization support!
|
||||
We're also releasing preliminary support for SAML 2.0 identity providers
|
||||
like Okta and OneLogin.
|
||||
|
||||
### Docker Support
|
||||
|
||||
Docker is now the preferred method for deploying Firezone. Our [
|
||||
automatic install script](https://raw.githubusercontent.com/firezone/firezone/master/scripts/docker_install.sh)
|
||||
now uses Docker by default, and we even have a new [Docker migration script
|
||||
](https://raw.githubusercontent.com/firezone/firezone/master/scripts/docker_migrate.sh)
|
||||
that will non-destructively migrate your Omnibus-based Firezone installation
|
||||
to a Docker-based one with minimal downtime.
|
||||
|
||||
#### How to Deploy
|
||||
|
||||
You can now deploy Firezone complete with valid SSL certificates and a
|
||||
provisioned administrator in just a couple minutes:
|
||||
|
||||
<AsciinemaPlayer
|
||||
src="https://asciinema.org/a/530197.cast"
|
||||
autoplay={true}
|
||||
rows={30}
|
||||
idleTimeLimit={3}
|
||||
preload={true}
|
||||
/>
|
||||
|
||||
This also means Firezone runs on any platform that supports Docker,
|
||||
like my Mac in the video above. The automatic install script will _probably_
|
||||
barf on Windows, though. In that case, try the
|
||||
[manual install method](/docs/deploy/docker/#option-2-manual-install)!
|
||||
|
||||
#### Why Docker?
|
||||
|
||||
Docker offers a number of benefits over the old Omnibus-based method of deploying
|
||||
Firezone:
|
||||
|
||||
- **Simpler, more robust upgrades**: In most cases, simply pull the latest `firezone/firezone`
|
||||
image and restart the container.
|
||||
- **Simpler configuration**: Most day-to-day configuration of Firezone can now
|
||||
be done in the web UI instead of the `/etc/firezone/firezone.rb` configuration
|
||||
file. All other configuration variables can be specified as ENV vars to the
|
||||
Firezone container.
|
||||
- **Smaller footprint**: The Firezone image weighs in at a couple dozen
|
||||
megabytes versus hundreds of megabytes for the Omnibus package.
|
||||
- **Portability**: Firezone now runs on any platform that supports Docker.
|
||||
- **Security**: Containerization providers better security isolation than
|
||||
simply running as an unprivileged local user.
|
||||
|
||||
It also makes it easier to build and test Firezone. CI pipelines rejoice!
|
||||
No more 4-hour long compiles and intermittent build failures.
|
||||
|
||||
#### What about Omnibus?
|
||||
|
||||
[Chef Omnibus](https://github.com/chef/omnibus) is a Ruby-based build system
|
||||
designed to make building and distributing complex software easier. You define
|
||||
your dependencies as source tarballs, configure options, and platform-specific
|
||||
build flags, and Omnibus automatically fetches, builds, and links all your
|
||||
dependencies automagically, emitting an OS-native installer artifact when
|
||||
complete.
|
||||
|
||||
Omnibus was a popular choice for distributing self-hosted software before
|
||||
Docker was popular -- GitLab and Mattermost are two popular self-hosted products
|
||||
that still support Omnibus-based deployments today. It's still used in many
|
||||
cases where Docker can't be used (on the \*BSDs, for example).
|
||||
|
||||
But, since Omnibus is [effectively EOL in 2024](https://docs.chef.io/versions/)
|
||||
due to its reliance on Chef Infra Client, we've decided to deprioritize
|
||||
reliance on it, and dedicate those resources to containerized deployments
|
||||
instead.
|
||||
|
||||
**Note**: Beginning with 0.6, Omnibus support in Firezone is **deprecated**.
|
||||
We'll be removing support for it completely in a future Firezone release.
|
||||
|
||||
#### How to migrate from Omnibus to Docker
|
||||
|
||||
We've written an in-depth migration guide to migrate your instance from Omnibus
|
||||
to Docker:
|
||||
|
||||
https://www.firezone.dev/docs/administer/migrate
|
||||
|
||||
Most instances will migrate without issue. If you're running Firezone in production
|
||||
for your team or business, [contact us](/contact/support)
|
||||
so we can better understand how we can help with your migration.
|
||||
|
||||
### SAML 2.0
|
||||
|
||||
Also in 0.6 is preliminary support for SAML 2.0 authentication. You'll need the
|
||||
IdP Metadata XML document to set it up. In most cases the identity provider
|
||||
will provide it for you. If not, you should be able to build it manually or
|
||||
using a tool such as
|
||||
[this nifty online IdP builder](https://www.samltool.com/idp_metadata.php).
|
||||
|
||||
In general we recommend using OpenID Connect integration over SAML whenever possible.
|
||||
It's simpler, tends to be implemented more consistently across identity providers,
|
||||
and much easier to debug when things go wrong.
|
||||
|
||||
Speaking of OIDC, 0.6 also introduces a couple improvements to make integrating
|
||||
your identity provider a more pleasant experience:
|
||||
|
||||
- `auto_create_oidc_users` is now a per-provider configuration setting. Enable or disable
|
||||
autocreation of users when logging into Firezone via that provider.
|
||||
- New web form for entering OIDC details, with improved validation and error checking:
|
||||
|
||||
<center>
|
||||
<img
|
||||
width="500"
|
||||
src="https://user-images.githubusercontent.com/167144/196735853-b2c8d505-285f-40ac-9d73-4b568358c5c3.png"
|
||||
alt="OIDC Form"
|
||||
/>
|
||||
</center>
|
||||
|
||||
#### IdP not supported?
|
||||
|
||||
If your IdP isn't supported or you'd like to learn about your options for
|
||||
custom integrations, [contact us](/contact/support) to learn more about custom integrations.
|
||||
@@ -1,138 +0,0 @@
|
||||
---
|
||||
slug: first-offsite-retro
|
||||
title: Lessons from Firezone’s first off-site
|
||||
description: In December, Firezone organized an off-site in California. Here's what we learned.
|
||||
authors: [jason]
|
||||
tags: [company, off-site]
|
||||
---
|
||||
|
||||
My first tech job was at [Strong](https://www.strong.app/), a workout journal app that was pretty popular at the time. The founders were “digital nomads,” and the team was fully remote.
|
||||
|
||||
Back in 2016, this was highly uncommon.
|
||||
|
||||
We spent a lot of time creating processes to work together effectively on opposite sides of the world. One of these was meeting up in person regularly.
|
||||
|
||||
<center>
|
||||
<img
|
||||
width="800"
|
||||
src="https://user-images.githubusercontent.com/52545545/211626078-6f64a4f4-ec37-40cd-8bb5-a6b9b122f351.png"
|
||||
alt="digital nomads"
|
||||
/>
|
||||
</center>
|
||||
|
||||
At first, it was by accident. Since everyone was traveling anyway, we would coordinate being in the same city at the same time.
|
||||
|
||||
After working in person, we quickly noticed the way we worked remotely improved. People were more comfortable sharing their ideas, better at giving constructive criticism, and happier in general.
|
||||
|
||||
It just _felt_ better to work together in person.
|
||||
|
||||
## Why try this at Firezone?
|
||||
|
||||
If you believe Firezone can take a sizable bite out of the usual suspects of legacy remote access products, we’ll need to use every advantage.
|
||||
|
||||
As a startup, our biggest advantage is the ability to move quickly as a team.
|
||||
|
||||
This is much easier when everyone is comfortable sharing ideas and engaging in lively debate. Plus, it’s a lot more fun.
|
||||
|
||||
So we decided to try it out. After much planning, canceled bookings, and a few long flights, our team met in Santa Rosa, California.
|
||||
|
||||
<center>
|
||||
<img
|
||||
width="600"
|
||||
src="https://user-images.githubusercontent.com/52545545/216130487-bde66005-e3e0-4d88-a2d0-f9a842efc715.png"
|
||||
alt="offsite office"
|
||||
/>
|
||||
</center>
|
||||
|
||||
## What did we do?
|
||||
|
||||
Our itinerary included architecture planning, a multi-day hackathon, and plenty of fun activities around the Bay Area.
|
||||
|
||||
<center>
|
||||
<img
|
||||
width="600"
|
||||
src="https://user-images.githubusercontent.com/52545545/211988059-02f3083a-116b-462e-a5ff-90af4fab63fc.png"
|
||||
alt="offsite office"
|
||||
/>
|
||||
</center>
|
||||
|
||||
The focus of the off-site was building. We each defined a few tasks that could realistically be completed by the end of the trip. So what did we work on?
|
||||
|
||||
- A new Firezone gateway (coming in 0.8!) that will eventually allow decoupling the web portal from the WireGuard data plane. A single Firezone web portal will soon be able to manage hundreds or even thousands of little Firezone gateways securing access to their respective private resources. More details to come!
|
||||
- A [new REST API in 0.7](https://github.com/firezone/firezone/releases) to allow configuring Firezone in a more automatable way. Users love our snappy web portal, but nothing beats the power of an API for automation.
|
||||
- Various documentation improvements to improve consistency between Omnibus and Docker sections, detail logging, and implement a v1 style guide.
|
||||
|
||||
Of course, no visit to the Bay Area would be complete without a tour of San Francisco. It rained most of the time, so we missed out on much of the picturesque hiking. But we still managed to snap some photos of the Golden Gate bridge and devour a few In-N-Out burgers.
|
||||
|
||||
Of special mention are the team dinners. Remote companies lack that familiar bond typically formed over team lunches in the office, so we sought to recreate that when we met in person. As an added bonus, we also split cooking duties. In many ways preparing food for your teammates is like opening a pull request: make something, request feedback on it, then merge and enjoy.
|
||||
|
||||
As someone whose culinary talents rival his passion for building security products, our resident chef [Jamil](https://twitter.com/jamilbk) led most of the culinary endeavors, including a 2-hour drive around Santa Rosa in search of live Dungeness crab.
|
||||
|
||||
<center>
|
||||
<img
|
||||
width="400"
|
||||
src="https://user-images.githubusercontent.com/167144/214394961-ecbff7d8-2f9c-48a6-a906-c387366169f3.jpeg"
|
||||
alt="team dinner"
|
||||
/>
|
||||
</center>
|
||||
|
||||
## Lessons learned for next time
|
||||
|
||||
Since this was our first off-site, some things could have gone better. Here’s a small list of hiccups and other things we’d do differently next time.
|
||||
|
||||
### Turn on low power mode
|
||||
|
||||
<center>
|
||||
<img
|
||||
width="400"
|
||||
src="https://user-images.githubusercontent.com/52545545/211503302-4b2e2e74-06e8-4929-aa5b-a336af25a450.png"
|
||||
alt="team dinner"
|
||||
/>
|
||||
</center>
|
||||
|
||||
If you’re booking an Airbnb, check for planned maintenance and outages! We were notified three days before arrival the power would be out during two full workdays.
|
||||
|
||||
Fortunately, we had a small power bank and mobile hotspot with unlimited data. Unfortunately, our lead Rust engineer’s beefy Linux machine only gets a single hour of battery life on a full charge.
|
||||
|
||||
When his machine died, we migrated to our local coffee shop, where power and WiFi were surprisingly abundant. _Editor’s note: Coffee shops in Santa Rosa are much more accommodating as a makeshift office than most in San Francisco._
|
||||
|
||||
When you’re building software, electricity and internet are vital -- splurge for that bigger battery bank and faster hotspot!
|
||||
|
||||
### Lumbar support is underrated
|
||||
|
||||
You’ll sacrifice some ergonomics when you work out of an Airbnb. Put a premium on large work surfaces, open common areas, and comfortable chairs. After a few days of working hunched over on a sofa, we learned the hard way.
|
||||
|
||||
Even better, leave heads down work until after the off-site. Instead, prioritize architecture discussions, brainstorming sessions, and design sprints.
|
||||
|
||||
### Stock the right fuel
|
||||
|
||||
We got carried away at Costco. Our out-of-town guests had never witnessed the spectacle of an American snack aisle. Fortunately, our talented engineers can turn Funyuns into elegant lines of Rust code (shoutout [@Gabi](https://github.com/conectado)).
|
||||
|
||||
All jokes aside, you’ll need the right fuel for your hackathons and deep product discussions. We recommend stocking up with plenty of coffee and healthy snacks.
|
||||
|
||||
### Plan ahead: it’ll pay off
|
||||
|
||||
As is often the case with startups, we planned the trip on short notice. This meant many last-minute restaurant bookings and trips to the store for basic supplies.
|
||||
|
||||
So, make a shopping list, book a few restaurants in advance, and have a backup plan. If you’re looking for a template, take a look at this [guide](https://posthog.com/handbook/company/offsites#how-to-plan-an-offsite-in-8-weeks---a-checklist) from our friends at PostHog. A great checklist is hard to beat.
|
||||
|
||||
## What’s next?
|
||||
|
||||
In a few short days, we:
|
||||
|
||||
- Aligned on Firezone’s product direction
|
||||
- Made critical architecture decisions for the gateway and client apps
|
||||
- Made significant progress on a few key features
|
||||
- Bonded over great food, conversation, and Mario Kart
|
||||
|
||||
We could have accomplished some of these over a few long Zoom calls and chat threads, but not as quickly. There’s something about mind melding over a few days of intense work that’s hard to replicate.
|
||||
|
||||
So, will we have another off-site? Definitely!
|
||||
|
||||
Until next time!
|
||||
|
||||
:::info 👋 thanks for reading
|
||||
Firezone secures remote access to private resources. This post doesn't have much to do about security, networking, or a fancy new feature. But hey, our product improves the remote work experience - organizing a great off-site helps too.
|
||||
|
||||
If you want to try it out, our [Docker install script](/docs/deploy) gets Firezone running in just a few minutes.
|
||||
:::
|
||||
@@ -1,8 +0,0 @@
|
||||
---
|
||||
slug: 3000-stars
|
||||
title: 3,000 GitHub Stars
|
||||
authors: [jamil]
|
||||
tags: [open-source, github]
|
||||
---
|
||||
|
||||
## 3,000 GitHub Stars
|
||||
@@ -1,181 +0,0 @@
|
||||
---
|
||||
slug: yc-oss-experience
|
||||
title: Going through YC as an open source company
|
||||
authors: [jason]
|
||||
tags: [open-source, ycombinator, company]
|
||||
---
|
||||
|
||||
# Going through YC as an open source company
|
||||
|
||||
During YC's three-month bootcamp, your goal is simple. Make meaningful progress.
|
||||
|
||||
In our batch, we met a company that made powdered breast milk. Multiple hospital networks as customers and $150k+ of MRR. Their problems were scaling production and FDA approval.
|
||||
|
||||
Firezone, our company, had launched a few weeks prior on HN. We had no revenue and only a small handful of users.
|
||||
|
||||
YC's challenge is to give advice that helps these two companies and everything in between.
|
||||
|
||||
Open-source security is a relatively new category for YC investments. About half of the 240 open-source YC investments made by YC since S05 (17 years ago) were made in the past 2 years. Only 7 are security companies.
|
||||
|
||||
During the batch, we had come up with our own interpretation of advice meant for traditional enterprise Saas or B2B freemium software companies. This post is my attempt at sharing what we did and learned in our journey.
|
||||
|
||||
## How it all started
|
||||
|
||||
As a business guy, I have long felt the business pains of a slow, clunky VPN.
|
||||
|
||||
Slow VPN speeds are an eroding pain. One that makes every task 10% slower. Like loading my Kibana dashboard, and having to wait an extra few seconds, so I go check my email or my phone. A 2 second wait that triggers a few minutes of lost productivity. A hiccup of 1 minute at the start of every zoom call that throws off all the prep I had coming into it. “How does my mic sound?”.
|
||||
|
||||
Big pains come from blockers. Halting the onboarding of a new contractor because our internal resources have not been segmented for least privilege. The contractor needs to build a website, but would get access to customer data and network access to production servers. There was no way we'd adopt a new tool for just this problem. In a past company we spent weeks installing a firewall appliance
|
||||
|
||||
When I met my co-founder Jamil last summer, he showed me a solution to these problems. A new faster VPN protocol called WireGuard (read more about that here) and a modern UX built for end users. One that's easy to self-serve for IT admins, SREs, and DevOps engineers.
|
||||
|
||||
The latter may seem like a silly differentiator, but it isn't. In the past software was sold top-down to large companies. The buyer was often not the user, so products with a laundry list of features won. They checked all the boxes.
|
||||
|
||||
In fact, for many of Firezone's users, a VPN was a checkbox. A feature that came with their legacy firewall that's cumbersome to deploy and configure. Not to mention that firewall is now sitting in an empty office as employees move to remote work.
|
||||
|
||||
This wasn't apparent to us at the beginning, but after we posted our project to HN, we quickly realized technical IT staff needed a product like Firezone.
|
||||
|
||||
## Why open-source?
|
||||
|
||||
Firezone is core IT infrastructure. It deals with network security and cryptography, and runs in pretty sensitive environments. On your employee's laptops and behind firewalls on your servers. Private data about your company and customers flow through our gateways and apps. And with remote work, almost every employee relies on it to get work done.
|
||||
|
||||
We don't expect many organization to run such critical software without knowing what's in it.
|
||||
|
||||
We also don't expect all organizations to leave control of their network to a third party. One that can experience outages, be targeted by hackers, or even snoop on your data themselves.
|
||||
|
||||
So we leave it all open for you to see and make it easy to host yourself.
|
||||
|
||||
Of course, there are other benefits of building in the open. We hired world class engineers, but with such a complex product mistakes can happen. More eyes on our code means vulnerabilities are spotted and resolved faster. As we've grown, we are even getting contributions from the community.
|
||||
|
||||
## Why Y Combinator?
|
||||
|
||||
After our ShowHN, a long list of feature requests appeared in our GitHub repo. A list we couldn't close alone. At least not within a reasonable amount of time.
|
||||
|
||||
For a new product with no revenue (yet), VC funding seemed to fit. It would allow us to create something for the community and in parallel investigate the right model to build a sustainable business. As first time founders, YC seemed like a good fit. After all, they helped GitLab and Mattermost get off the ground.
|
||||
|
||||
A brief summary for those that don't know. For a stake in your company, YC offers 3 things: capital, advice, and community.
|
||||
|
||||
When we accepted the invitation, YC's investment was $125k for 7% of our company. A few weeks into the batch we were offered an additional $375k as an uncapped MFN safe. Lucky us! You can read more about it here.
|
||||
|
||||
Advice comes in the form of interactive workshops and long-form posts. They are invaluable resources and often come with snappy titles, like “how not to fail”.
|
||||
|
||||
Community is YC's magic. Thousands of past founders who can make introductions to investors, give advice, and even become users of your product. They can help you understand what “how not to fail” should mean to an open-source security company. Same with general advice on setting metrics, talking to users, and pricing.
|
||||
|
||||
Here's some of our learnings.
|
||||
|
||||
## Should I collect telemetry?
|
||||
|
||||
As a VC backed-startup, probably yes.
|
||||
|
||||
Even with a crystal ball on what users want, metrics can still help identify reliability issues and add insight to reported bugs.
|
||||
|
||||
From a business point of view, they tell you who and how many people like your product and which features are getting used.
|
||||
|
||||
It's a great way to focus the team on what matters.
|
||||
|
||||
Best of all when the data-points start lining up like a hockey stick, it can get you the funding you need to build a great product.
|
||||
|
||||
YC's advice is to set a primary metric that accurately captures the value you're delivering to users. This primary metric should be paired with secondary metrics that drive the primary metric and you can actionably move and iterate on.
|
||||
|
||||
In case you're curious, we've set users in production as our primary metric. Our secondary metrics help add context to the growth.
|
||||
|
||||
For example, here are 3 different graphs of our progress near demo day. Our star count, number of live instances, and number of devices. Each graph tells a slightly different story. Star count shows growing awareness in the open-source community. Instances show steady growth in actual adoption. Number of users tell us more about the deployments of Firezone. Since it outpaced the growth of instances, we knew larger teams were adopting Firezone over time and existing deployments were growing inside organizations.
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
So, how do you measure usage? Not as simple as you think.
|
||||
|
||||
For most software products, telemetry is a small script in the header of your website and an annoying cookie banner. Sometimes it's also a few lines of code sprinkled through the backend. Most users expect to be tracked by the hosted services they use. They may not like it, but they generally won't fuss about it.
|
||||
|
||||
Open-source is different.
|
||||
|
||||
Though it's getting more common, not everyone expects a self-hosted open-source project to report their usage. We had to be careful what we tracked, how we anonymized it, and how we communicate it to users.
|
||||
|
||||
We spoke to a few other open source companies we respected. Here's the advice we received.
|
||||
|
||||
- Explain why you do it: Document what you track, how it's stored, and what you use it for. We took heavy inspiration from companies like Mattermost and made our own page in our documentation.
|
||||
- Make it clear and easy to opt-out: To make it simple for users, we created a deployment script that streamlines the install process. In the script we explicitly ask for permission and make it easy to switch off later directly in the UI.
|
||||
- Don't unnecessarily expose user data to third parties: Those annoying cookie banners on websites you visit generally mean one thing. You're being tracked, and your information is being sent to third party tools like CRMs and ad platforms. If you've signed up for an account and checked the box for terms and conditions, you're agreeing to that as well. With Firezone, we try to use open-source and self-hosted products whenever possible. This includes our telemetry platform as well.
|
||||
|
||||
So, now we know about users in aggregate.
|
||||
|
||||
But, our product is early and legacy VPNs are painful in many ways. We need more information to prioritize what to build first. The best way to do that is by talking to users.
|
||||
|
||||
## We don't know who our users are
|
||||
|
||||
“Write code and talk to users” is consistently echoed during YC.
|
||||
|
||||
A great summary why is in “do things that don't scale”. I recommend reading the article, but it boils down to this:
|
||||
|
||||
You often build the initial product for yourself. The MVP is usually not good enough - it's never quite right. You should get it in front of users as soon as it provides utility so you can get feedback to iterate and improve.
|
||||
|
||||
The average user of Firezone is technical. Usually a system admin, IT manager, or DevOps engineer. They're fully capable of setting up Firezone and reading our docs to figure out what the product can do.
|
||||
|
||||
We get frequent GitHub issues and Discourse posts pointing at issues or desired features. Sometimes they'll even fix it for us!
|
||||
|
||||
However, Firezone does not require a valid email to sign up. It's hosted entirely on your infrastructure. It would be weird to lock anything behind a signup.
|
||||
|
||||
I would be equally distasteful to hijack discussions with requests for a user interview.
|
||||
|
||||
So, to generate more conversations, we increased the surface area of how users can reach us. It's important to note who you're getting feedback from as well. Often for developer facing products, the person that's deploying the product is not the person who decides what to use, what the budget is, or even the only one benefiting from it.
|
||||
|
||||
Firezone ties into security playbooks, compliance requirements, hiring plans for contractors globally, and risk planning from risk departments.
|
||||
|
||||
Here's how we're currently reaching them:
|
||||
Source Types of conversations Who we speak with
|
||||
Install script email (opt-in) Deployment issues ICs, IT Managers
|
||||
Slack Group and Discourse threads Deployment and configuration issues ICs, IT Managers
|
||||
GitHub issues Feature requests ICs, IT Managers, IT Leaders
|
||||
Inbound sales leads Required functionality, pricing discussions CTO, CISO, IT Leaders
|
||||
Outbound leads Problem discovery, product roadmap planning CTO, CISO, IT Leaders
|
||||
|
||||
One example of why it's important to dig deeper involves a request to “load a custom logo”. When we got on a Zoom call, we would uncover a group of re-sellers who want to white-label our product with their clients. Turns out they have other requirements they'd be happy to pay for if we had them.
|
||||
|
||||
These conversations helped make the product better and form our view on our business model.
|
||||
|
||||
This leads into the final piece of advice from YC, pricing.
|
||||
|
||||
## Paying user feedback > free users
|
||||
|
||||
Figuring out your pricing model and generating meaningful revenue is the great filter between early MVPs and successful companies.
|
||||
|
||||
The main question however is when.
|
||||
|
||||
With limited resources, generating revenue is almost always a tradeoff. Less growth, slower development of features, and the potential to ruin a perfectly good story for investors. Queue Silicon Valley:
|
||||
|
||||
<iframe width="560" height="315" src="https://www.youtube.com/embed/BzAdXyPYKQo" title="YouTube video player" frameborder="0" allow="accelerometer; autoplay; clipboard-write; encrypted-media; gyroscope; picture-in-picture" allowfullscreen></iframe>
|
||||
|
||||
So, when to figure out revenue?
|
||||
|
||||
For B2B software, the answer should probably be “right now”.
|
||||
|
||||
Steering early user conversations toward pricing tells you if the product is viable and solves a big enough pain. YC echoes this advice.
|
||||
|
||||
A startup I previously worked at, Kite, failed partly because we punted the question of “will people pay?” too many times. It was an AI powered co-pilot, an early iteration of GitHub Copilot.
|
||||
|
||||
When we finally tried, it was clear the product needed to evolve to generate meaningful revenue. By the time we realized that, it was too late. Adam, the founder of Kite and an investor in Firezone, recently open-sourced the codebase and wrote a great post-mortem:
|
||||
|
||||
https://www.kite.com/blog/product/kite-is-saying-farewell/
|
||||
|
||||
For self-hosted open-source software the answer is not as clear.
|
||||
|
||||
[As a self-hosted security product, layering feature gating logic into the core product is problematic. Feature flags are complex to write, and even harder to maintain as our product evolves. Being critical infrastructure for remote work, we also don't want your company to come to a halt when your credit card expires. There's more to say here, but I'll leave this to a future deep-dive from my co-founder, Jamil.]
|
||||
|
||||
So, similar to other successful open-source projects, our early goal was to grow the community. During YC we focused on building out the core parts of our platform, driving adoption, and optimizing for learning from our users. One of things we wanted to learn was how to build a business around Firezone.
|
||||
|
||||
As usage grew, a pattern emerged when talking to users. Our largest deployments all started with an individual spinning Firezone up without ever speaking to us.
|
||||
|
||||
As usage grew, they reached out to inquire about additional features and services.
|
||||
|
||||
As we continue to develop our pricing model, we want to ensure the following:
|
||||
- Individuals and hobbyists can use Firezone for free
|
||||
- Small teams can use Firezone for free (if they support it themselves)
|
||||
- Large organizations can run a PoC without any calls with sales
|
||||
|
||||
If this sounds familiar, it's similar to how GitLab thinks about their pricing. We're obviously big fans.
|
||||
|
||||
## Paying it forward (still writing this part...)
|
||||
|
||||
[not sure how to end this]
|
||||
|
||||
- https://a16z.com/2019/10/04/open-source-from-community-to-commercialization/
|
||||
@@ -1,544 +0,0 @@
|
||||
---
|
||||
slug: ebpf-firewall
|
||||
title: How We Built an eBPF-based General Purpose Packet Filter
|
||||
authors: [conectado]
|
||||
tags: [ebpf, firewall, rust, aya]
|
||||
---
|
||||
|
||||
## Introduction
|
||||
|
||||
As part of our migration to multi-site in Firezone the VPN and Firewall were rewritten in Rust. As part of that rewrite we decided to improve how we were handling the firewall.
|
||||
|
||||
In the past we were using [nftables](https://netfilter.org/projects/nftables/), the way we did this was shelling-out to the console and use the nft cli.
|
||||
|
||||
This has a number of problems, for one shelling out can be prone to error, inefficient and hard to unit-test, also there's no Rust lib to call into nftables and even the existing libraries in C can be too complicated to use. Furthermore, we were limited to nft's data structure which meant doing a lot of work to not mess up the rules, this in turn made doing improvements really slow.
|
||||
|
||||
So after a lot of consideration we decided that creating our own firewall using [ebpf](https://ebpf.io/).
|
||||
|
||||
## eBPF
|
||||
|
||||
We will briefly go into what eBPF is, however If you want a more detailed introduction you can take a look at [the official introduction](https://ebpf.io/what-is-ebpf).
|
||||
|
||||
### What is eBPF
|
||||
|
||||
eBPF stands for extended Berkeley Packet Filter, which is an upgrade from BPF(Berkely Packet Filter), while eBPF brings a lot of improvements over BPF the gist is the same, run user-defined packet-filtering code inside of the kernel as part of the packet processing pipeline.
|
||||
|
||||
This is an oversimplification because eBPF programs can be hooked into multiple different events in the kernel but for our intent and purposes, we just want to hook into the packet-classifier pipeline.
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
### How the kernel safely run user-defined code
|
||||
|
||||
eBPF has its own ISA and there is a runtime for said ISA in the kernel (JIT'd), the instructions allows calling into parts of the kernel that we might need and gives us the necessary context to process a given packet.
|
||||
|
||||
Furthermore, to prevent crashes in the kernel and hogging out resources before an eBPF program gets loaded into the kernel it goes through a verification process, a verificator program sets a bunch of limitations to the program to prevent situations like infinite loops and crashes:
|
||||
|
||||
* It sets an upper-bound for the number of times a loop within the code can run (or strictly prohibits them in older kernel versions).
|
||||
* An upper-bound in the number of instructions the program can execute in total.
|
||||
* Keeps tracks of read/writes to know that you are using valid memory locations.
|
||||
|
||||
To know the specifics of how it works, you should take a look at the [kernel's doc](https://www.kernel.org/doc/Documentation/networking/filter.txt) and even more in details you can take a look at [cillium's docs](https://docs.cilium.io/en/stable/bpf/#bpf-guide).
|
||||
|
||||
### Packet pipeline
|
||||
|
||||
Without getting into the specific an eBPF program can be hooked into different hooks on the packet processing pipeline for the linux kernel. eBPF allows hooking into [XDP](https://www.iovisor.org/technology/xdp) which runs just after the packet reached the NIC. However, [XDP doesn't support Wireguard](https://lore.kernel.org/netdev/20200813195816.67222-1-Jason@zx2c4.com/T/) since wireguard doesn't have L2 headers, for more info on this see [this fly.io blogpost](https://fly.io/blog/bpf-xdp-packet-filters-and-udp/#xdp).
|
||||
|
||||
Fret not, for eBPF can also hook into the network's [TC Ingress](https://man7.org/linux/man-pages/man8/tc-bpf.8.html) that doesn't make any assumption about the packet's header.
|
||||
|
||||
### Maps
|
||||
|
||||
Maps are the kernel structures that enables us to share data between the eBPF kernel program and a user-space program. Maps, as their name suggest allow us to store relations as `Key -> Value` the types of maps offered by eBPF is limited however there are a lot of them. For our use case we just need to concern us with [trie](https://github.com/torvalds/linux/blob/master/kernel/bpf/lpm_trie.c) and hash maps.
|
||||
|
||||
Again I reffer to [cillium's documentation](https://docs.cilium.io/en/v1.12/bpf/#maps) for more information.
|
||||
|
||||
### TL;DR
|
||||
|
||||
eBPF is an ISA and its corresponding implementation for user-defined programs that run in the kernel that we used for filtering packets, however, the programs we can run have some severe limitations so that they don't crash the kernel.
|
||||
|
||||
## Firewall
|
||||
|
||||
With this in mind we wanted to write a Firewall that can allow/deny traffic based on the following:
|
||||
|
||||
- Destination CIDR
|
||||
- Possibly multiple sender IPs
|
||||
- Possibly a port-range along associated with UDP, TCP or both
|
||||
|
||||
We took an additional simplification to make the implementation easier(we will see why further along), you can configure the firewall to allow all or deny all, then when a packet match a rule it'd invert that behavior:
|
||||
> A firewall that denies all traffic with a rule for destination `10.20.30.40`, would deny all traffic from all sources to all destinations except for traffic for `10.20.30.40` from any destination.
|
||||
|
||||
### Aya
|
||||
|
||||
When implementing the firewall in Rust two possible libraries:
|
||||
|
||||
- [aya](https://github.com/aya-rs/aya)
|
||||
- [redbpf](https://github.com/foniod/redbpf)
|
||||
|
||||
`redbpf` relies on bindings to `libbpf` while `aya` only relies on `libc`, also, aya's tooling seems to be easier to use and it uses cargo's target for ebpf instead of relying on `cargo bpf` which is easier when writing the Firewall as a library.
|
||||
|
||||
So taking that into account we went with `aya`.
|
||||
|
||||
Normally, the way an aya program is structured: we have a user-space crate that loads the eBPF program and is a proxy between it and the user and a crate that targets eBPF which has more limitations(such as being `no-std`).
|
||||
|
||||
Aya normally expects to be run as a binary and not as a library or as a separate userspace/bpf library, so we needed to do some tuning for the template to be able to run it as we wanted, a single library crate that you include.
|
||||
|
||||
More about how we did this in a separate blogpost.
|
||||
|
||||
### Architecture
|
||||
|
||||
** TODO: ** Add diagrams
|
||||
|
||||
So, with this information, we can plan an architecture.
|
||||
|
||||
Thinking about the steps how ideally, the firewall would work:
|
||||
|
||||
1. A packet arrives
|
||||
2. The source is classified into a `user_id` if any
|
||||
3. Check existing rules if match
|
||||
4. Decide REJECT/ACCEPT action based on previous step
|
||||
|
||||
Let's go over how we can achieve this.
|
||||
|
||||
### The anatomy of a rule
|
||||
|
||||
As we said before a rule has 3 components
|
||||
|
||||
- Associated `user_id`
|
||||
- Destination CIDR
|
||||
- Destination Port Ranges
|
||||
|
||||
The `user_id` is an arbitrary name, the idea is that a single rule can associate multiple source ips, so we can associate a rule with an `id` and then we can update the `id` association with multiple ips during runtime.
|
||||
|
||||
Rules need to be stored in eBPF's maps, that way we can update the maps during run-time from userspace to be able to update the rules.
|
||||
|
||||
And we need to be able to lookup those maps using information from the incoming packets.
|
||||
|
||||
The way we did this is having the following maps:
|
||||
|
||||
- `SOURCE_MAP`: A hashmap mapping source ips to `id`s
|
||||
- `RULE_MAP`: A trie mapping CIDR to port ranges
|
||||
|
||||
** Note: ** There is actually an ipv6 and ipv4 version for both of those maps, so we have 4 maps in total.
|
||||
|
||||
### `SOURCE_MAP`
|
||||
|
||||
The `SOURCE_MAP` is really simple, we store the mapping IP -> ID, so we can associate let's say IP `10.10.10.3` and `10.10.10.4` with id `4` and `10.1.1.5` with id `7`. Now when a packet comes from `10.10.10.4` we lookup the map and get `4` and for `10.1.1.5` we get `7`.
|
||||
|
||||
### `RULE_MAP`
|
||||
|
||||
[Tries](https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Trie) are prefix-matching trees, they let us efficiently store and lookup ranges grouped by prefix. For ips this is exactly how [CIDR](https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Classless_Inter-Domain_Routing) works.
|
||||
|
||||
The nodes in the trie tree correspond to a an ip and a prefix, so `10.5.8.0/24` corresponds to to the bits of `10.5.8.0` and 24 bits so that node would match with `10.5.8.0` to `10.5.8.255` but if you store `10.5.8.128/25` that'd match with `10.5.8.128` to `10.5.8.255`.
|
||||
|
||||
Both nodes, `10.5.8.0/24 and `10.5.8.128/25`, could be stored but the `lookup` method in the `trie` only allows us to find the node with the most specific match. so `10.5.8.110` would match with `10.5.8.0/24` and `10.5.8.170` would match with `10.5.8.128/25` but we would never learn that it also match with `10.5.8.0/24`.
|
||||
|
||||
So a trie would give us a way to associate CIDR with... something? The question is what's this "something".
|
||||
|
||||
Well, we don't need an action, since we know the action is just inverting the default one. What we still lack to know if the rule matches is a port-range(With its protocol) and the associated `id`.
|
||||
|
||||
However, if we store multiple rules, all associated with the same destination IP we would need to lookup all the rules for each packet and this is incredibly inefficient. But there's a solution, we can easily store the ID and protocol in the key!
|
||||
|
||||
So instead of storing as the key `10.5.8.0/24` and when we do lookup we get all the other data we store as the key `6.TCP.10.5.8.0` and the prefix instead of 24 is 33, 4 extra bytes for the id, 1 for the protocol(We use the protocol number).
|
||||
|
||||
If this is still unclear we will see more when we discuss the specific of the code, just know that we store the id and protocol as part of the key, so we can compose the number `id.protocol.ip` with the prefix and look that up.
|
||||
|
||||
The result value will be the port range, which we have to map to the port of the incoming packet, we will talk more about how we do this below.
|
||||
|
||||
For sources with no id we use `0` as the id. For non-TCP/UDP packets, we store the rule in both the TCP and UDP key and look up TCP(arbitrarily) but only match for port 0 (which we use to encode all ports), for rules with both protocols, we store the rule twice once for TCP and once for UDP.
|
||||
|
||||
### Another look at the ip matching
|
||||
|
||||
Let's look again at the steps when a packet arrives:
|
||||
|
||||
1. Packet arrives
|
||||
2. Lookup destination IP get an ID or use 0
|
||||
3. Create the lookup key (ID.PROTOCOL.DESTINATION_IP)
|
||||
4. Use the lookup key to get the port ranges
|
||||
5. Lookup the port in the port ranges
|
||||
6. REJECT/ACCEPT based on that
|
||||
|
||||
Basically, this is a high-level on how the ebpf side works. Now, let's take a look at the userspace-side.
|
||||
|
||||
### Userspace
|
||||
|
||||
Now that we know how we access the rules let's see how we need to store them from userspace.
|
||||
|
||||
Remember, that the Trie map provided by the kernel, for search, only have its lookup method that let us know the longest prefix. So let's think about this scenario:
|
||||
|
||||
We store these rules:
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
10.0.0.0/24 port 80 Allowed
|
||||
10.0.0.1/32 port 23 Allowed
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
now a packet comes from 10.0.0.1 with port 80, and we use the Trie lookup method to see if it's allowed, the lookup method returns all the ports from the longest prefix, meaning port 23 is allowed but the packet has port 80 so it's denied.
|
||||
|
||||
This is of course, erroneous because IP `10.0.0.1` is part of range `10.0.0.0/24` which has port 80 is allowed. So what do we do about this? Changing the trie API is impossible without modifying the kernel and even if we submit the PR for that the new API would only be included in the latest kernels.
|
||||
|
||||
We could lookup manually each range before deciding an action, so when packet with `10.0.0.1` comes we check `10.0.0.1/32` then `10.0.0.0/31` the `10.0.0.0/30` so on and so on before taking a decision. The performance of this is bad, specially if we are going to do that about each packet.
|
||||
|
||||
What we can do, is from userspace present an API that when adding rules, it propagates them to all pertinent ips, so:
|
||||
|
||||
If you have:
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
10.0.0.1/32 port 23 Allowed
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
and you want to add `10.0.0.0/24 port 80`, the API would automatically propagate it to:
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
10.0.0.1/32 port 23, 80 Allowed
|
||||
10.0.0.0/24 port 80 Allowed
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
and if you have:
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
10.0.0.0/24 port 80 Allowed
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
then you add `10.0.0.1/32 port 23` the api actually updates the rules like:
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
10.0.0.1/32 port 23, 80 Allowed
|
||||
10.0.0.0/24 port 80 allowed
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
So you see, how the api automatically propagates rules to have a consistent table.
|
||||
|
||||
### Port Ranges
|
||||
|
||||
## At last, CODE!
|
||||
|
||||
With the previous section you should have a clear picture at the architecture of what we built and why but from now on we will **need** to see code.
|
||||
|
||||
Will not go over how Aya's API or eBPF code works, hopefully it will be self-evident with the explanations until now enough to understand the gist of it.
|
||||
|
||||
### Code structure
|
||||
|
||||
We have 3 crates in our repo:
|
||||
* Userspace
|
||||
* Common (This contains the codebase shared by both)
|
||||
* eBPF
|
||||
|
||||
From userspace we have the `Firewall` which is the entrypoint for everything. You first initialize and load a firewall by calling `Firewall::new` for a given interface.
|
||||
|
||||
The most interesting part is the `RuleTracker` this is an internal struct (which is almost directly exposed by `Firewall` using pass-through methods), this is where the magic happens, userspace `Rule`s are converted into valid eBPF `Rule`, we keep track of them to propagate them and obviously add them to the maps in eBPF.
|
||||
|
||||
So let's see how that happens.
|
||||
|
||||
### A rule
|
||||
|
||||
#### eBPF
|
||||
|
||||
So, how does a rule looks in reality:
|
||||
|
||||
```rs
|
||||
#[repr(C)]
|
||||
pub struct RuleStore {
|
||||
// Sorted non-overlapping ranges
|
||||
// bit 0-15: port-start
|
||||
// bit 16-31: port-end
|
||||
rules: [u32; MAX_RULES],
|
||||
rules_len: u32,
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Structs in eBPF need to be `repr(C)`, which just means it uses C's ABI, eBPF structs need to be simple array of bytes (with no padding to convince the eBPF verifier that we never read uninitialized memory).
|
||||
|
||||
So, let's analyze this struct, this is the value that we are going to store in the map. This only need to be the port-ranges (remember that the key already stores the `id`, `destination`, `protocol`).
|
||||
|
||||
So we store the rules as an array of port-ranges. With a range being the inclusive intervals of the port covered by the rule. we use the first 2 bytes for the starting port and the last 2 bytes for the ending port.
|
||||
|
||||
Then in `rules_len` we just have the number of rules stored (the rest is padded with 0).
|
||||
|
||||
#### Useraspace
|
||||
|
||||
From userspace we have many different structs that represent a rule at different stage of processing, these are not complex but we have different parts of the code that require different information for what to do with the rule.
|
||||
|
||||
But for user-facing API a rule looks like:
|
||||
|
||||
```rs
|
||||
pub enum Rule {
|
||||
V4(RuleImpl<Ipv4Net>),
|
||||
V6(RuleImpl<Ipv6Net>),
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Alright, not very interesting without knowing how `RuleImpl` looks:
|
||||
|
||||
```rs
|
||||
pub struct RuleImpl<T> {
|
||||
pub(crate) id: Option<u32>,
|
||||
pub(crate) dest: T,
|
||||
pub(crate) port_range: Option<PortRange>,
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
So we see that a rule in userspace contains all the information for a rule but the important part is:
|
||||
|
||||
```rs
|
||||
pub(crate) struct PortRange {
|
||||
pub(crate) ports: RangeInclusive<u16>,
|
||||
pub(crate) proto: Protocol,
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Cool! Use rust's `RangeInclusive<T>` to represent ports with `u16` as a port and a `Protocol` (which is just an enum to indicate the kind of rule)
|
||||
|
||||
So when we do `Firewall::add_rule(rule)` we need to make it arrive to eBPF with the struct we previously saw.
|
||||
|
||||
We also need to propagate correctly like we saw in the previous userspace architecture, so let's walk through how does that work!
|
||||
|
||||
#### Translation
|
||||
|
||||
So at some point we want to add the `rule` to the eBPF map. For that, we first need to determine the key that we are going to use.
|
||||
|
||||
That's easy:
|
||||
|
||||
```rs
|
||||
// Convert the id to big endian bytes
|
||||
let key_id = id.to_be_bytes();
|
||||
|
||||
// Convert the ip to bytes
|
||||
let key_cidr = ip.normalize().as_octets();
|
||||
let mut key_data = [0u8; N];
|
||||
|
||||
// Store in a new `key_data`: protocol.id.ip
|
||||
let (left_key_data, cidr) = key_data.split_at_mut(5);
|
||||
let (id, prot) = left_key_data.split_at_mut(4);
|
||||
prot[0] = proto;
|
||||
id.copy_from_slice(&key_id);
|
||||
cidr.copy_from_slice(key_cidr.as_ref());
|
||||
|
||||
// Calculate the prefix and return the eBPF key
|
||||
Key::new(
|
||||
u32::from(ip.prefix()) + (left_key_data.len() * 8) as u32,
|
||||
key_data,
|
||||
)
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Cool, this is the key that we are going to insert to the eBPF map
|
||||
|
||||
Now we need to calculate the value that we are going to insert.
|
||||
|
||||
Remember that the `rule` field in the ebpf `RuleStore` looked like this:
|
||||
|
||||
```rs
|
||||
rules: [u32; MAX_RULES],
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
So we have a maximum number of rules, one reason for this, is that we need to store an array, we can't store a vector (we can't share heap allocations). But this number is also limited by the lookup algorithm.
|
||||
|
||||
Remember, that the verifier imposes a limit on the number of times a loop can run, so if we linearly search all ranges we were getting capped at around 1000 intervals we would reach the upper limit on loops, this is okay, this would be enough but we can do better.
|
||||
|
||||
If we can somehow sort the port ranges we could do binary search, this means less loop iterations and faster lookup in general. But how to sort it exactly?
|
||||
|
||||
This is actually the reason each rule, doesn't have an Accept/Reject instead it only inverts the default behavior, also why we store all UDP rules together and TCP rules together.
|
||||
|
||||
To sort, we just need to merge intervals. Merging intervals is a well studied problem that can be done in `O(N)` and since it's from userspace we could afford worse performance.
|
||||
|
||||
Mergining intervals just means that from the existing intervals we create a series of new non-overlapping intervals that cover the same area and we sort them.
|
||||
|
||||
So `[10-20, 15-30, 6-9]` would become `[6-9, 10-30]`. Then we can do binary search on this interval. We will see below the specific of that but this is the code to get the intervals from a series of port ranges:
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
```rs
|
||||
fn resolve_overlap(port_ranges: &mut [&PortRange<T>]) -> Vec<(u16, u16)>
|
||||
{
|
||||
let mut res = Vec::new();
|
||||
|
||||
// Sort the ranges by the starting potr
|
||||
port_ranges.sort_by_key(|p| p.ports.ports.start());
|
||||
|
||||
Get the first prot into the result
|
||||
if let Some(range) = port_ranges.first() {
|
||||
res.push((*range.ports.ports.start(), *range.ports.ports.end()));
|
||||
} else {
|
||||
return res;
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// Go through each range
|
||||
for range in &port_ranges[1..] {
|
||||
let last_res = res
|
||||
.last_mut()
|
||||
.expect("should contain at least the first element of port_ranges");
|
||||
|
||||
// If the new range fall within the last one extend it
|
||||
if last_res.1 >= *range.ports.ports.start() {
|
||||
*last_res = (last_res.0, last_res.1.max(*range.ports.ports.end()));
|
||||
// Otherwise, add a new range
|
||||
} else {
|
||||
res.push((*range.ports.ports.start(), *range.ports.ports.end()));
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
res
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
As you see doing this is really easy. We still need to do some small work to get it from `Vec<(u16, u16)>` to `[u32; RULE_MAX]` but you can imagine it's pretty trivial.
|
||||
|
||||
### Propagating Rules
|
||||
|
||||
Then the last interesting part from userspace is how to propagate the rules.
|
||||
|
||||
So when you insert a new rule, you need to keep track of all the rules that would include it, since when a lookup happen it would return the new rule because it's more specific. So basically the gist is traverse all rules and include all the port ranges from those "above" in the new rule.
|
||||
|
||||
```rs
|
||||
(The code here requires a lot of context on the specifics of how we did this but it's nothing interesting, check if you can rewrite it in a "context-free" way)
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
And then there could be more specific rules that are included in the new rule, you need to propagate the new rule (the port-range) to those.
|
||||
|
||||
```rs
|
||||
(The code here requires a lot of context on the specifics of how we did this but it's nothing interesting, check if you can rewrite it in a "context-free" way)
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
### eBPF Rule lookup
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
When a packet arrives we first extract the network headers (source, destination, protocol and port).
|
||||
|
||||
```rs
|
||||
let (source, dest, proto) = load_ntw_headers(&ctx, version)?;
|
||||
let port = get_port(&ctx, version, proto)?;
|
||||
let class = source_class(source_map, source);
|
||||
let action = get_action(class, dest, rule_map, port, proto);
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Then, we get the source id:
|
||||
|
||||
```rs
|
||||
unsafe fn source_class<const N: usize>(
|
||||
source_map: &HashMap<[u8; N], u32>,
|
||||
address: [u8; N],
|
||||
) -> Option<[u8; 4]> {
|
||||
source_map.get(&address).map(|x| u32::to_be_bytes(*x))
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
Then we try to calculate what action we should take:
|
||||
|
||||
```rs
|
||||
fn get_action<const N: usize, const M: usize>(
|
||||
group: Option<[u8; 4]>,
|
||||
address: [u8; N],
|
||||
rule_map: &LpmTrie<[u8; M], RuleStore>,
|
||||
port: u16,
|
||||
proto: u8,
|
||||
) -> i32 {
|
||||
let proto = if port == 0 { TCP } else { proto };
|
||||
let default_action = get_default_action();
|
||||
|
||||
let rule_store = rule_map.get(&Key::new((M * 8) as u32, get_key(group, proto, address)));
|
||||
if is_stored(&rule_store, port) {
|
||||
return invert_action(default_action);
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
if group.is_some() {
|
||||
let rule_store = rule_map.get(&Key::new((M * 8) as u32, get_key(None, proto, address)));
|
||||
if is_stored(&rule_store, port) {
|
||||
return invert_action(default_action);
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
default_action
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Here we try to extract the action from the existing map, we get the `RuleStore` by constructing the key corresponding to that packet:
|
||||
|
||||
```rs
|
||||
fn get_key<const N: usize, const M: usize>(
|
||||
group: Option<[u8; 4]>,
|
||||
proto: u8,
|
||||
address: [u8; N],
|
||||
) -> [u8; M] {
|
||||
let group = group.unwrap_or_default();
|
||||
let mut res = [0; M];
|
||||
let (res_left, res_address) = res.split_at_mut(5);
|
||||
let (res_group, res_proto) = res_left.split_at_mut(4);
|
||||
res_group.copy_from_slice(&group);
|
||||
res_proto[0] = proto;
|
||||
res_address.copy_from_slice(&address);
|
||||
res
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
And most importantly we lookup in the rulestore if the `port` that arrived exists.
|
||||
|
||||
```rs
|
||||
pub fn lookup(&self, val: u16) -> bool {
|
||||
// 0 means all ports
|
||||
if self.rules_len > 0 {
|
||||
// SAFETY: We know that rules_len < MAX_RULES
|
||||
if start(*unsafe { self.rules.get_unchecked(0) }) == 0 {
|
||||
return true;
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// We test for 0 in all non tcp/udp packets
|
||||
// it's worth returning early for those cases.
|
||||
if val == 0 {
|
||||
return false;
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// Reimplementation of partition_point to satisfy verifier
|
||||
let mut size = self.rules_len as usize;
|
||||
// appeasing the verifier
|
||||
if size >= MAX_RULES {
|
||||
return false;
|
||||
}
|
||||
let mut left = 0;
|
||||
let mut right = size;
|
||||
#[cfg(not(feature = "user"))]
|
||||
let mut i = 0;
|
||||
while left < right {
|
||||
let mid = left + size / 2;
|
||||
|
||||
// This can never happen but we need the verifier to believe us
|
||||
let r = if mid < MAX_RULES {
|
||||
// SAFETY: We are already bound checking
|
||||
*unsafe { self.rules.get_unchecked(mid) }
|
||||
} else {
|
||||
return false;
|
||||
};
|
||||
let cmp = start(r) <= val;
|
||||
if cmp {
|
||||
left = mid + 1;
|
||||
} else {
|
||||
right = mid;
|
||||
}
|
||||
size = right - left;
|
||||
|
||||
#[cfg(not(feature = "user"))]
|
||||
{
|
||||
i += 1;
|
||||
// This should never happen, here just to satisfy verifier
|
||||
if i >= MAX_ITER {
|
||||
return false;
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
if left == 0 {
|
||||
false
|
||||
} else {
|
||||
let indx = left - 1;
|
||||
if indx >= MAX_RULES {
|
||||
return false;
|
||||
}
|
||||
// SAFETY: Again, we are already bound checking
|
||||
end(*unsafe { self.rules.get_unchecked(indx) }) >= val
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
If 0 is included we consider it to be "all ports".
|
||||
|
||||
Otherwise we basically do binary search on the starting port to see the maximum starting port that is less than the port we are checking for and then we check for the ending port to see if it's more than the port we are checking.
|
||||
|
||||
Binary search for the maximum that keeps a predicate as true is an algorithm that already exists in Rust called partition point, we needed to reimplement it to make it compatible with eBPF due to the verifier limitations.
|
||||
|
||||
## Conclusion
|
||||
|
||||
ebpf is awesome but complicated! (something along those lines) and future for firezone rearchitecture and check it out!
|
||||
@@ -1,16 +0,0 @@
|
||||
jamil:
|
||||
name: Jamil Bou Kheir
|
||||
title: Co-founder
|
||||
url: https://github.com/jamilbk
|
||||
image_url: https://www.gravatar.com/avatar/3c8434814eec26026718e992322648c8
|
||||
|
||||
jason:
|
||||
name: Jason Gong
|
||||
title: Co-founder
|
||||
url: https://github.com/gongjason
|
||||
image_url: https://www.gravatar.com/avatar/d688e2280a36287f61c4426334dce065
|
||||
|
||||
conectado:
|
||||
name: Gabriel Steinberg
|
||||
title: Senior Rust Engineer
|
||||
url: https://github.com/conectado
|
||||
@@ -1,49 +0,0 @@
|
||||
---
|
||||
title: Overview
|
||||
sidebar_position: 1
|
||||
---
|
||||
|
||||
[Firezone](/) is an open-source secure remote access
|
||||
platform that can be deployed on your own infrastructure in minutes.
|
||||
Use it to **quickly and easily** secure access to
|
||||
your private network and internal applications from an intuitive web UI.
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
These docs explain how to deploy, configure, and use Firezone.
|
||||
|
||||
## Quick start
|
||||
|
||||
1. [Deploy](deploy): A step-by-step walk-through setting up Firezone.
|
||||
Start here if you are new.
|
||||
1. [Authenticate](authenticate): Set up authentication using local
|
||||
email/password, OpenID Connect, or SAML 2.0 and optionally enable
|
||||
TOTP-based MFA.
|
||||
1. [Administer](administer): Day to day administration of the Firezone
|
||||
server.
|
||||
1. [User Guides](user-guides): Useful guides to help you learn how to use
|
||||
Firezone and troubleshoot common issues. Consult this section
|
||||
after you successfully deploy the Firezone server.
|
||||
|
||||
## Common configuration guides
|
||||
|
||||
1. [Split Tunneling](./user-guides/use-cases/split-tunnel):
|
||||
Only route traffic to certain IP ranges through the VPN.
|
||||
1. [Setting up a NAT Gateway with a Static IP](./user-guides/use-cases/nat-gateway):
|
||||
Configure Firezone with a static IP address to provide
|
||||
a single egress IP for your team's traffic.
|
||||
1. [Reverse Tunnels](./user-guides/use-cases/reverse-tunnel):
|
||||
Establish tunnels between multiple peers.
|
||||
|
||||
import SupportOptions from "@site/src/partials/_support_options.mdx";
|
||||
<SupportOptions />;
|
||||
|
||||
## Contribute to firezone
|
||||
|
||||
We deeply appreciate any and all contributions to the project and do our best to
|
||||
ensure your contribution is included. To get started, see [CONTRIBUTING.md
|
||||
](https://github.com/firezone/firezone/blob/master/CONTRIBUTING.md).
|
||||
|
||||
<!-- Leaving these disabled until they're ready -->
|
||||
<!-- <feedback /> -->
|
||||
<!-- <newsletter /> -->
|
||||
@@ -1,11 +0,0 @@
|
||||
---
|
||||
title: Administer
|
||||
sidebar_position: 4
|
||||
---
|
||||
|
||||
```mdx-code-block
|
||||
import DocCardList from '@theme/DocCardList';
|
||||
import {useCurrentSidebarCategory} from '@docusaurus/theme-common';
|
||||
|
||||
<DocCardList items={useCurrentSidebarCategory().items}/>
|
||||
```
|
||||
@@ -1,101 +0,0 @@
|
||||
---
|
||||
title: Backup and Restore
|
||||
sidebar_position: 4
|
||||
---
|
||||
|
||||
Firezone can be safely backed up and restored in a couple of minutes under
|
||||
most circumstances.
|
||||
|
||||
:::info
|
||||
This guide is written for Firezone deployments using **Docker Engine** on **Linux** only.
|
||||
:::
|
||||
|
||||
Unless your hosting provider supports taking live VM snapshots, you'll
|
||||
need to stop Firezone before backing it up. This ensures the Postgres data
|
||||
directory is in a consistent state when the backup is performed. Backing up a
|
||||
running Firezone instance will **most likely** result in data loss when restored;
|
||||
you have been warned.
|
||||
|
||||
After stopping Firezone, backing up Firezone is mostly a matter of copying the relevant
|
||||
[files and directories](/docs/reference/file-and-directory-locations/) to a location of your
|
||||
choosing.
|
||||
|
||||
See the steps below for specific examples for Docker and Omnibus.
|
||||
|
||||
<Tabs>
|
||||
<TabItem label="Docker" value="docker" default>
|
||||
|
||||
### Backup
|
||||
|
||||
For Docker-based deployments, this will consist of backing up the `$HOME/.firezone`
|
||||
directory along with the Postgres data directory, typically located at
|
||||
`/var/lib/docker/volumes/firezone_postgres-data` on Linux if you're using the default
|
||||
Docker compose template.
|
||||
|
||||
1. Stop Firezone (warning: this **will** disconnect any users connected to the VPN):
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
docker compose -f $HOME/.firezone/docker-compose.yml down
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
2. Copy relevant files and folders. If your made any customizations to `/etc/docker/daemon.json`
|
||||
(for example, for IPv6 support), be sure to include that in the backup as well.
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
tar -zcvfp $HOME/firezone-back-$(date +'%F-%H-%M').tgz $HOME/.firezone /var/lib/docker/volumes/firezone_postgres-data
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
A backup file named `firezone-back-TIMESTAMP.tgz` will then be stored in `$HOME/`.
|
||||
|
||||
### Restore
|
||||
|
||||
1. Copy the files back to their original location:
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
tar -zxvfp /path/to/firezone-back.tgz -C / --numeric-owner
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
2. Optionally, enable Docker to boot on startup:
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
systemctl enable docker
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
</TabItem>
|
||||
<TabItem label="Omnibus" value="omnibus">
|
||||
|
||||
### Backup
|
||||
|
||||
1. Stop Firezone (warning: this **will** disconnect any users connected to the VPN):
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
firezone-ctl stop
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
2. Copy relevant files and folders:
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
tar -zcvfp $HOME/firezone-back-$(date +'%F-%H-%M').tgz /var/opt/firezone /opt/firezone /usr/bin/firezone-ctl /etc/systemd/system/firezone-runsvdir-start.service /etc/firezone
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
A backup file named `firezone-back-TIMESTAMP.tgz` will then be stored in `$HOME/`.
|
||||
|
||||
### Restore
|
||||
|
||||
1. Copy the files back to their original location:
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
tar -zxvfp /path/to/firezone-back.tgz -C / --numeric-owner
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
2. Reconfigure Firezone to ensure configuration is applied to the host system:
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
firezone-ctl reconfigure
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
</TabItem>
|
||||
</Tabs>
|
||||
|
||||
import SupportOptions from "@site/src/partials/_support_options.mdx";
|
||||
<SupportOptions />;
|
||||
@@ -1,54 +0,0 @@
|
||||
---
|
||||
title: Debug Logs
|
||||
sidebar_position: 8
|
||||
description:
|
||||
Docker deployments of Firezone generate and store debug logs to a JSON
|
||||
file on the host machine.
|
||||
---
|
||||
|
||||
:::note
|
||||
This article is written for Docker based deployments of Firezone.
|
||||
:::
|
||||
|
||||
Docker deployments of Firezone consist of 3 running containers:
|
||||
|
||||
| Container | Function | Example logs |
|
||||
| --------- | ------------- | --------------------------------------------- |
|
||||
| firezone | Web portal | HTTP requests received and responses provided |
|
||||
| postgres | Database | |
|
||||
| caddy | Reverse proxy | |
|
||||
|
||||
Each container generates and stores logs to a JSON file on the host
|
||||
machine. These files can be found at
|
||||
`var/lib/docker/containers/{CONTAINER_ID}/{CONTAINER_ID}-json.log`.
|
||||
|
||||
Run the `docker compose logs` command to view the log output from all running
|
||||
containers. Note, `docker compose` commands need to be run in the Firezone
|
||||
root directory. This is `$HOME/.firezone` by default.
|
||||
|
||||
See additional options of the `docker compose logs` command
|
||||
[here](https://docs.docker.com/engine/reference/commandline/compose_logs/).
|
||||
|
||||
## Managing and configuring Docker logs
|
||||
|
||||
By default, Firezone uses the `json-file` logging driver without
|
||||
[additional configuration](https://docs.docker.com/config/containers/logging/json-file/).
|
||||
This means logs from each container are individually stored in a file format
|
||||
designed to be exclusively accessed by the Docker daemon. Log rotation is not
|
||||
enabled, so logs on the host can build up and consume excess storage space.
|
||||
|
||||
For production deployments of Firezone you may want to configure how logs are
|
||||
collected and stored. Docker provides
|
||||
[multiple mechanisms](https://docs.docker.com/config/containers/logging/configure/)
|
||||
to collect information from running containers and services.
|
||||
|
||||
Examples of popular plugins, configurations, and use cases are:
|
||||
|
||||
- Export container logs to your SIEM or observability platform (i.e.
|
||||
[Splunk](https://docs.docker.com/config/containers/logging/splunk/)
|
||||
or
|
||||
[Google Cloud Logging](https://docs.docker.com/config/containers/logging/gcplogs/)
|
||||
)
|
||||
- Enable log rotation and max file size.
|
||||
- [Customize log driver output](https://docs.docker.com/config/containers/logging/log_tags/)
|
||||
with tags.
|
||||
@@ -1,74 +0,0 @@
|
||||
---
|
||||
title: Migrate to Docker
|
||||
sidebar_position: 2
|
||||
---
|
||||
|
||||
# Migrate from Omnibus to Docker
|
||||
|
||||
Chef Infra Client, the configuration system Chef Omnibus relies on, has been
|
||||
[scheduled for End-of-Life in 2024](https://docs.chef.io/versions/).
|
||||
Firezone 0.7 will be the last version to offer Omnibus-based deployments.
|
||||
Users are encouraged to migrate to a Docker-based deployment of Firezone using
|
||||
this guide.
|
||||
|
||||
Existing Omnibus-based deployments of Firezone will continue to function as-is,
|
||||
but no officially supported RedHat or Debian packages will be published for
|
||||
Firezone 0.8 and above.
|
||||
|
||||
See this [GitHub issue tracking discussion
|
||||
](https://github.com/firezone/firezone/issues/1304) for more details.
|
||||
|
||||
Follow this guide to migrate from an Omnibus-based deployment to a Docker-based
|
||||
deployment. In most cases this can be done with minimal downtime and without
|
||||
requiring you to regenerate WireGuard configurations for each device.
|
||||
|
||||
Heavily customized deployments (such as those using an external database or
|
||||
custom reverse proxy) will likely need extra troubleshooting and manual
|
||||
steps taken to perform a successful migration.
|
||||
|
||||
Take a look at the [migration script source
|
||||
](https://github.com/firezone/firezone/blob/master/scripts/docker_migrate.sh)
|
||||
to get a detailed idea of the steps involved.
|
||||
|
||||
Estimated time to complete: **2 hours**.
|
||||
|
||||
## Steps to migrate
|
||||
|
||||
1. **Back up** your server. This ensures you have a working state to roll back to
|
||||
in case anything goes terribly wrong. At a _bare minimum_ you'll want to back up the
|
||||
[file and directories Firezone uses
|
||||
](/docs/reference/file-and-directory-locations/), but we recommend taking a full
|
||||
snapshot of your VPS if possible.
|
||||
1. Ensure you're running the latest version of Firezone. See our [upgrade guide
|
||||
](/docs/administer/upgrade/) if not.
|
||||
1. Install the latest version of [**Docker**
|
||||
](https://docs.docker.com/engine/install/) and [Docker Compose
|
||||
](https://docs.docker.com/compose/install/linux/#install-compose)
|
||||
for your OS. **Docker Compose version 2 or higher is required**.
|
||||
We recommend using Docker Server for Linux. Docker Desktop will work too, but is not
|
||||
preferred for production use cases at this time because it rewrites packets under
|
||||
some conditions and may cause unexpected issues with Firezone.
|
||||
1. Download and run the migration script:
|
||||
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
bash <(curl -fsSL https://github.com/firezone/firezone/raw/master/scripts/docker_migrate.sh)
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
This will ask you a few questions, then attempt to migrate your installation to
|
||||
Docker. If all goes well, your Firezone instance should be running with Docker, data intact.
|
||||
|
||||
## Rolling back
|
||||
|
||||
If anything goes wrong, you can abort the migration by simply bringing the Docker
|
||||
services down and the Omnibus ones back up:
|
||||
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
docker-compose down
|
||||
sudo firezone-ctl start
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
If you've found a bug, please [open a GitHub issue](https://github.com/firezone/firezone/issues) with the error output and
|
||||
any steps needed to reproduce.
|
||||
|
||||
import SupportOptions from "@site/src/partials/_support_options.mdx";
|
||||
<SupportOptions />;
|
||||
@@ -1,67 +0,0 @@
|
||||
---
|
||||
title: Regenerate Secret Keys
|
||||
sidebar_position: 7
|
||||
---
|
||||
|
||||
When you install Firezone, secrets are generated for encrypting database
|
||||
fields, securing WireGuard tunnels, securing cookie sessions, and more.
|
||||
|
||||
If you're looking to regenerate one or more of these secrets, it's possible
|
||||
to do so using the same bootstrap scripts that were used when installing
|
||||
Firezone.
|
||||
|
||||
## Regenerate secrets
|
||||
|
||||
:::warning
|
||||
Replacing the `DATABASE_ENCRYPTION_KEY` will render all encrypted data in the
|
||||
database useless. This **will** break your Firezone install unless you are
|
||||
starting with an empty database. You have been warned.
|
||||
:::
|
||||
|
||||
:::caution
|
||||
Replacing `GUARDIAN_SECRET_KEY`, `SECRET_KEY_BASE`, `LIVE_VIEW_SIGNING_SALT`,
|
||||
`COOKIE_SIGNING_SALT`, and `COOKIE_ENCRYPTION_SALT` will reset all browser
|
||||
sessions and REST API tokens.
|
||||
:::
|
||||
|
||||
Use the procedure below to regenerate secrets:
|
||||
|
||||
<Tabs>
|
||||
<TabItem value="docker" label="Docker" default>
|
||||
|
||||
Navigate to the Firezone installation directory, then:
|
||||
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
mv .env .env.bak
|
||||
docker run firezone/firezone bin/gen-env > .env
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Now, move desired env vars from `.env.bak` back to `.env`, keeping
|
||||
the new secrets intact.
|
||||
|
||||
</TabItem>
|
||||
</Tabs>
|
||||
|
||||
## Regenerate WireGuard private key
|
||||
|
||||
:::warning
|
||||
Replacing the WireGuard private key will render all existing device configs
|
||||
invalid. Only do so if you're prepared to also regenerate device configs
|
||||
after regenerating the WireGuard private key.
|
||||
:::
|
||||
|
||||
To regenerate WireGuard private key, simply move or rename the private key file.
|
||||
Firezone will generate a new one on next start.
|
||||
|
||||
<Tabs>
|
||||
<TabItem value="docker" label="Docker" default>
|
||||
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
cd $HOME/.firezone
|
||||
docker-compose stop firezone
|
||||
sudo mv firezone/private_key firezone/private_key.bak
|
||||
docker-compose start firezone
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
</TabItem>
|
||||
</Tabs>
|
||||
@@ -1,153 +0,0 @@
|
||||
---
|
||||
title: Troubleshoot
|
||||
sidebar_position: 6
|
||||
description: Troubleshoot common connectivity and configuration issues with Firezone's WireGuard®-based secure access platform.
|
||||
---
|
||||
|
||||
This guide documents common configuration and connectivity issues. For
|
||||
any problems that arise, a good first bet is to check the Firezone logs.
|
||||
|
||||
<Tabs>
|
||||
<TabItem value="docker" label="Docker" default>
|
||||
|
||||
Each container stores logs as a JSON file on the host machine. These can be shown with the
|
||||
`docker logs {CONTAINER}` command. Log files are found at
|
||||
`var/lib/docker/containers/{CONTAINER_ID}/{CONTAINER_ID}-json.log` by default.
|
||||
|
||||
See [debug logs](../debug-logs) for additional details.
|
||||
|
||||
</TabItem>
|
||||
</Tabs>
|
||||
|
||||
## Application crash loop preventing config changes
|
||||
|
||||
In cases where the application is crash looping because of corrupt, inaccessible, or
|
||||
invalid OIDC or SAML configuration in the DB, you can try clearing the affected fields.
|
||||
|
||||
For example, to clear OIDC configs:
|
||||
|
||||
<Tabs>
|
||||
<TabItem value="docker" label="Docker" default>
|
||||
|
||||
```text
|
||||
psql -d firezone -h 127.0.0.1 -U postgres -c "UPDATE configurations SET openid_connect_providers = '[]'"
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Similarly, to clear SAML configs:
|
||||
|
||||
```text
|
||||
psql -d firezone -h 127.0.0.1 -U postgres -c "UPDATE configurations SET saml_identity_providers = '[]'"
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
</TabItem>
|
||||
</Tabs>
|
||||
|
||||
## Debugging WebSocket connectivity issues
|
||||
|
||||
The Web UI requires a secure websocket connection to function.
|
||||
If a secure websocket connection can't be established, you'll see a red dot
|
||||
indicator in the upper-right portion of the Firezone web UI and a corresponding
|
||||
message when you hover over it:
|
||||
|
||||
```text
|
||||
Secure websocket not connected! ...
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
If you're accessing Firezone using the same URL defined in your
|
||||
`EXTERNAL_URL` variable from above, the issue is likely to be in your reverse
|
||||
proxy configuration. Ensure your reverse proxy has WebSocket support enabled
|
||||
for Firezone. If you're using the default Caddy reverse proxy, WebSocket
|
||||
is enabled and configured automatically.
|
||||
|
||||
In most cases, you'll find clues in one or more of the following locations:
|
||||
|
||||
<Tabs></Tabs>
|
||||
|
||||
## Debugging WireGuard connectivity issues
|
||||
|
||||
Most connectivity issues with Firezone are caused by other `iptables` or
|
||||
`nftables` rules which interfere with Firezone's operation. If you have rules
|
||||
active, you'll need to ensure these don't conflict with the Firezone rules.
|
||||
|
||||
### Internet connectivity drops when tunnel is active
|
||||
|
||||
If your Internet connectivity drops whenever you activate your WireGuard
|
||||
tunnel, you should make sure that the `FORWARD` chain allows packets
|
||||
from your WireGuard clients to the destinations you want to allow through
|
||||
Firezone.
|
||||
|
||||
If you're using `ufw`, this can be done by making sure the default routing
|
||||
policy is `allow`:
|
||||
|
||||
```text
|
||||
ubuntu@fz:~$ sudo ufw default allow routed
|
||||
Default routed policy changed to 'allow'
|
||||
(be sure to update your rules accordingly)
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
A `ufw` status for a typical Firezone server might look like this:
|
||||
|
||||
```text
|
||||
ubuntu@fz:~$ sudo ufw status verbose
|
||||
Status: active
|
||||
Logging: on (low)
|
||||
Default: deny (incoming), allow (outgoing), allow (routed)
|
||||
New profiles: skip
|
||||
|
||||
To Action From
|
||||
-- ------ ----
|
||||
22/tcp ALLOW IN Anywhere
|
||||
80/tcp ALLOW IN Anywhere
|
||||
443/tcp ALLOW IN Anywhere
|
||||
51820/udp ALLOW IN Anywhere
|
||||
22/tcp (v6) ALLOW IN Anywhere (v6)
|
||||
80/tcp (v6) ALLOW IN Anywhere (v6)
|
||||
443/tcp (v6) ALLOW IN Anywhere (v6)
|
||||
51820/udp (v6) ALLOW IN Anywhere (v6)
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
## Admin login isn't working
|
||||
|
||||
If the password for the account with email `DEFAULT_ADMIN_EMAIL` isn't working, you can
|
||||
reset it using the process below.
|
||||
|
||||
<Tabs>
|
||||
<TabItem value="docker" label="Docker" default>
|
||||
|
||||
First change directory to your Firezone installation directory
|
||||
(`$HOME/.firezone` by default), then run the `bin/create-or-reset-admin` script
|
||||
to reset the admin user's password. The password for the user specified by
|
||||
`DEFAULT_ADMIN_EMAIL`
|
||||
in `$HOME/.firezone/.env` will be reset to the `DEFAULT_ADMIN_PASSWORD` variable.
|
||||
|
||||
```shell
|
||||
cd $HOME/.firezone
|
||||
docker compose exec firezone bin/create-or-reset-admin
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
**Note**: If local authentication is disabled, resetting the admin user's
|
||||
password will not re-enable it.
|
||||
|
||||
</TabItem>
|
||||
</Tabs>
|
||||
|
||||
## Re-enable local authentication via CLI
|
||||
|
||||
If you've configured an [OIDC](/docs/authenticate/oidc/) or [SAML](/docs/authenticate/saml/)
|
||||
provider, you can consider disabling local authentication for additional security.
|
||||
|
||||
If, however, issues arise with your identity provider integration, it's possible you
|
||||
could be locked out of the admin portal. To re-enable local authentication so
|
||||
you can log in and resolve the issue, you can temporarily re-enable local authentication
|
||||
via the [REST API](/docs/reference/rest-api/configurations).
|
||||
|
||||
If that's not an option, you can re-enable local authentication by
|
||||
running the following commands on the host of your Firezone instance:
|
||||
|
||||
```shell
|
||||
cd $HOME/.firezone
|
||||
docker compose exec postgres psql -U postgres -h 127.0.0.1 -d firezone -c "UPDATE configurations SET local_auth_enabled = 't'"
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
import SupportOptions from "@site/src/partials/_support_options.mdx";
|
||||
<SupportOptions />;
|
||||
@@ -1,37 +0,0 @@
|
||||
---
|
||||
title: Uninstall
|
||||
sidebar_position: 5
|
||||
---
|
||||
|
||||
Firezone can be uninstalled using the steps below.
|
||||
|
||||
:::warning
|
||||
This will irreversibly destroy ALL Firezone data and can't be undone.
|
||||
:::
|
||||
|
||||
<Tabs>
|
||||
<TabItem label="Docker" value="docker" default>
|
||||
|
||||
For docker-based deployments, simply bring the firezone services down,
|
||||
then delete the working directory where you installed the Firezone docker
|
||||
files (`$HOME/.firezone` by default):
|
||||
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
# default install dir
|
||||
installDir=$HOME/.firezone
|
||||
docker compose -f $installDir/docker-compose.yml down -v
|
||||
rm -rf $installDir
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
</TabItem>
|
||||
<TabItem label="Omnibus" value="omnibus">
|
||||
|
||||
To completely remove Omnibus-based deployments of Firezone run the [uninstall.sh
|
||||
script](https://github.com/firezone/firezone/blob/master/scripts/omnibus-uninstall.sh):
|
||||
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
sudo /bin/bash -c "$(curl -fsSL https://github.com/firezone/firezone/raw/master/scripts/omnibus-uninstall.sh)"
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
</TabItem>
|
||||
</Tabs>
|
||||
@@ -1,283 +0,0 @@
|
||||
---
|
||||
title: Upgrade
|
||||
sidebar_position: 3
|
||||
---
|
||||
|
||||
Upgrading Firezone will pause all VPN sessions and temporarily bring
|
||||
down the web UI.
|
||||
|
||||
:::info
|
||||
Automatic rollbacks are still under development. We recommend backing up
|
||||
relevant [files and folders](/docs/reference/file-and-directory-locations/)
|
||||
before upgrading in case anything goes wrong.
|
||||
:::
|
||||
|
||||
Follow the steps below to upgrade Firezone:
|
||||
|
||||
<Tabs>
|
||||
<TabItem label="Docker" value="docker" default>
|
||||
|
||||
1. Change to your Firezone installation directory, by default `$HOME/.firezone`:
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
cd $HOME/.firezone
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
1. If your `.env` file has a `VERSION` variable, update it to the desired version.
|
||||
By default `latest` is assumed if not set. This variable is read in newer versions
|
||||
of the docker-compose.yml template to populate the `image:` key for the `firezone`
|
||||
service.
|
||||
1. Update service images:
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
docker compose pull
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
1. Re-up the services (**warning: this will restart updated services**):
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
docker compose up -d
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
</TabItem>
|
||||
<TabItem label="Omnibus" value="omnibus">
|
||||
|
||||
1. If not setup already, install our package repository based on your distro's
|
||||
package format:
|
||||
|
||||
- [deb packages](https://cloudsmith.io/~firezone/repos/firezone/setup/#formats-deb)
|
||||
- [rpm packages](https://cloudsmith.io/~firezone/repos/firezone/setup/#formats-rpm)
|
||||
|
||||
1. Upgrade the `firezone` package using your distro's package manager.
|
||||
1. Run `firezone-ctl reconfigure` to pick up the new changes.
|
||||
1. Run `firezone-ctl restart` to restart services.
|
||||
|
||||
</TabItem>
|
||||
</Tabs>
|
||||
|
||||
If you hit any issues, please let us know by [filing an
|
||||
issue](https://github.com/firezone/firezone/issues/new/choose).
|
||||
|
||||
## Upgrading to 0.7.x
|
||||
|
||||
Firezone 0.7.0 introduces a new [REST API](/docs/reference/rest-api/) that allows administrators
|
||||
to automate much of the day to day configuration of Firezone.
|
||||
|
||||
The REST API `/v0/configuration` endpoint supersedes some of the previous environment
|
||||
variables used for WireGuard server configuration.
|
||||
|
||||
If you're running Firezone < 0.6, we recommend updating to the latest
|
||||
0.6.x release **before** upgrading to 0.7. This will ensure any environment variables
|
||||
are properly parsed and migrated into the DB as runtime `configurations`.
|
||||
|
||||
**Note**: Omnibus deployments are deprecated in 0.7.x and will be removed in Firezone
|
||||
0.8 and above. We recommend [migrating your installation](/docs/administer/migrate/) to
|
||||
Docker if you haven't done so already.
|
||||
|
||||
## Upgrading to >= 0.6.12
|
||||
|
||||
### WIREGUARD\_\* env vars
|
||||
|
||||
Firezone 0.6.12 moves the `WIREGUARD_ALLOWED_IPS`, `WIREGUARD_PERSISTENT_KEEPALIVE`,
|
||||
and `WIREGUARD_DNS` environment variables to the database to be configured in the
|
||||
UI at `/settings/client_defaults`. If the corresponding value at
|
||||
`/settings/client_defaults` was empty, the environment variable's value was used to
|
||||
populate the field.
|
||||
|
||||
This is a small step in our quest to move more runtime configuration from environment
|
||||
variables to the DB.
|
||||
|
||||
### `AUTH_OIDC_JSON` config
|
||||
|
||||
Similar to the `WIREGUARD_*` env vars above, the `AUTH_OIDC_JSON` env var has similarly
|
||||
been moved to the database and can be configured at `/settings/site`. In Firezone 0.7 this
|
||||
is now configurable via the [REST API](/docs/reference/rest-api/configurations) as well.
|
||||
|
||||
### Fix IPv6
|
||||
|
||||
0.6.12 fixes IPv6 routing within Docker networks.
|
||||
To enable, add IPv6 addresses to your `$HOME/.firezone/docker-compose.yml` by setting the following fields:
|
||||
|
||||
```yaml
|
||||
services:
|
||||
firezone:
|
||||
networks:
|
||||
firezone-network:
|
||||
ipv6_address: 2001:3990:3990::99
|
||||
|
||||
# ...
|
||||
networks:
|
||||
firezone-network:
|
||||
ipam:
|
||||
config:
|
||||
- subnet: 2001:3990:3990::/64
|
||||
- gateway: 2001:3990:3990::1
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
You also need to update the Docker daemon to enable IPv6. See our [IPv6 guide](/docs/deploy/docker/#step-4-enable-ipv6-optional) for more info.
|
||||
|
||||
## Upgrading from 0.5.x to 0.6.x
|
||||
|
||||
Firezone 0.6 introduces **Docker support**, SAML 2.0 authentication,
|
||||
more granular user provisioning options, and a slew of minor improvements and bugfixes.
|
||||
|
||||
### Migrate to Docker
|
||||
|
||||
Docker is now the preferred way to deploy and manage Firezone. See the [migration
|
||||
guide](/docs/administer/migrate/) to migrate today. In most cases this can be done in a few minutes
|
||||
using our automatic migration script.
|
||||
|
||||
### Update Configuration
|
||||
|
||||
Some configuration variables have recently moved to the DB in order to be configurable
|
||||
at runtime. Check the [configure guide](/docs/deploy/configure/) for more information.
|
||||
|
||||
## Upgrading from < 0.5.0 to >= 0.5.0
|
||||
|
||||
0.5.0 introduces a few breaking changes and configuration updates that will need
|
||||
to be addressed. Read more below.
|
||||
|
||||
### Bundled Nginx non_ssl_port (HTTP) requests removed
|
||||
|
||||
0.5.0 and above removes the `force_ssl` and `non_ssl_port` settings for
|
||||
Nginx. SSL is required for Firezone to function; if you're using (or would like
|
||||
to use) your own reverse proxy, we recommend disabling the bundle Nginx service
|
||||
by setting `default['firezone']['nginx']['enabled'] = false` and pointing your
|
||||
reverse proxy directly to the Phoenix app on port 13000 (by default).
|
||||
|
||||
Read more about setting up a custom reverse proxy
|
||||
[here](/docs/deploy/advanced/reverse-proxy/).
|
||||
|
||||
### ACME protocol support
|
||||
|
||||
0.5.0 introduces ACME protocol support for automatically renewing SSL
|
||||
certificates with the bundled Nginx service. To enable,
|
||||
|
||||
- Make sure `default['firezone']['external_url']` contains a valid FQDN that
|
||||
resolves to your server's public IP address.
|
||||
|
||||
- Ensure port `80/tcp` is reachable
|
||||
|
||||
- Enable ACME protocol support with
|
||||
`default['firezone']['ssl']['acme']['enabled'] = true` in your config file.
|
||||
|
||||
### Overlapping egress rule destinations
|
||||
|
||||
Firezone 0.5.0 removes the ability to add rules with overlapping destinations.
|
||||
When upgrading to 0.5.0, our migration script will automatically detect these
|
||||
cases and **keep only the rules whose destination encompasses the other rule**.
|
||||
If this is OK, **there is nothing you need to do**.
|
||||
|
||||
Otherwise, we recommend modifying your ruleset to eliminate these cases before
|
||||
upgrading.
|
||||
|
||||
### Preconfigured Okta and Google SSO
|
||||
|
||||
Firezone 0.5.0 removes support for the old-style Okta and Google SSO
|
||||
configuration in favor of the new, more flexible OIDC-based configuration.
|
||||
If you have any configuration under the
|
||||
`default['firezone']['authentication']['okta']` or
|
||||
`default['firezone']['authentication']['google']` keys, **you need to migrate
|
||||
these to our OIDC-based configuration using the guide below.**
|
||||
|
||||
#### Existing Google OAuth configuration
|
||||
|
||||
Remove these lines containing the old Google OAuth configs from your configuration
|
||||
file located at `/etc/firezone/firezone.rb`
|
||||
|
||||
```rb
|
||||
default['firezone']['authentication']['google']['enabled']
|
||||
default['firezone']['authentication']['google']['client_id']
|
||||
default['firezone']['authentication']['google']['client_secret']
|
||||
default['firezone']['authentication']['google']['redirect_uri']
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Then, follow the instructions [here](/docs/authenticate/oidc/google/) to configure Google
|
||||
as an OIDC provider.
|
||||
|
||||
#### Existing Okta OAuth configuration
|
||||
|
||||
Remove these lines containing the old Okta OAuth configs from your configuration
|
||||
file located at `/etc/firezone/firezone.rb`
|
||||
|
||||
```rb
|
||||
default['firezone']['authentication']['okta']['enabled']
|
||||
default['firezone']['authentication']['okta']['client_id']
|
||||
default['firezone']['authentication']['okta']['client_secret']
|
||||
default['firezone']['authentication']['okta']['site']
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Then, follow the instructions [here](/docs/authenticate/oidc/okta/) to configure Okta as
|
||||
an OIDC provider.
|
||||
|
||||
## Upgrading from 0.3.x to >= 0.3.16
|
||||
|
||||
Follow the instructions below based on your current version and setup:
|
||||
|
||||
### I have an existing OIDC integration
|
||||
|
||||
Upgrading to >= 0.3.16 requires the `offline_access` scope for some OIDC providers
|
||||
to obtain a refresh token.
|
||||
This ensures Firezone syncs with the identity provider and VPN access is terminated
|
||||
once the user is removed. Previous versions of Firezone do not have this capability.
|
||||
Users who are removed from your identity provider will still have active VPN sessions
|
||||
in some cases.
|
||||
|
||||
For OIDC providers that support the `offline_access` scope, you will need to add
|
||||
`offline_access` to the `scope` parameter of your OIDC config. The
|
||||
Firezone configuration file can be found at `/etc/firezone/firezone.rb` and requires
|
||||
running `firezone-ctl reconfigure` to pick up the changes.
|
||||
|
||||
If Firezone is able to successfully retrieve the refresh token, you will see
|
||||
the **OIDC Connections** heading in the user details page of the web UI for
|
||||
users authenticated through your OIDC provider.
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
If this does not work, you will need to delete your existing OAuth app
|
||||
and repeat the OIDC setup steps to
|
||||
[create a new app integration](/docs/authenticate/oidc/) .
|
||||
|
||||
### I have an existing OAuth integration
|
||||
|
||||
Prior to 0.3.11, Firezone used pre-configured OAuth2 providers. Follow the
|
||||
instructions [here](/docs/authenticate/oidc/) to migrate to OIDC.
|
||||
|
||||
### I have not integrated an identity provider
|
||||
|
||||
No action needed. You can follow the instructions
|
||||
[here](/docs/authenticate/oidc)
|
||||
to enable SSO through an OIDC provider.
|
||||
|
||||
## Upgrading from 0.3.1 to >= 0.3.2
|
||||
|
||||
The configuration option `default['firezone']['fqdn']` has been removed in favor
|
||||
of `default['firezone']['external_url']`. Please set this to the
|
||||
publicly-accessible URL of your Firezone web portal. If left unspecified it will
|
||||
default to `https://` + the FQDN of your server.
|
||||
|
||||
Reminder, the configuration file can be found at `/etc/firezone/firezone.rb`.
|
||||
For an exhaustive list of configuration variables and their descriptions, see the
|
||||
[configuration file reference](/docs/reference/configuration-file).
|
||||
|
||||
## Upgrading from 0.2.x to 0.3.x
|
||||
|
||||
Starting with version 0.3.0, Firezone no longer stores device private
|
||||
keys on the Firezone server. Any existing devices should continue to function
|
||||
as-is, but you will not be able to re-download or view these configurations in
|
||||
the Firezone Web UI.
|
||||
|
||||
## Upgrading from 0.1.x to 0.2.x
|
||||
|
||||
Firezone 0.2.x contains some configuration file changes that will need to be
|
||||
handled manually if you're upgrading from 0.1.x. Run the commands below as root
|
||||
to perform the needed changes to your `/etc/firezone/firezone.rb` file.
|
||||
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
cp /etc/firezone/firezone.rb /etc/firezone/firezone.rb.bak
|
||||
sed -i "s/\['enable'\]/\['enabled'\]/" /etc/firezone/firezone.rb
|
||||
echo "default['firezone']['connectivity_checks']['enabled'] = true" >> /etc/firezone/firezone.rb
|
||||
echo "default['firezone']['connectivity_checks']['interval'] = 3_600" >> /etc/firezone/firezone.rb
|
||||
firezone-ctl reconfigure
|
||||
firezone-ctl restart
|
||||
```
|
||||
@@ -1,93 +0,0 @@
|
||||
---
|
||||
title: Authenticate
|
||||
sidebar_position: 3
|
||||
---
|
||||
|
||||
Firezone supports the following authentication methods:
|
||||
|
||||
1. [Local email/password (default)](local-auth)
|
||||
1. [SSO authentication via OpenID Connect](oidc)
|
||||
1. [SSO authentication via SAML 2.0](saml)
|
||||
|
||||
:::note
|
||||
If your Identity Provider doesn't work with the methods listed above,
|
||||
[contact us](/contact/support) about a custom integration.
|
||||
:::
|
||||
|
||||
## Integrate an SSO provider
|
||||
|
||||
We've included instructions on how to set up Firezone with several popular
|
||||
identity providers using our Generic OIDC integration:
|
||||
|
||||
- [Okta](oidc/okta)
|
||||
- [Azure Active Directory](oidc/azuread)
|
||||
- [Google](oidc/google)
|
||||
- [Onelogin](oidc/onelogin)
|
||||
- [JumpCloud](saml/jumpcloud)
|
||||
- [Keycloak](oidc/keycloak)
|
||||
- [Zitadel](oidc/zitadel)
|
||||
- [Auth0](oidc/auth0)
|
||||
|
||||
If your identity provider is not listed above, but has a generic OIDC or SAML
|
||||
connector, please consult their documentation to find instructions on obtaining
|
||||
the configuration settings required. Instructions for setting up Firezone with any
|
||||
generic OIDC provider can be found [here](oidc).
|
||||
|
||||
Open a [Github issue](https://github.com/firezone/firezone/issues)
|
||||
to request documentation or submit a pull request to add documentation for your
|
||||
provider.
|
||||
|
||||
### The OIDC redirect URI
|
||||
|
||||
For each OIDC provider a corresponding URL is created for redirecting to
|
||||
the configured provider's sign-in URL. The URL format is `https://firezone.example.com/auth/oidc/CONFIG_ID`
|
||||
where `CONFIG_ID` is the OIDC Config ID for that particular provider.
|
||||
|
||||
For example, the OIDC config below:
|
||||
|
||||
<center>
|
||||
<img
|
||||
width="509"
|
||||
alt="config-oidc"
|
||||
src="https://user-images.githubusercontent.com/167144/216438674-a2b64b3b-2ed6-43dc-b554-de9c055dc741.png"
|
||||
/>
|
||||
</center>
|
||||
|
||||
would generate the following OIDC login URL:
|
||||
|
||||
- `https://firezone.example.com/auth/oidc/google`
|
||||
|
||||
This URL could then be distributed to end users for direct navigation to
|
||||
the identity provider's login portal for authentication to Firezone.
|
||||
|
||||
## Enforce periodic re-authentication
|
||||
|
||||
Periodic re-authentication can be enforced by changing the setting in
|
||||
`settings/security`. This can be used to ensure a user must sign in to Firezone
|
||||
periodically in order to maintain their VPN session.
|
||||
|
||||
You can set the session length to a minimum of **1 hour** and maximum of **90 days**.
|
||||
Setting this to Never disables this setting, allowing VPN sessions indefinitely.
|
||||
This is the default.
|
||||
|
||||
### Re-authentication
|
||||
|
||||
To re-authenticate an expired VPN session, a user will need to turn off their
|
||||
VPN session and sign in to the Firezone portal (URL specified during
|
||||
[deployment](../deploy#prepare-to-deploy)).
|
||||
|
||||
See detailed Client Instructions on how to re-authenticate your session
|
||||
[here](../user-guides/client-instructions).
|
||||
|
||||
#### VPN connection status
|
||||
|
||||
A user's connection status is shown on the Users page under the table column
|
||||
`VPN Connection`. The connection statuses are:
|
||||
|
||||
- ENABLED - The connection is enabled.
|
||||
- DISABLED - The connection is disabled by an administrator or OIDC refresh failure.
|
||||
- EXPIRED - The connection is disabled due to authentication expiration or a user
|
||||
has not signed in for the first time.
|
||||
|
||||
import SupportOptions from "@site/src/partials/_support_options.mdx";
|
||||
<SupportOptions />;
|
||||
@@ -1,30 +0,0 @@
|
||||
---
|
||||
title: Local Authentication
|
||||
sidebar_position: 1
|
||||
---
|
||||
|
||||
# Local authentication (email & password)
|
||||
|
||||
By default, Firezone will use local email / password for authenticating users to
|
||||
the Firezone portal. Administrators can add users and assign their passwords on
|
||||
the `/users` page. See [Add users](/docs/user-guides/add-users/) for more details.
|
||||
|
||||
:::caution
|
||||
Although local authentication is quick and easy to get started with, you can
|
||||
limit attack surface by [disabling local authentication](#disabling-local-authentication)
|
||||
altogether. See our [OIDC](/docs/authenticate/oidc/) or [SAML](/docs/authenticate/saml/) guides
|
||||
for details. For production deployments it's usually a good idea to **disable
|
||||
local authentication** and enforce MFA through your identity provider.
|
||||
:::
|
||||
|
||||
If you choose to keep Local authentication enabled, we recommend [enabling TOTP-based MFA
|
||||
](/docs/authenticate/multi-factor/) for any accounts that use the local authentication method.
|
||||
|
||||
## Disabling local authentication
|
||||
|
||||
Local authentication can be enabled or disabled from the `/settings/security` page
|
||||
or via the [REST API](/docs/reference/rest-api/configurations).
|
||||
If you've disabled local authentication and can no longer authenticate to the portal
|
||||
to re-enable it, see our [troubleshooting guide
|
||||
](/docs/administer/troubleshoot#re-enable-local-authentication-via-cli) for re-enabling
|
||||
local authentication from the CLI.
|
||||
@@ -1,40 +0,0 @@
|
||||
---
|
||||
title: Multi-Factor Authentication
|
||||
sidebar_position: 2
|
||||
description:
|
||||
Enforce multi-factor authentication with Firezone's WireGuard®-based
|
||||
secure access platform.
|
||||
---
|
||||
|
||||
# Multi-factor authentication (MFA)
|
||||
|
||||
You have two options for activating MFA with Firezone:
|
||||
|
||||
1. Enable a TOTP-based second factor for the local email/password
|
||||
authentication method.
|
||||
1. Configure Firezone to SSO via one of our [supported identity providers
|
||||
](../#integrate-an-sso-provider) and enable MFA through the identity provider.
|
||||
|
||||
## MFA with Firezone
|
||||
|
||||
Firezone currently supports using a time-based one time password
|
||||
(TOTP) as an additional factor. This is supported with the local authentication
|
||||
method only; for SSO authentication we recommend enabling your provider's MFA
|
||||
functionality [as described below](#mfa-with-identity-provider).
|
||||
|
||||
Admins can visit `/settings/account/register_mfa` in the admin portal to
|
||||
generate a QR code to be scanned by your authenticator app.
|
||||
|
||||
Unprivileged users can visit `/user_account/register_mfa` after logging into
|
||||
the user portal.
|
||||
|
||||
## MFA with your identity provider
|
||||
|
||||
Most identity providers support additional authentication factors in addition to
|
||||
email/password. Consult your provider's documentation to enforce an
|
||||
additional factor. We have included links to a few common providers below:
|
||||
|
||||
* [Okta](https://help.okta.com/en-us/Content/Topics/Security/mfa/mfa-home.htm)
|
||||
* [Azure AD](https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/azure/active-directory/authentication/concept-mfa-howitworks)
|
||||
* [Google](https://support.google.com/a/answer/175197)
|
||||
* [Onelogin](https://www.onelogin.com/getting-started/free-trial-plan/add-mfa)
|
||||
@@ -1,66 +0,0 @@
|
||||
---
|
||||
title: OpenID Connect
|
||||
sidebar_position: 10
|
||||
description: Setup single sign-on with your identity provider. Integrate
|
||||
providers like Okta, Google, Azure, and JumpCloud using Firezone's
|
||||
OpenID Connect (OIDC) connector.
|
||||
---
|
||||
|
||||
# Integrate your identity provider using OIDC
|
||||
|
||||
Firezone supports Single Sign-On (SSO) via OpenID Connect (OIDC).
|
||||
|
||||
## Supported identity providers
|
||||
|
||||
In general, most identity providers that offer OIDC support work with Firezone. Some providers
|
||||
that only implement the OIDC partially or use uncommon configurations may have
|
||||
issues, however. If your identity provider falls into this category, [contact us
|
||||
](/contact/support) about a custom integration.
|
||||
|
||||
The following OIDC providers are known to work well with Firezone:
|
||||
|
||||
| Provider | Support Status | Notes |
|
||||
| ------------------------------------- | ------------------------------ | ------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------ |
|
||||
| [Azure Active Directory](azuread) | **Fully tested and supported** | Ensure the [`email` claim](https://learn.microsoft.com/en-us/azure/active-directory/develop/active-directory-optional-claims) is present in the token. |
|
||||
| [Okta](okta) | **Fully tested and supported** | |
|
||||
| [Onelogin](onelogin) | **Fully tested and supported** | |
|
||||
| [Keycloak](https://www.keycloak.org/) | **Fully tested and supported** | |
|
||||
| [Auth0](auth0) | **Fully tested and supported** | Auth0 does not provide an `end_session_uri` in its OIDC discovery document. Signing out of Auth0 from Firezone is not supported. |
|
||||
| [Google Workspace](google) | **Fully tested and supported** | Google does not provide an `end_session_uri` in its OIDC discovery document. Signing out of Google Workspace from Firezone is not supported. |
|
||||
| [Zitadel](zitadel) | Untested but known to work | |
|
||||
| [Authentik](https://goauthentik.io/) | Untested but known to work | |
|
||||
|
||||
## General setup guide
|
||||
|
||||
If you're using an OIDC provider not listed above, the following OIDC attributes
|
||||
are required for setting up an OIDC provider in Firezone:
|
||||
|
||||
1. `discovery_document_uri`: The
|
||||
[OpenID Connect provider configuration URI](https://openid.net/specs/openid-connect-discovery-1_0.html#ProviderConfig)
|
||||
which returns a JSON document used to construct subsequent requests to this
|
||||
OIDC provider. Some providers refer to this as the "well-known URL".
|
||||
1. `client_id`: The client ID of the application.
|
||||
1. `client_secret`: The client secret of the application.
|
||||
1. `redirect_uri`: Instructs OIDC provider where to redirect after authentication.
|
||||
This should be your Firezone `EXTERNAL_URL + /auth/oidc/<provider_key>/callback/`
|
||||
(e.g. `https://firezone.example.com/auth/oidc/google/callback/`).
|
||||
1. `response_type`: Set to `code`.
|
||||
1. `scope`: [OIDC scopes](https://openid.net/specs/openid-connect-basic-1_0.html#Scopes)
|
||||
to obtain from your OIDC provider. At a minimum, Firezone requires the `openid`
|
||||
and `email` scopes.
|
||||
1. `label`: The button label text displayed on the Firezone portal login page.
|
||||
|
||||
### PKCE
|
||||
|
||||
Firezone supports Proof Key for Code Exchange (PKCE) for increased login security.
|
||||
We recommend you enable PKCE in your IdP's settings whenever available. [Read more
|
||||
about PKCE here](https://oauth.net/2/pkce/).
|
||||
|
||||
### OIDC logout URI
|
||||
|
||||
The OpenID Connect standard [defines a mechanism](https://openid.net/specs/openid-connect-rpinitiated-1_0.html)
|
||||
for a Relying Party (RP) to request that an OpenID Provider log out the End-User.
|
||||
|
||||
Unfortunately, not all IdPs support this (e.g. Google, Auth0). For the providers
|
||||
that do support this mechanism, Firezone automatically detects the `end_session_uri`
|
||||
found in the provider's discovery document and uses that to log out the End-User.
|
||||
@@ -1,69 +0,0 @@
|
||||
---
|
||||
title: Auth0
|
||||
sidebar_position: 1
|
||||
description:
|
||||
Enforce 2FA/MFA for users of Firezone's WireGuard®-based
|
||||
secure access platform. This guide walks through integrating Auth0
|
||||
for single sign-on using OpenID Connect (OIDC).
|
||||
---
|
||||
|
||||
# Enable SSO with Auth0 (OIDC)
|
||||
|
||||
Firezone supports Single Sign-On (SSO) using Auth0
|
||||
through the generic OIDC connector. This guide will walk you through how to
|
||||
obtain the following config settings required for the integration:
|
||||
|
||||
1. **Config ID**: The provider's config ID. (e.g. `auth0`)
|
||||
1. **Label**: The button label text that shows up on your Firezone login screen. (e.g. `Auth0`)
|
||||
1. **Scope**: [OIDC scopes](https://openid.net/specs/openid-connect-basic-1_0.html#Scopes)
|
||||
to obtain from your OIDC provider. This should be set to `openid email profile`
|
||||
to provide Firezone with the user's email in the returned claims.
|
||||
1. **Response type**: Set to `code`.
|
||||
1. **Client ID**: The client ID of the application.
|
||||
1. **Client secret**: The client secret of the application.
|
||||
1. **Discovery Document URI**: The
|
||||
[OpenID Connect provider configuration URI](https://openid.net/specs/openid-connect-discovery-1_0.html#ProviderConfig)
|
||||
which returns a JSON document used to construct subsequent requests to this OIDC
|
||||
provider.
|
||||
|
||||
## Step 1: Obtain OIDC configuration parameters
|
||||
|
||||
In the Auth0 dashboard, create an application.
|
||||
Select **Regular Web Application** as the application type.
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
Next, visit the settings tab on the application details page. Take note and
|
||||
modify the following parameters:
|
||||
|
||||
1. **Name**: `Firezone`
|
||||
1. **Domain**: The domain will be used to construct
|
||||
the url to retrieve the OIDC discovery document - `https://<AUTH0_DOMAIN>/.well-known/openid-configuration`
|
||||
1. **Icon**:
|
||||
[Firezone icon](https://user-images.githubusercontent.com/52545545/156854754-da66a9e1-33d5-47f5-877f-eff8b330ab2b.png)
|
||||
(save link as).
|
||||
1. Set **Allowed Callback URLs** to `EXTERNAL_URL + /auth/oidc/<Config ID>/callback/`
|
||||
(e.g. `https://firezone.example.com/auth/oidc/auth0/callback/`).
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||

|
||||
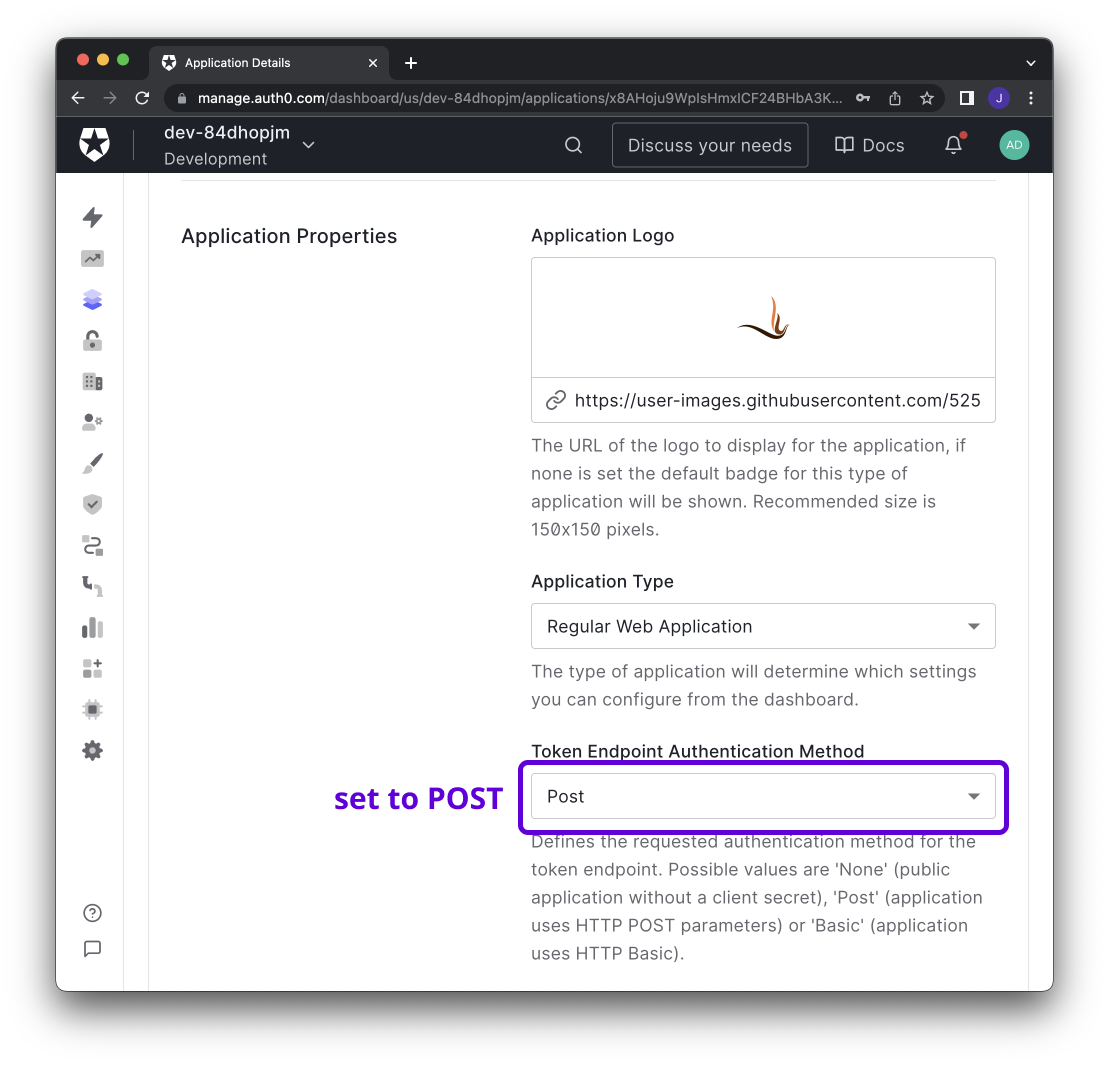
|
||||
|
||||
## Step 2: Integrate with Firezone
|
||||
|
||||
Navigate to the `/settings/security` page in the admin portal, click
|
||||
"Add OpenID Connect Provider" and enter the details you obtained in the steps
|
||||
above.
|
||||
|
||||
Enable or disable the **Auto create users** option to automatically create
|
||||
an unprivileged user when signing in via this authentication mechanism.
|
||||
|
||||
And that's it! The configuration should be updated immediately.
|
||||
You should now see a `Sign in with Auth0` button on the sign in page.
|
||||
|
||||
## Step 3 (optional): Restrict access to specific users
|
||||
|
||||
Auth0 supports setting access policies to control which users
|
||||
can access the Firezone application. See Auth0's
|
||||
[Documentation](https://auth0.com/docs/manage-users/user-accounts/manage-user-access-to-applications)
|
||||
for details.
|
||||
@@ -1,82 +0,0 @@
|
||||
---
|
||||
title: Azure Active Directory
|
||||
sidebar_position: 2
|
||||
description: Enforce 2FA/MFA for users of Firezone's WireGuard®-based
|
||||
secure access platform. This guide walks through integrating Azure AD
|
||||
for single sign-on using OpenID Connect (OIDC).
|
||||
---
|
||||
|
||||
# Enable SSO with Azure Active Directory (OIDC)
|
||||
|
||||
Firezone supports Single Sign-On (SSO) using Azure Active Directory through the generic
|
||||
generic OIDC connector. This guide will walk you through how to obtain the following
|
||||
config settings required for the integration:
|
||||
|
||||
1. **Config ID**: The provider's config ID. (e.g. `azure`)
|
||||
1. **Label**: The button label text that shows up on your Firezone login screen. (e.g. `Azure`)
|
||||
1. **Scope**: [OIDC scopes](https://openid.net/specs/openid-connect-basic-1_0.html#Scopes)
|
||||
to obtain from your OIDC provider. This should be set to `openid email profile offline_access`
|
||||
to provide Firezone with the user's email in the returned claims.
|
||||
1. **Response type**: Set to `code`.
|
||||
1. **Client ID**: The client ID of the application.
|
||||
1. **Client secret**: The client secret of the application.
|
||||
1. **Discovery Document URI**: The
|
||||
[OpenID Connect provider configuration URI](https://openid.net/specs/openid-connect-discovery-1_0.html#ProviderConfig)
|
||||
which returns a JSON document used to construct subsequent requests to this
|
||||
OIDC provider.
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
## Step 1: Obtain configuration parameters
|
||||
|
||||
_This guide is adapted from the [Azure Active Directory documentation](https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/azure/active-directory/fundamentals/auth-oidc)._
|
||||
|
||||
Navigate to the Azure Active Directory page on the Azure portal.
|
||||
Select the App registrations link under the Manage menu, click
|
||||
`New Registration`, and register after entering the following:
|
||||
|
||||
1. **Name**: `Firezone`
|
||||
1. **Supported account types**: `(Default Directory only - Single tenant)`
|
||||
1. **Redirect URI**: This should be your Firezone `EXTERNAL_URL + /auth/oidc/<Config ID>/callback/`
|
||||
(e.g. `https://firezone.example.com/auth/oidc/azure/callback/`). **Make sure you include the trailing slash both
|
||||
when saving the provider in Firezone and in Azure AD (`redirect_uri` field on the screenshot below).**
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
After registering, open the details view of the application and copy the
|
||||
`Application (client) ID`. **This will be the `client_id` value**. Next, open
|
||||
the endpoints menu to retrieve the `OpenID Connect metadata document`.
|
||||
**This will be the `discovery_document_uri` value**.
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
Next, select the Certificates & secrets link under the Manage menu and
|
||||
create a new client secret. Copy the client secret - **this will be the
|
||||
`client_secret` value**.
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
Lastly, select the API permissions link under the Manage menu,
|
||||
click `Add a permission`, and select `Microsoft Graph`. Add `email`, `openid`,
|
||||
`offline_access` and `profile` to the required permissions.
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
## Step 2: Integrate with Firezone
|
||||
|
||||
Navigate to the `/settings/security` page in the admin portal, click
|
||||
"Add OpenID Connect Provider" and enter the details you obtained in the steps
|
||||
above.
|
||||
|
||||
Enable or disable the **Auto create users** option to automatically create
|
||||
an unprivileged user when signing in via this authentication mechanism.
|
||||
|
||||
And that's it! The configuration should be updated immediately.
|
||||
You should now see a `Sign in with Azure` button on the sign in page.
|
||||
|
||||
## Step 3 (optional): Restrict access to specific users
|
||||
|
||||
Azure AD allows admins to restrict OAuth application access to a subset of users
|
||||
within your organization. See Microsoft's
|
||||
[documentation](https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/azure/active-directory/develop/howto-restrict-your-app-to-a-set-of-users)
|
||||
for more information on how to do this.
|
||||
@@ -1,92 +0,0 @@
|
||||
---
|
||||
title: Google Workspace
|
||||
sidebar_position: 3
|
||||
description:
|
||||
Enforce 2FA/MFA for users of Firezone's WireGuard®-based
|
||||
secure access platform. This guide walks through integrating Google Workspace
|
||||
for single sign-on using OpenID Connect (OIDC).
|
||||
---
|
||||
|
||||
# Enable SSO with Google Workspace (OIDC)
|
||||
|
||||
Firezone supports Single Sign-On (SSO) using Google Workspace and Cloud Identity
|
||||
through the generic OIDC connector. This guide will walk you through how to
|
||||
obtain the following config settings required for the integration:
|
||||
|
||||
1. **Config ID**: The provider's config ID. (e.g. `google`)
|
||||
1. **Label**: The button label text that shows up on your Firezone login screen. (e.g. `Google`)
|
||||
1. **Scope**: [OIDC scopes](https://openid.net/specs/openid-connect-basic-1_0.html#Scopes)
|
||||
to obtain from your OIDC provider. This should be set to `openid email profile`
|
||||
to provide Firezone with the user's email in the returned claims.
|
||||
1. **Response type**: Set to `code`.
|
||||
1. **Client ID**: The client ID of the application.
|
||||
1. **Client secret**: The client secret of the application.
|
||||
1. **Discovery Document URI**: The
|
||||
[OpenID Connect provider configuration URI](https://openid.net/specs/openid-connect-discovery-1_0.html#ProviderConfig)
|
||||
which returns a JSON document used to construct subsequent requests to this
|
||||
OIDC provider.
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
## Step 1: Configure OAuth consent screen
|
||||
|
||||
If this is the first time you are creating a new OAuth client ID, you will
|
||||
be asked to configure a consent screen.
|
||||
|
||||
**IMPORTANT**: Select `Internal` for user type. This ensures only accounts
|
||||
belonging to users in your Google Workspace Organization can create device configs.
|
||||
DO NOT select `External` unless you want to enable anyone with a valid Google Account
|
||||
to create device configs.
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
On the App information screen:
|
||||
|
||||
1. **App name**: `Firezone`
|
||||
1. **App logo**: [Firezone logo](https://user-images.githubusercontent.com/52545545/156854754-da66a9e1-33d5-47f5-877f-eff8b330ab2b.png)
|
||||
(save link as).
|
||||
1. **Application home page**: the URL of your Firezone instance.
|
||||
1. **Authorized domains**: the top level domain of your Firezone instance.
|
||||
|
||||
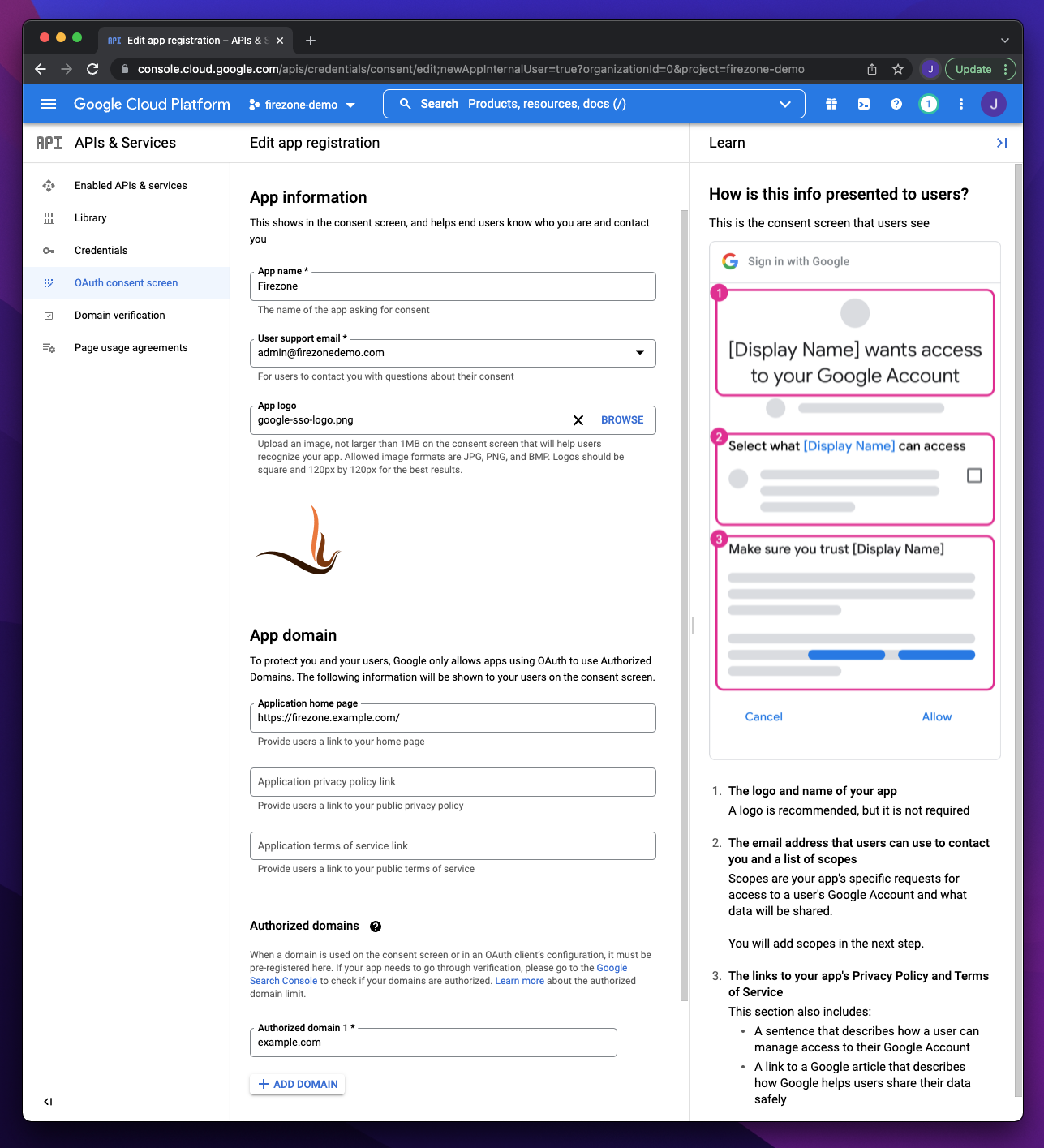
|
||||
|
||||
On the next step add the following scopes:
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
## Step 2: Create OAuth client
|
||||
|
||||
_This section is based off Google's own documentation on
|
||||
[setting up OAuth 2.0](https://support.google.com/cloud/answer/6158849)._
|
||||
|
||||
Visit the Google Cloud Console
|
||||
[Credentials page](https://console.cloud.google.com/apis/credentials)
|
||||
page, click `+ Create Credentials` and select `OAuth client ID`.
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
On the OAuth client ID creation screen:
|
||||
|
||||
1. Set `Application Type` to `Web application`
|
||||
1. Add your Firezone `EXTERNAL_URL + /auth/oidc/<Config ID>/callback/`
|
||||
(e.g. `https://firezone.example.com/auth/oidc/google/callback/`) as an entry to
|
||||
Authorized redirect URIs.
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
After creating the OAuth client ID, you will be given a Client ID and Client Secret.
|
||||
These will be used together with the redirect URI in the next step.
|
||||
|
||||
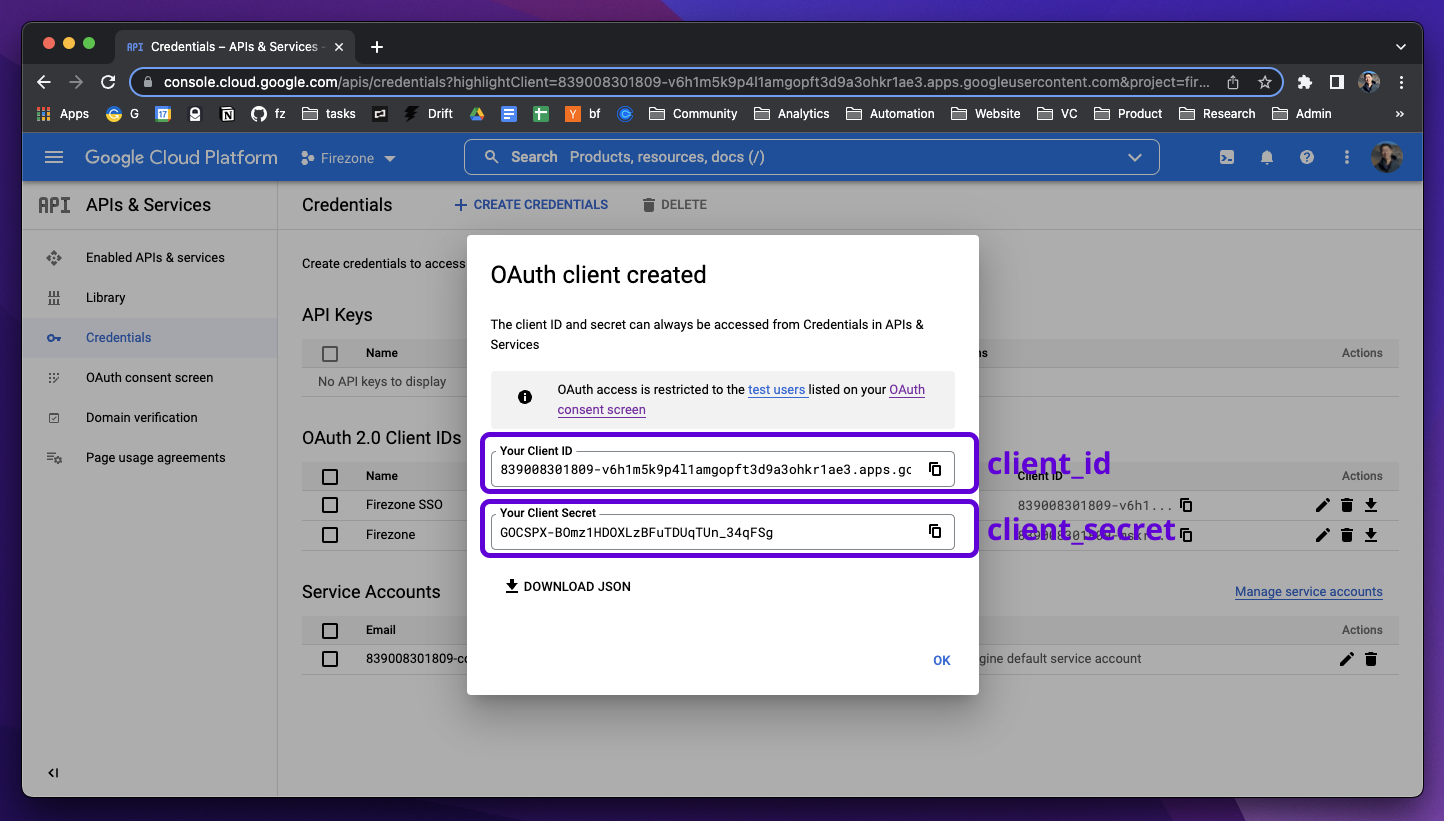
|
||||
|
||||
## Step 3: Integrate with Firezone
|
||||
|
||||
Navigate to the `/settings/security` page in the admin portal, click
|
||||
"Add OpenID Connect Provider" and enter the details you obtained in the steps
|
||||
above.
|
||||
|
||||
Enable or disable the **Auto create users** option to automatically create
|
||||
an unprivileged user when signing in via this authentication mechanism.
|
||||
|
||||
And that's it! The configuration should be updated immediately.
|
||||
You should now see a `Sign in with Google` button on the sign in page.
|
||||
@@ -1,80 +0,0 @@
|
||||
---
|
||||
title: Keycloak
|
||||
sidebar_position: 4
|
||||
description:
|
||||
Enforce 2FA/MFA for users of Firezone's WireGuard®-based
|
||||
secure access platform. This guide walks through integrating Keycloak
|
||||
for single sign-on using OpenID Connect (OIDC).
|
||||
---
|
||||
|
||||
# Enable SSO with Keycloak (OIDC)
|
||||
|
||||
Firezone supports Single Sign-On (SSO) using Keycloak
|
||||
through the generic OIDC provider. This guide will walk you through how to
|
||||
obtain the following config settings required for the integration:
|
||||
|
||||
1. **Config ID**: The provider's config ID. (e.g. `keycloak`)
|
||||
1. **Label**: The button label text that shows up on your Firezone login screen. (e.g. `Keycloak`)
|
||||
1. **Scope**: [OIDC scopes](https://openid.net/specs/openid-connect-basic-1_0.html#Scopes)
|
||||
to obtain from your OIDC provider. This should be set to `openid email profile offline_access`
|
||||
to provide Firezone with the user's email in the returned claims.
|
||||
1. **Response type**: Set to `code`.
|
||||
1. **Client ID**: The client ID of the application.
|
||||
1. **Client secret**: The client secret of the application.
|
||||
1. **Discovery Document URI**: The
|
||||
[OpenID Connect provider configuration URI](https://openid.net/specs/openid-connect-discovery-1_0.html#ProviderConfig)
|
||||
which returns a JSON document used to construct subsequent requests to this
|
||||
OIDC provider.
|
||||
|
||||
## Step 1: Obtain configuration parameters
|
||||
|
||||
In the Keycloak Admin Console, make sure the realm you want to use with Firezone
|
||||
is selected.
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
### Create Firezone OAuth client
|
||||
|
||||
Create a new Client for Firezone by navigating to **Clients > Create Client** and
|
||||
configure the following:
|
||||
|
||||
1. **Client type**: `OpenID Connect`
|
||||
1. **Client ID**: `firezone`
|
||||
1. **Name**: `Firezone`
|
||||
1. Click **Next**.
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
1. Toggle **Client authentication** to `On` to generate the client secret.
|
||||
1. Click **Save**.
|
||||
|
||||
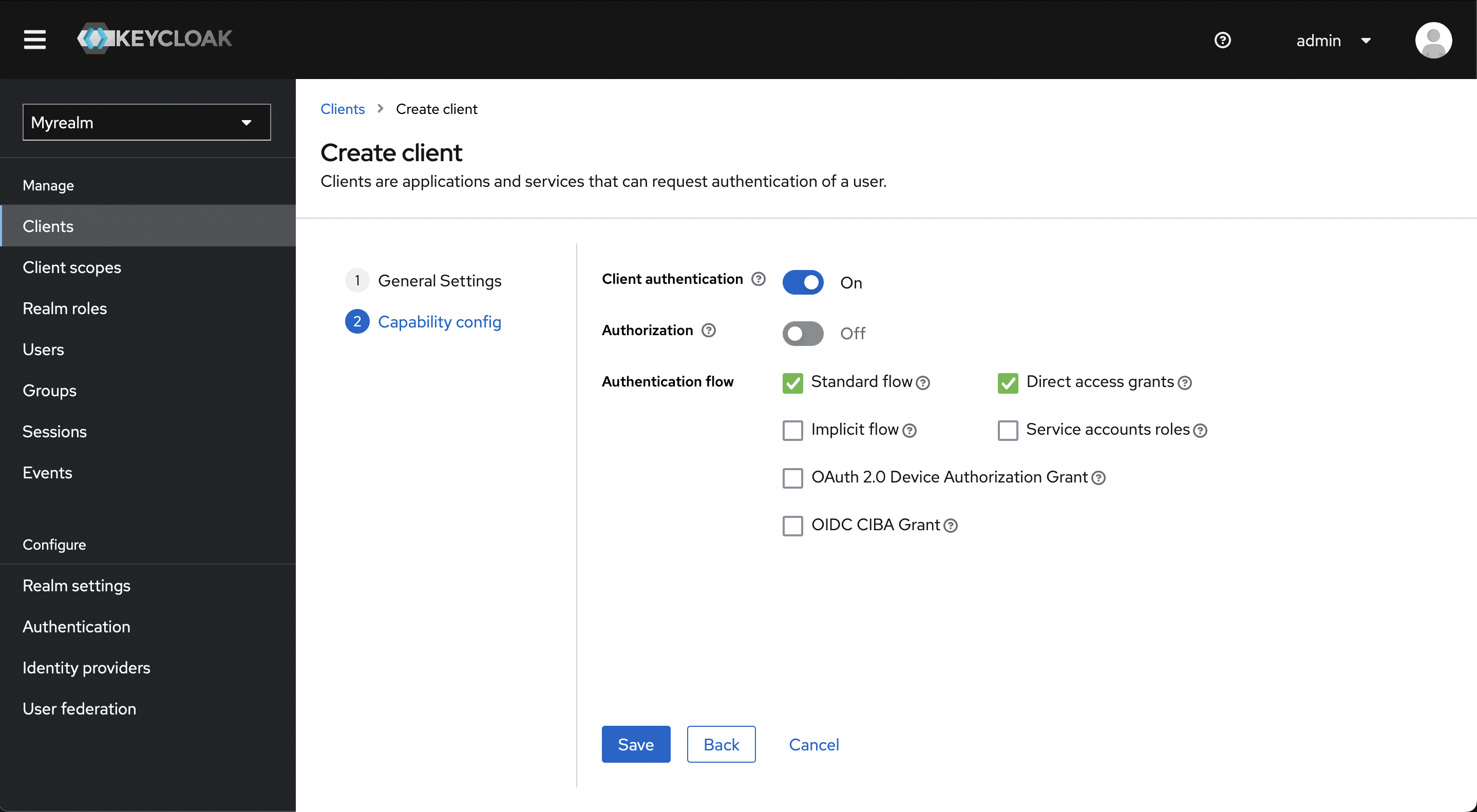
|
||||
|
||||
Click **Access settings** to jump to that section and configure the valid redirect URI:
|
||||
|
||||
1. **Valid Redirect URIs**: This should be your Firezone `EXTERNAL_URL + /auth/oidc/<Config ID>/callback/`
|
||||
(e.g. `https://firezone.example.com/auth/oidc/keycloak/callback/`).
|
||||
1. Click **Add valid redirect URIs**
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
Click the **Credentials** tab and copy the client secret.
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
Navigate to the **Realm Settings** page to get the **Discovery Document URI** by
|
||||
copying the **OpenID Endpoint Configuration** link at the bottom of the page.
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
## Step 2: Integrate with Firezone
|
||||
|
||||
Navigate to the `/settings/security` page in the admin portal, click
|
||||
"Add OpenID Connect Provider" and enter the details you obtained in the steps
|
||||
above.
|
||||
|
||||
Enable or disable the **Auto create users** option to automatically create
|
||||
an unprivileged user when signing in via this authentication mechanism.
|
||||
|
||||
And that's it! The configuration should be updated immediately.
|
||||
You should now see a `Sign in with Keycloak` button on the sign in page.
|
||||
@@ -1,83 +0,0 @@
|
||||
---
|
||||
title: Okta
|
||||
sidebar_position: 5
|
||||
description:
|
||||
Enforce 2FA/MFA for users of Firezone's WireGuard®-based
|
||||
secure access platform. This guide walks through integrating Okta
|
||||
for single sign-on using OpenID Connect (OIDC).
|
||||
---
|
||||
|
||||
# Enable SSO with Okta (OIDC)
|
||||
|
||||
Firezone supports Single Sign-On (SSO) using Okta
|
||||
through the generic OIDC connector. This guide will walk you through how to
|
||||
obtain the following config settings required for the integration:
|
||||
|
||||
1. **Config ID**: The provider's config ID. (e.g. `okta`)
|
||||
1. **Label**: The button label text that shows up on your Firezone login screen. (e.g. `Okta`)
|
||||
1. **Scope**: [OIDC scopes](https://openid.net/specs/openid-connect-basic-1_0.html#Scopes)
|
||||
to obtain from your OIDC provider. This should be set to `openid email profile offline_access`
|
||||
to provide Firezone with the user's email in the returned claims.
|
||||
1. **Response type**: Set to `code`.
|
||||
1. **Client ID**: The client ID of the application.
|
||||
1. **Client secret**: The client secret of the application.
|
||||
1. **Discovery Document URI**: The
|
||||
[OpenID Connect provider configuration URI](https://openid.net/specs/openid-connect-discovery-1_0.html#ProviderConfig)
|
||||
which returns a JSON document used to construct subsequent requests to this
|
||||
OIDC provider.
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
## Step 1: Create Okta app integration
|
||||
|
||||
_This section of the guide is based on
|
||||
[Okta's documentation](https://help.okta.com/en/prod/Content/Topics/Apps/Apps_App_Integration_Wizard_OIDC.htm)._
|
||||
|
||||
In the Admin Console, go to **Applications > Applications** and click
|
||||
**Create App Integration**. Set **Sign-in method** to **OICD - OpenID Connect**
|
||||
and **Application type** to **Web application**.
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
On the following screen, configure the following settings:
|
||||
|
||||
1. **App Name**: `Firezone`
|
||||
1. **App logo**:
|
||||
[Firezone logo](https://user-images.githubusercontent.com/52545545/155907625-a4f6c8c2-3952-488d-b244-3c37400846cf.png)
|
||||
(save link as).
|
||||
1. **Proof Key for Code Exchange (PKCE)**: Check `Require PKCE as additional verification` if you're running Firezone
|
||||
0.6.8 or higher. [PKCE](https://oauth.net/2/pkce/) is recommended for increased security whenever possible.
|
||||
1. **Grant Type**: Check the **Refresh Token** box. This ensures Firezone syncs
|
||||
with the identity provider and VPN access is terminated once the user is removed.
|
||||
1. **Sign-in redirect URIs**: Add your Firezone `EXTERNAL_URL + /auth/oidc/<Config ID>/callback/`
|
||||
(e.g. `https://firezone.example.com/auth/oidc/okta/callback/`) as an entry to
|
||||
Authorized redirect URIs.
|
||||
1. **Assignments**:
|
||||
Limit to the groups you wish to provide access to your Firezone instance.
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
Once settings are saved, you will be given a **Client ID**, **Client Secret**,
|
||||
and **Okta Domain**. These 3 values will be used in Step 2 to configure Firezone.
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
## Step 2: Integrate with Firezone
|
||||
|
||||
Navigate to the `/settings/security` page in the admin portal, click
|
||||
"Add OpenID Connect Provider" and enter the details you obtained in the steps
|
||||
above.
|
||||
|
||||
Enable or disable the **Auto create users** option to automatically create
|
||||
an unprivileged user when signing in via this authentication mechanism.
|
||||
|
||||
And that's it! The configuration should be updated immediately.
|
||||
You should now see a `Sign in with Okta` button on the sign in page.
|
||||
|
||||
## Step 3 (optional): Restrict Access to specific users
|
||||
|
||||
Okta can limit the users with access to the Firezone app. To do this,
|
||||
go to the Assignments tab of the Firezone App Integration in your Okta
|
||||
Admin Console.
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
@@ -1,65 +0,0 @@
|
||||
---
|
||||
title: OneLogin
|
||||
sidebar_position: 6
|
||||
description:
|
||||
Enforce 2FA/MFA for users of Firezone's WireGuard®-based
|
||||
secure access platform. This guide walks through integrating OneLogin
|
||||
for single sign-on using OpenID Connect (OIDC).
|
||||
---
|
||||
|
||||
# Enable SSO with OneLogin (OIDC)
|
||||
|
||||
Firezone supports Single Sign-On (SSO) using OneLogin
|
||||
through the generic OIDC connector. This guide will walk you through how to
|
||||
obtain the following config settings required for the integration:
|
||||
|
||||
1. **Config ID**: The provider's config ID. (e.g. `onelogin`)
|
||||
1. **Label**: The button label text that shows up on your Firezone login screen. (e.g. `OneLogin`)
|
||||
1. **Scope**: [OIDC scopes](https://openid.net/specs/openid-connect-basic-1_0.html#Scopes)
|
||||
to obtain from your OIDC provider. This should be set to `openid email profile`
|
||||
to provide Firezone with the user's email in the returned claims.
|
||||
1. **Response type**: Set to `code`.
|
||||
1. **Client ID**: The client ID of the application.
|
||||
1. **Client secret**: The client secret of the application.
|
||||
1. **Discovery Document URI**: The
|
||||
[OpenID Connect provider configuration URI](https://openid.net/specs/openid-connect-discovery-1_0.html#ProviderConfig)
|
||||
which returns a JSON document used to construct subsequent requests to this
|
||||
OIDC provider.
|
||||
|
||||
## Step 1: Create custom connector
|
||||
|
||||
Create a new OIDC connector by visiting **Appliances > Custom Connectors**.
|
||||
|
||||
1. **App name**: `Firezone`
|
||||
1. **Icon**: [Firezone logo](https://user-images.githubusercontent.com/52545545/156854754-da66a9e1-33d5-47f5-877f-eff8b330ab2b.png)
|
||||
or
|
||||
[Firezone icon](https://user-images.githubusercontent.com/52545545/156854754-da66a9e1-33d5-47f5-877f-eff8b330ab2b.png)
|
||||
(save link as).
|
||||
1. **Sign on method**: select **OpenID Connect**
|
||||
1. **Redirect URI**: Add your Firezone `<EXTERNAL_URL> + /auth/oidc/<Config ID>/callback/`
|
||||
(e.g. `https://firezone.example.com/auth/oidc/onelogin/callback/`).
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
## Step 2: Obtain configuration parameters
|
||||
|
||||
Next, click **Add App to Connector** to create an OIDC application.
|
||||
Visit the **SSO** tab, then change the token endpoint authentication method
|
||||
to **POST**.
|
||||
|
||||
You will find the values for the config settings required by Firezone
|
||||
on this page as well.
|
||||
|
||||
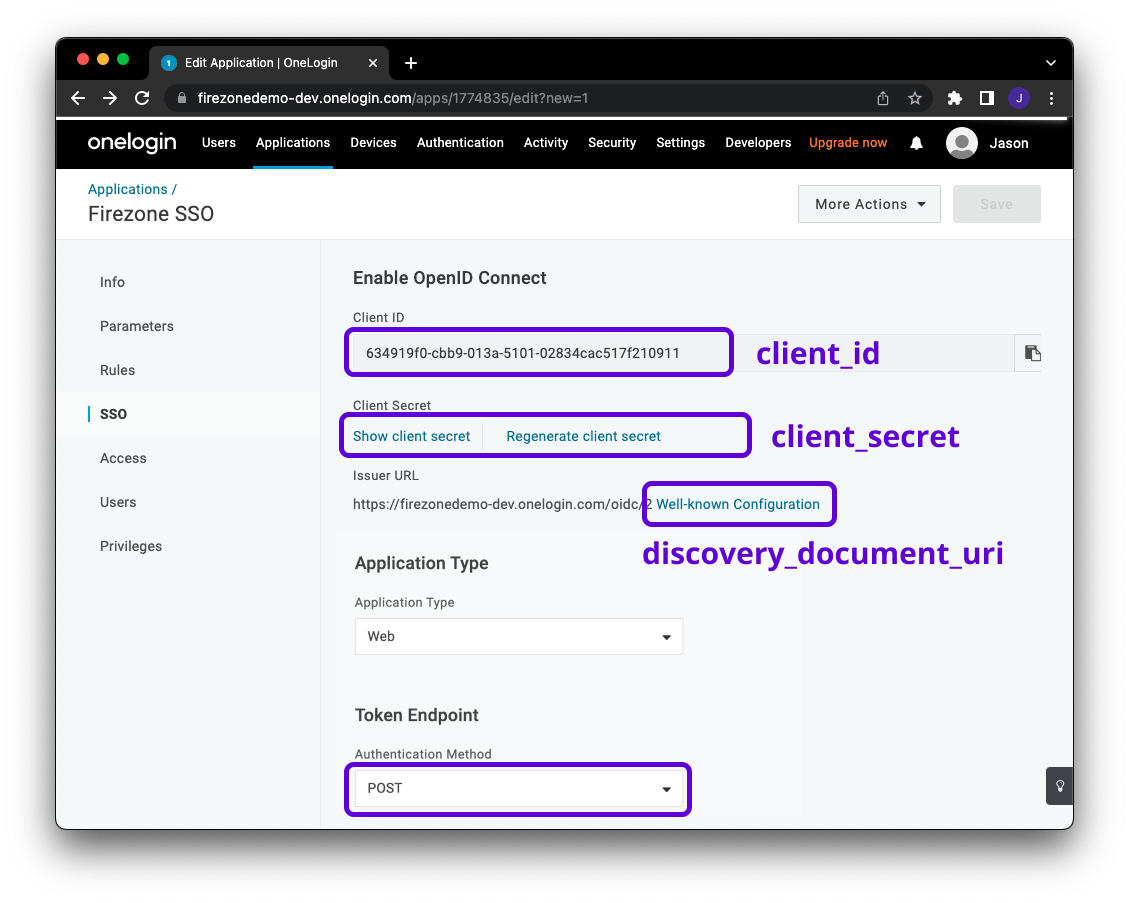
|
||||
|
||||
## Step 3: Integrate with Firezone
|
||||
|
||||
Navigate to the `/settings/security` page in the admin portal, click
|
||||
"Add OpenID Connect Provider" and enter the details you obtained in the steps
|
||||
above.
|
||||
|
||||
Enable or disable the **Auto create users** option to automatically create
|
||||
an unprivileged user when signing in via this authentication mechanism.
|
||||
|
||||
And that's it! The configuration should be updated immediately.
|
||||
You should now see a `Sign in with OneLogin` button on the sign in page.
|
||||
@@ -1,103 +0,0 @@
|
||||
---
|
||||
title: Zitadel
|
||||
sidebar_position: 7
|
||||
description:
|
||||
Enforce 2FA/MFA for users of Firezone's WireGuard®-based
|
||||
secure access platform. This guide walks through integrating Zitadel
|
||||
for single sign-on using OpenID Connect (OIDC).
|
||||
---
|
||||
|
||||
# Enable SSO with Zitadel (OIDC)
|
||||
|
||||
Firezone supports Single Sign-On (SSO) using Zitadel
|
||||
through the generic OIDC connector. This guide will walk you through how to
|
||||
obtain the following config settings required for the integration:
|
||||
|
||||
1. **Config ID**: The provider's config ID. (e.g. `zitadel`)
|
||||
1. **Label**: The button label text that shows up on your Firezone login screen. (e.g. `Zitadel`)
|
||||
1. **Scope**: [OIDC scopes](https://openid.net/specs/openid-connect-basic-1_0.html#Scopes)
|
||||
to obtain from your OIDC provider. This should be set to `openid email profile offline_access`
|
||||
to provide Firezone with the user's email in the returned claims.
|
||||
1. **Response type**: Set to `code`.
|
||||
1. **Client ID**: The client ID of the application.
|
||||
1. **Client secret**: The client secret of the application.
|
||||
1. **Discovery Document URI**: The
|
||||
[OpenID Connect provider configuration URI](https://openid.net/specs/openid-connect-discovery-1_0.html#ProviderConfig)
|
||||
which returns a JSON document used to construct subsequent requests to this
|
||||
OIDC provider.
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
## Requirements
|
||||
|
||||
* Setup your own [Zitadel Cloud](https://zitadel.cloud/) account.
|
||||
* Create your first Zitadel instance in the
|
||||
[Zitadel Customer portal](https://zitadel.cloud/admin/instances)
|
||||
* Login to your Zitadel instance and create a project (i.e. "Internal")
|
||||
|
||||
More information about these steps can be found in
|
||||
[Zitadel's documentation](https://docs.zitadel.com/docs/guides/start/quickstart#try-out-zitadel-cloud).
|
||||
|
||||
## Create Zitadel Application
|
||||
|
||||
In the Instance Console, go to **Projects** and select the project you want,
|
||||
then click **New**.
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
Give the application a name (e.g. "Firezone") and select **WEB**
|
||||
for the application type.
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
Select **CODE** for the authentication method.
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
Specify the redirect URI and post logout URI.
|
||||
|
||||
1. **Redirect URIs**: `EXTERNAL_URL + /auth/oidc/<Config ID>/callback/`
|
||||
(e.g. `https://vpn.example.com/auth/oidc/zitadel/callback/`)
|
||||
1. **Post Logout URIs**: `EXTERNAL_URL` (e.g. `https://vpn.example.com`)
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
Double-check the configuration, then click **Create**.
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
Copy the **ClientId** and **ClientSecret** as it will be used for the Firezone
|
||||
configuration.
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
In the application **Configuration** click **Refresh Token** and then on
|
||||
**Save**. The refresh token is optional for some features of Firezone.
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
In the application **Token Settings** select **User roles inside ID Token** and
|
||||
**User Info inside ID Token**. Save it with a click on **Save**.
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
## Integrate With Firezone
|
||||
|
||||
Navigate to the `/settings/security` page in the admin portal, click
|
||||
"Add OpenID Connect Provider" and enter the details you obtained in the steps
|
||||
above.
|
||||
|
||||
Enable or disable the **Auto create users** option to automatically create
|
||||
an unprivileged user when signing in via this authentication mechanism.
|
||||
|
||||
And that's it! The configuration should be updated immediately.
|
||||
You should now see a `Sign in with Zitadel` button on the sign in page.
|
||||
|
||||
## Step 3 (optional): Restrict access to specific users
|
||||
|
||||
Zitadel can limit which users have access to Firezone. To do this,
|
||||
go to the project where your created your application. In **General** you can
|
||||
find **Check Authorization on Authentication** which allows only users with at
|
||||
least one role to login to Firezone.
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
@@ -1,81 +0,0 @@
|
||||
---
|
||||
title: SAML 2.0
|
||||
sidebar_position: 11
|
||||
description: Enforce single sign-on with your identity provider. Integrate
|
||||
providers like Okta, Google, OneLogin, and JumpCloud using Firezone's
|
||||
SAML 2.0 connector.
|
||||
---
|
||||
|
||||
# Integrate your identity provider using SAML 2.0
|
||||
|
||||
Firezone supports Single Sign-On (SSO) via SAML 2.0.
|
||||
|
||||
## Supported identity providers
|
||||
|
||||
In general, most identity providers that support SAML 2.0 should work with
|
||||
Firezone.
|
||||
|
||||
| Provider | Support Status | Notes |
|
||||
| -------------------------- | ------------------------ | ---------------------------------- |
|
||||
| [Okta](okta) | **Tested and supported** | |
|
||||
| [Google Workspace](google) | **Tested and supported** | Uncheck `Require signed envelopes` |
|
||||
| [OneLogin](onelogin) | **Tested and supported** | |
|
||||
| [JumpCloud](jumpcloud) | **Tested and supported** | Uncheck `Require signed envelopes` |
|
||||
|
||||
Occasionally, providers that don't implement the full SAML 2.0 standard or use
|
||||
uncommon configurations may be problematic. If this is the case, [contact us](/contact/support)
|
||||
about a custom integration.
|
||||
|
||||
## Custom SAML cert and keyfile
|
||||
|
||||
SAML 2.0 requires a set of private and public keys using the RSA or
|
||||
DSA algorithms along with an X.509 certificate that contains the public key.
|
||||
|
||||
Firezone automatically generates these for on both Docker and Omnibus-based
|
||||
deployments. If you'd like to use your own cert and key, however, you can generate
|
||||
them with `openssl`:
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
openssl req -x509 -sha256 -nodes -days 365 -newkey rsa:2048 -keyout saml.key -out saml.crt
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Then use them with your Firezone installation:
|
||||
|
||||
<Tabs>
|
||||
<TabItem value="docker" label="Docker" default>
|
||||
|
||||
Set the `SAML_KEYFILE_PATH` and `SAML_CERTFILE_PATH` environment variables to
|
||||
the path containing your `saml.key` and `saml.crt` above. If using our [example
|
||||
docker compose file](https://github.com/firezone/firezone/blob/master/docker-compose.prod.yml),
|
||||
which includes a volume for mapping configuration,
|
||||
save these files to `$HOME/.firezone/firezone` on the Docker host and set the
|
||||
`SAML_KEYFILE_PATH=/var/firezone/saml.key` and
|
||||
`SAML_CERTFILE_PATH=/var/firezone/saml.crt` environment variables for the Firezone
|
||||
container.
|
||||
|
||||
</TabItem>
|
||||
</Tabs>
|
||||
|
||||
## General setup instructions
|
||||
|
||||
Once you've configured Firezone with an X.509 certificate and corresponding
|
||||
private key as shown above, you'll need a few more things to set up a generic
|
||||
SAML integration.
|
||||
|
||||
### IdP metadata document
|
||||
|
||||
You'll need to get the SAML Metadata XML document from your identity provider. In most
|
||||
cases this can be downloaded from your IdP's SAML App configuration dashboard.
|
||||
|
||||
### ACS URL
|
||||
|
||||
Firezone constructs the ACS URL based on the Base URL and Configuration ID entered
|
||||
in the Firezone SAML configuration, defaulting to: `EXTERNAL_URL/auth/saml/sp/consume/:config_id`,
|
||||
e.g. `https://firezone.company.com/auth/saml/sp/consume/okta`.
|
||||
|
||||
### Entity ID
|
||||
|
||||
The Firezone Entity ID can be configured with the `SAML_ENTITY_ID` environment variable
|
||||
and defaults to `urn:firezone.dev:firezone-app` if not set.
|
||||
|
||||
See the [environment variable reference](/docs/reference/env-vars) for more information.
|
||||
@@ -1,54 +0,0 @@
|
||||
---
|
||||
title: Google Workspace
|
||||
sidebar_position: 2
|
||||
description:
|
||||
Enforce 2FA/MFA using Google Workspace for users of Firezone's WireGuard®-based
|
||||
secure access platform. This guide walks through integrating Google Workspace
|
||||
for single sign-on using the SAML 2.0 connector.
|
||||
---
|
||||
|
||||
# Enable SSO with Google Workspace (SAML 2.0)
|
||||
|
||||
Firezone supports Single Sign-On (SSO) using Google through the generic SAML 2.0
|
||||
connector. This guide will walk you through how to configure the integration.
|
||||
|
||||
## Step 1: Create a SAML connector
|
||||
|
||||
In the Google Workspace admin portal, create a new SAML app under
|
||||
the Application > Web and mobile apps tab. Use the following config values during setup:
|
||||
|
||||
| Setting | Value |
|
||||
| --------------- | ---------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- |
|
||||
| App name | Firezone |
|
||||
| App icon | [save link as](https://user-images.githubusercontent.com/52545545/202567638-513dba14-ea8c-4da8-8f75-341310f1e456.png) |
|
||||
| ACS URL | This is your Firezone `EXTERNAL_URL/auth/saml/sp/consume/:config_id` (e.g., `https://firezone.company.com/auth/saml/sp/consume/google`). |
|
||||
| Entity ID | This should be the same as your Firezone `SAML_ENTITY_ID`, defaults to `urn:firezone.dev:firezone-app`. |
|
||||
| Signed response | Unchecked. |
|
||||
| Name ID format | Unspecified |
|
||||
| Name ID | Basic Information > Primary email |
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
Once complete, save the changes and download the SAML metadata document. You'll need
|
||||
to copy-paste the contents of this document into the Firezone portal in the next step.
|
||||
|
||||
## Step 2: Add SAML identity provider to Firezone
|
||||
|
||||
In the Firezone portal, add a SAML identity provider under the Security tab
|
||||
by filling out the following information:
|
||||
|
||||
| Setting | Value | Notes |
|
||||
| ------------------------- | --------------- | ------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- |
|
||||
| Config ID | google | Firezone uses this value to construct endpoints required in the SAML authentication flow (e.g., receiving assertions, login requests). |
|
||||
| Label | Google | Appears on the sign in button for authentication. |
|
||||
| Metadata | see note | Paste the contents of the SAML metadata document you downloaded in the previous step from Google. |
|
||||
| Sign assertions | Checked. | |
|
||||
| Sign metadata | Checked. | |
|
||||
| Require signed assertions | Checked. | |
|
||||
| Require signed envelopes | **Unchecked.** | |
|
||||
| Auto create users | Default `false` | Enable this setting to automatically create users when signing in with this connector for the first time. Disable to manually create users. |
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
After saving the SAML config, you should see a `Sign in with Google` button
|
||||
on your Firezone portal sign-in page.
|
||||
@@ -1,71 +0,0 @@
|
||||
---
|
||||
title: JumpCloud
|
||||
sidebar_position: 4
|
||||
description:
|
||||
Enforce 2FA/MFA using JumpCloud for users of Firezone's WireGuard®-based
|
||||
secure access platform. This guide walks through integrating JumpCloud
|
||||
for single sign-on using the SAML 2.0 connector.
|
||||
---
|
||||
|
||||
# Enable SSO with JumpCloud (SAML 2.0)
|
||||
|
||||
:::note
|
||||
This guide assumes you have completed the prerequisite steps
|
||||
(e.g. generate self-signed X.509 certificates) outlined [here](/docs/authenticate/saml#prerequisites).
|
||||
:::
|
||||
|
||||
Firezone supports Single Sign-On (SSO) using JumpCloud through the generic SAML 2.0 connector.
|
||||
This guide will walk you through how to configure the integration.
|
||||
|
||||
## Step 1: Create a SAML connector
|
||||
|
||||
In the JumpCloud admin portal, create a new App under
|
||||
the SSO tab. At the bottom of the popup window, click `Custom SAML App`.
|
||||
|
||||
After entering your desired value for `Display Label`, click the `SSO` tab,
|
||||
then use the following configuration values:
|
||||
|
||||
| Setting | Value |
|
||||
| ------------------------- | ------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------ |
|
||||
| IdP Entity ID | Any unique string will work, e.g. `firezone-jumpcloud`. |
|
||||
| SP Entity ID | This should be the same as your Firezone `SAML_ENTITY_ID`, defaults to `urn:firezone.dev:firezone-app`. |
|
||||
| ACS URL | This is your Firezone `EXTERNAL_URL/auth/saml/sp/consume/:config_id`, e.g. `https://firezone.company.com/auth/saml/sp/consume/jumpcloud`. |
|
||||
| SAMLSubject NameID | `email` |
|
||||
| SAMLSubject NameID Format | Leave at the default. |
|
||||
| Signature Algorithm | `RSA-SHA256` |
|
||||
| Sign Assertion | **Checked**. |
|
||||
| Login URL | This is your Firezone `EXTERNAL_URL/auth/saml/auth/signin/:config_id`, e.g. `https://firezone.company.com/auth/saml/auth/signin/jumpcloud` |
|
||||
|
||||
Leave the rest of the settings unchanged, then click the `activate` button at the bottom-right.
|
||||
|
||||
Your JumpCloud configuration should now resemble the following:
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
Now, download the IdP Metadata document by selecting the App you just created
|
||||
and then clicking the `export metadata` button in the upper-right. You'll need
|
||||
to copy-paste the contents of this document into the Firezone portal in the next step.
|
||||
|
||||
## Step 2: Add SAML identity provider to Firezone
|
||||
|
||||
In the Firezone portal, add a SAML identity provider under the Security tab
|
||||
by filling out the following information:
|
||||
|
||||
| Setting | Value | Notes |
|
||||
| ------------------------- | ---------------- | ------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- |
|
||||
| Config ID | `jumpcloud` | Firezone uses this value to construct endpoints required in the SAML authentication flow (e.g., receiving assertions, login requests). |
|
||||
| Label | `JumpCloud` | Appears on the sign in button for authentication. |
|
||||
| Base URL | Leave unchanged. | |
|
||||
| Metadata | see note | Copy-paste the contents of the SAML metadata document you downloaded in the previous step from JumpCloud. |
|
||||
| Sign assertions | Checked. | |
|
||||
| Sign metadata | Checked. | |
|
||||
| Require signed assertions | Checked. | |
|
||||
| Require signed envelopes | **Unchecked.** | |
|
||||
| Auto create users | Default `false` | Enable this setting to automatically create users when signing in with this connector for the first time. Disable to manually create users. |
|
||||
|
||||
Your Firezone configuration should now resemble the following:
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
After saving the SAML config, you should see a `Sign in with JumpCloud` button
|
||||
on your Firezone portal sign-in page.
|
||||
@@ -1,62 +0,0 @@
|
||||
---
|
||||
title: Okta
|
||||
sidebar_position: 1
|
||||
description: Enforce 2FA/MFA using Okta for users of Firezone's WireGuard®-based
|
||||
secure access platform. This guide walks through integrating Okta
|
||||
for single sign-on using the SAML 2.0 connector.
|
||||
---
|
||||
|
||||
# Enable SSO with Okta (SAML 2.0)
|
||||
|
||||
:::note
|
||||
This guide assumes you have completed the prerequisite steps
|
||||
(e.g. generate self-signed X.509 certificates) outlined [here](/docs/authenticate/saml#prerequisites).
|
||||
:::
|
||||
|
||||
Firezone supports Single Sign-On (SSO) using Okta through the generic SAML 2.0 connector. This guide will walk you through how to configure the integration.
|
||||
|
||||
## Step 1: Create a SAML connector
|
||||
|
||||
In the Okta admin portal, create a new app integration under
|
||||
the Application tab. Select `SAML 2.0` as the authentication method.
|
||||
Use the following config values during setup:
|
||||
|
||||
| Setting | Value |
|
||||
| ------------------------------ | -------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- |
|
||||
| App name | Firezone |
|
||||
| App logo | [save link as](https://user-images.githubusercontent.com/52545545/155907625-a4f6c8c2-3952-488d-b244-3c37400846cf.png) |
|
||||
| Single sign on URL | This is your Firezone `EXTERNAL_URL/auth/saml/sp/consume/:config_id` (e.g., `https://firezone.company.com/auth/saml/sp/consume/okta`). |
|
||||
| Audience (EntityID) | This should be the same as your Firezone `SAML_ENTITY_ID`, defaults to `urn:firezone.dev:firezone-app`. |
|
||||
| Name ID format | EmailAddress |
|
||||
| Application username | Email |
|
||||
| Update application username on | Create and update |
|
||||
|
||||
[Okta's documentation](https://help.okta.com/oie/en-us/Content/Topics/Apps/Apps_App_Integration_Wizard_SAML.htm)
|
||||
contains additional details on the purpose of each configuration setting.
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
After creating the SAML connector, visit the `View SAML setup instructions` link in
|
||||
the Sign On tab to download the metadata document. You'll need
|
||||
to copy-paste the contents of this document into the Firezone portal in the next step.
|
||||
|
||||
## Step 2: Add SAML identity provider to Firezone
|
||||
|
||||
In the Firezone portal, add a SAML identity provider under the Security tab
|
||||
by filling out the following information:
|
||||
|
||||
| Setting | Value | Notes |
|
||||
| ------------------------- | --------------- | ------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- |
|
||||
| Config ID | Okta | Used to construct endpoints required in the SAML authentication flow (e.g., receiving assertions, login requests). |
|
||||
| Label | Okta | Appears on the sign in button for authentication. |
|
||||
| Metadata | see note | Paste the contents of the SAML metadata document you downloaded in the previous step from Okta. |
|
||||
| Sign assertions | Checked. | |
|
||||
| Sign metadata | Checked. | |
|
||||
| Require signed assertions | Checked. | |
|
||||
| Require signed envelopes | Checked. | |
|
||||
| Auto create users | Default `false` | Enable this setting to automatically create users when signing in with this connector for the first time. Disable to manually create users. |
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
After saving the SAML config, you should see a `Sign in with Okta` button
|
||||
on your Firezone portal sign-in page.
|
||||
@@ -1,67 +0,0 @@
|
||||
---
|
||||
title: OneLogin
|
||||
sidebar_position: 3
|
||||
description:
|
||||
Enforce 2FA/MFA using Onelogin for users of Firezone's WireGuard®-based
|
||||
secure access platform. This guide walks through integrating OneLogin
|
||||
for single sign-on using the SAML 2.0 connector.
|
||||
---
|
||||
|
||||
# Enable SSO with OneLogin (SAML 2.0)
|
||||
|
||||
:::note
|
||||
This guide assumes you have completed the prerequisite steps
|
||||
(e.g. generate self-signed X.509 certificates) outlined [here](/docs/authenticate/saml#prerequisites).
|
||||
:::
|
||||
|
||||
Firezone supports Single Sign-On (SSO) using OneLogin through the generic SAML 2.0 connector.
|
||||
This guide will walk you through how to configure the integration.
|
||||
|
||||
## Step 1: Create a SAML connector
|
||||
|
||||
In the OneLogin admin portal, add an app under the application tab.
|
||||
Select `SAML Custom Connector (Advanced)` and provide the appropriate
|
||||
configuration settings under the under the configuration tab.
|
||||
|
||||
The following fields should be filled out on this page:
|
||||
|
||||
| Setting | Value |
|
||||
| ---------------------- | ----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- |
|
||||
| Audience (EntityID) | This should be the same as your Firezone `SAML_ENTITY_ID`, defaults to `urn:firezone.dev:firezone-app`. |
|
||||
| Recipient | This is your Firezone `EXTERNAL_URL/auth/saml/sp/consume/:config_id` (e.g., `https://firezone.company.com/auth/saml/sp/consume/onelogin`). |
|
||||
| ACS URL Validator | This field is regex to ensure OneLogin posts the response to the correct URL. For the sample URL below, we can use `^https:\/\/firezone\.company\.com\/auth\/saml\/sp\/consume\/onelogin` |
|
||||
| ACS URL | This is your Firezone `EXTERNAL_URL/auth/saml/sp/consume/:config_id` (e.g., `https://firezone.company.com/auth/saml/sp/consume/onelogin`). |
|
||||
| Login URL | This is your Firezone `EXTERNAL_URL/auth/saml/auth/signin/:config_id` (e.g., `https://firezone.company.com/auth/saml/sp/consume/onelogin`). |
|
||||
| SAML initiator | Service Provider |
|
||||
| SAML signature element | Both |
|
||||
| Encrypt Assertion | Checked. |
|
||||
|
||||
[OneLogin's docs](https://onelogin.service-now.com/support?id=kb_article&sys_id=912bb23edbde7810fe39dde7489619de&kb_category=93e869b0db185340d5505eea4b961934)
|
||||
provide a good overview of each field's purpose.
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
Once complete, save the changes and download the SAML metadata document
|
||||
found unde the `More Actions` dropdown. You'll need
|
||||
to copy-paste the contents of this document into the Firezone portal in the next step.
|
||||
|
||||
## Step 2: Add SAML identity provider to Firezone
|
||||
|
||||
In the Firezone portal, add a SAML identity provider under the Security tab
|
||||
by filling out the following information:
|
||||
|
||||
| Setting | Value | Notes |
|
||||
| ------------------------- | --------------- | ------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- |
|
||||
| Config ID | `onelogin` | Used to construct endpoints required in the SAML authentication flow (e.g., receiving assertions, login requests). |
|
||||
| Label | `OneLogin` | Appears on the sign in button for authentication. |
|
||||
| Metadata | see note | Paste the contents of the SAML metadata document you downloaded in the previous step from OneLogin. |
|
||||
| Sign assertions | Checked. | |
|
||||
| Sign metadata | Checked. | |
|
||||
| Require signed assertions | Checked. | |
|
||||
| Require signed envelopes | Checked. | |
|
||||
| Auto create users | Default `false` | Enable this setting to automatically create users when signing in with this connector for the first time. Disable to manually create users. |
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
After saving the SAML config, you should see a `Sign in with OneLogin` button
|
||||
on your Firezone portal sign-in page.
|
||||
@@ -1,90 +0,0 @@
|
||||
---
|
||||
title: Deploy
|
||||
sidebar_position: 2
|
||||
description:
|
||||
Install Firezone's WireGuard®-based secure access platform on a support
|
||||
host using our Docker (recommended) or Omnibus deployment methods.
|
||||
---
|
||||
|
||||
# Deploy Firezone
|
||||
|
||||
Firezone can be deployed on most Docker-supported platforms in a couple of minutes.
|
||||
Read more below to get started.
|
||||
|
||||
## Step 1: Prepare to deploy
|
||||
|
||||
Regardless of which deployment method you choose, you'll need to follow the
|
||||
preparation steps below before deploying Firezone to production.
|
||||
|
||||
1. [Create a DNS record](#create-a-dns-record)
|
||||
1. [Set up SSL](#set-up-ssl)
|
||||
1. [Open required firewall ports](#open-required-firewall-ports)
|
||||
|
||||
### Create a DNS record
|
||||
|
||||
Firezone requires a fully-qualified domain name (e.g. `firezone.company.com`)
|
||||
for production use. You'll need to create the appropriate DNS record at your
|
||||
registrar to achieve this. Typically this is either an A, CNAME, or AAAA record
|
||||
depending on your requirements.
|
||||
|
||||
### Set up SSL
|
||||
|
||||
You'll need a valid SSL certificate to use Firezone in a production capacity.
|
||||
Firezone supports ACME for automatic provisioning of SSL certificates for both
|
||||
Docker-based and Omnibus-based installations. This is recommended in most cases.
|
||||
|
||||
<Tabs>
|
||||
<TabItem value="docker" label="Docker" default>
|
||||
|
||||
#### Setting up ACME for Docker-based deployments
|
||||
|
||||
For Docker-based deployments, the simplest way to provision an SSL
|
||||
certificate is to use our Caddy service example in docker-compose.yml.
|
||||
Caddy uses ACME to automatically provision SSL certificates as long as
|
||||
it's available on port 80/tcp and the DNS record for the server is valid.
|
||||
|
||||
See the [Docker deployment guide](docker) for more info.
|
||||
|
||||
</TabItem>
|
||||
</Tabs>
|
||||
|
||||
### Open required firewall ports
|
||||
|
||||
By default, Firezone requires ports `443/tcp` and `51820/udp` to be
|
||||
accessible for HTTPS and WireGuard traffic respectively.
|
||||
These ports can change based on what you've configured in the configuration file.
|
||||
See the
|
||||
[configuration file reference](../reference/configuration-file)
|
||||
for details.
|
||||
|
||||
### Resource requirements
|
||||
|
||||
We recommend **starting with 1 vCPU and 1 GB of RAM and scaling up** as the
|
||||
number of users and devices grows.
|
||||
|
||||
For Omnibus-based deployments on servers with less than 1GB of memory, we
|
||||
recommend turning on swap to prevent the Linux kernel from killing
|
||||
Firezone processes unexpectedly. When this happens, it's often difficult to
|
||||
debug and results in strange, unpredictable failure modes.
|
||||
|
||||
For the VPN tunnels themselves, Firezone uses in-kernel WireGuard, so its
|
||||
performance should be very good. 1 vCPU should be more than enough to saturate
|
||||
a 1 Gbps link.
|
||||
|
||||
## Step 2: Deploy
|
||||
|
||||
You have two options for deploying Firezone:
|
||||
|
||||
1. [Docker](docker) (recommended)
|
||||
1. [Omnibus](omnibus)
|
||||
|
||||
Docker is the easiest way to install, manage, and upgrade Firezone and is the
|
||||
preferred method of deployment.
|
||||
|
||||
:::warning
|
||||
Chef Infra Client, the configuration system Chef Omnibus relies on, has been
|
||||
[scheduled for End-of-Life in 2024](https://docs.chef.io/versions/). As such,
|
||||
support for Omnibus-based deployments will be removed starting with Firezone 0.8.
|
||||
To transition to Docker from Omnibus today, follow our [migration guide
|
||||
](../administer/migrate).
|
||||
:::
|
||||
@@ -1,11 +0,0 @@
|
||||
---
|
||||
title: Advanced
|
||||
sidebar_position: 8
|
||||
---
|
||||
|
||||
```mdx-code-block
|
||||
import DocCardList from '@theme/DocCardList';
|
||||
import {useCurrentSidebarCategory} from '@docusaurus/theme-common';
|
||||
|
||||
<DocCardList items={useCurrentSidebarCategory().items}/>
|
||||
```
|
||||
@@ -1,91 +0,0 @@
|
||||
---
|
||||
title: Build From Source
|
||||
sidebar_position: 1
|
||||
---
|
||||
|
||||
Building from source allows you to bring Firezone to unsupported platforms.
|
||||
|
||||
:::warning
|
||||
You're entering unsupported territory. This is not for the faint of heart and
|
||||
will require being able to figure out snags you may hit on your own.
|
||||
|
||||
If you're very comfortable with your environment of choice, then read on to
|
||||
learn how to build Firezone from source.
|
||||
:::
|
||||
|
||||
:::info
|
||||
You will need to setup your own service management for Firezone (eg. `runit`,
|
||||
`systemd`, shell scripts). You will also need to install and configure your
|
||||
own database (eg. `postgres`) and reverse proxy (eg. `caddy`, `nginx`).
|
||||
|
||||
Info about database configuration is [here](../external-database/#configure-firezone-to-connect),
|
||||
and info about configuring a reverse proxy is [here](../reverse-proxy/#proxy-requirements).
|
||||
:::
|
||||
|
||||
# Prerequisites
|
||||
|
||||
:::info
|
||||
Check the `.tool-versions` file [here](https://github.com/firezone/firezone/blob/master/.tool-versions)
|
||||
for the versions we use for Erlang, Elixir, and Node. If your system supports it,
|
||||
you can install these using [asdf-vm](https://asdf-vm.com/guide/getting-started.html)
|
||||
using a similar `.tool-versions` of your own to match versions. Your system's package
|
||||
manager may have them as well.
|
||||
:::
|
||||
|
||||
**These must be available in the user's path that runs Firezone.**
|
||||
|
||||
- [Erlang/OTP](https://www.erlang.org)
|
||||
- [Elixir](https://elixir-lang.org)
|
||||
- [NodeJS](https://nodejs.org)
|
||||
|
||||
# Steps
|
||||
|
||||
From your terminal, run these steps to build Firezone:
|
||||
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
git clone https://github.com/firezone/firezone
|
||||
cd firezone
|
||||
mix local.rebar --force
|
||||
mix local.hex --force
|
||||
MIX_ENV=prod mix deps.get
|
||||
MIX_ENV=prod mix release
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
After the release build finishes, you should have a shiny new Firezone release artifact in
|
||||
`<CURRENT_DIR>/_build/dev/rel/firezone`. In the `bin` folder, the `firezone` binary
|
||||
can be used to start up Firezone. If you run it without any arguments you should see
|
||||
a list of available commands like this:
|
||||
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
Usage: firezone COMMAND [ARGS]
|
||||
|
||||
The known commands are:
|
||||
|
||||
start Starts the system
|
||||
start_iex Starts the system with IEx attached
|
||||
daemon Starts the system as a daemon
|
||||
daemon_iex Starts the system as a daemon with IEx attached
|
||||
eval "EXPR" Executes the given expression on a new, non-booted system
|
||||
rpc "EXPR" Executes the given expression remotely on the running system
|
||||
remote Connects to the running system via a remote shell
|
||||
restart Restarts the running system via a remote command
|
||||
stop Stops the running system via a remote command
|
||||
pid Prints the operating system PID of the running system via a remote command
|
||||
version Prints the release name and version to be booted
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Most deployment-related configuration is handled with environment variables.
|
||||
You'll probably want to at least set variables related to your reverse proxy
|
||||
and database. See the [ENV var reference](/docs/reference/env-vars/) for an exhaustive list.
|
||||
|
||||
Now all you need are the database and reverse proxy that you've previously set up.
|
||||
Once that's done, you can use `firezone start` to start Firezone and run
|
||||
`create-or-reset-admin` (in the same `bin` dir) to create the admin user and use
|
||||
it to log into Firezone from a web browser to start setting up your brand new
|
||||
custom instance that you built by hand with a little bit of elbow grease :)
|
||||
|
||||
:::info
|
||||
As mentioned at the top, it's recommended to use some sort of service management
|
||||
to start and stop Firezone easily without having to manually do it using the
|
||||
`firezone` binary directly. But the choice is yours, since you're in control!
|
||||
:::
|
||||
@@ -1,58 +0,0 @@
|
||||
---
|
||||
title: Custom External Database
|
||||
sidebar_position: 2
|
||||
---
|
||||
|
||||
Firezone uses [Postgresql DB](https://postgresql.org) as its primary data store.
|
||||
|
||||
## Compatibility
|
||||
|
||||
Firezone should work fine on Postgres versions 12 and above, but we recommend
|
||||
using the latest stable version whenever possible. If you find an issue with
|
||||
your particular version of Postgres, [please open a GitHub issue
|
||||
](https://github.com/firezone/firezone/issues).
|
||||
|
||||
In general, Firezone should also work fine using external Postgres-based
|
||||
database services like Amazon RDS. See the [configuration
|
||||
](#configure-firezone-to-connect) section below for more information configuring
|
||||
Firezone with an external DB.
|
||||
|
||||
:::warning
|
||||
Configuring Firezone to use an external database can be complicated and
|
||||
error-prone. We recommend using the bundled Postgres for Omnibus-based
|
||||
deployments or the official Postgres Docker image for Docker-based deployments
|
||||
if possible.
|
||||
:::
|
||||
|
||||
## Configure Firezone to Connect
|
||||
|
||||
<Tabs>
|
||||
<TabItem value="docker" label="Docker" default>
|
||||
|
||||
The Firezone Docker image uses the following environment
|
||||
variables to connect to the DB (fields in bold required):
|
||||
|
||||
| Name | Description | Format | Default |
|
||||
| ----------------------------- | --------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- | --------------------- | ------------------------------------ |
|
||||
| **`DATABASE_ENCRYPTION_KEY`** | The base64-encoded symmetric encryption key used to encrypt and decrypt sensitive fields. | base64-encoded String | None -- must be generated on install |
|
||||
| `DATABASE_HOST` | Database host | IP or hostname | `postgres` |
|
||||
| `DATABASE_PORT` | Database port | Integer | `5432` |
|
||||
| `DATABASE_NAME` | Name of database | String | `firezone` |
|
||||
| `DATABASE_USER` | User | String | `postgres` |
|
||||
| `DATABASE_PASSWORD` | Password | String | `postgres` |
|
||||
| `DATABASE_POOL` | Size of the Firezone connection pool | Integer | `10` |
|
||||
| `DATABASE_SSL` | Whether to connect to the database over SSL | Boolean | `false` |
|
||||
| `DATABASE_SSL_OPTS` | Map of options to send to the `:ssl_opts` option when connecting over SSL. See [Ecto.Adapters.Postgres documentation](https://hexdocs.pm/ecto_sql/Ecto.Adapters.Postgres.html#module-connection-options) | JSON-encoded String | `{}` |
|
||||
| `DATABASE_PARAMETERS` | Map of parameters to send to the `:parameters` option when connecting to the database. See [Ecto.Adapters.Postgres documentation](https://hexdocs.pm/ecto_sql/Ecto.Adapters.Postgres.html#module-connection-options). | JSON-encoded String | `{}` |
|
||||
|
||||
For more information, see the [environment variable reference
|
||||
](/docs/reference/env-vars/).
|
||||
|
||||
:::note
|
||||
The official `postgres` docker image can be configured by setting
|
||||
environment variables for the container. See the Postgres image
|
||||
[documentation](https://hub.docker.com/_/postgres) for more details.
|
||||
:::
|
||||
|
||||
</TabItem>
|
||||
</Tabs>
|
||||
@@ -1,105 +0,0 @@
|
||||
---
|
||||
title: Custom Reverse Proxy
|
||||
sidebar_position: 3
|
||||
---
|
||||
|
||||
:::warning
|
||||
Using a custom reverse proxy is an advanced configuration. The default bundled
|
||||
Nginx proxy (Omnibus-based deployments) and Caddy (Docker-based deployments) is
|
||||
suitable for the vast majority of use cases and is recommended for most users.
|
||||
There are important security risks if the reverse proxy is not set up correctly.
|
||||
:::
|
||||
|
||||
## Introduction
|
||||
|
||||
Firezone comes with bundled [Nginx](https://www.nginx.com/) (Omnibus-based
|
||||
deployments) or uses Caddy (Docker-based deployments) by default. However, in
|
||||
some cases you might want to deploy your own server such as when using
|
||||
your own load balancer.
|
||||
|
||||
## Prerequisites
|
||||
|
||||
Below you will find the requirements in order to setup Firezone with a custom
|
||||
reverse proxy.
|
||||
|
||||
### Firezone configuration requirements
|
||||
|
||||
- Disable the bundled Nginx by setting `default['firezone']['nginx']['enabled']`
|
||||
to `false` in the config file.
|
||||
- If you have any immediate proxies between your primary reverse proxy and the
|
||||
Firezone web app, add their IPs to
|
||||
`default['firezone']['phoenix']['external_trusted_proxies']`. Because of the
|
||||
way the [X-Forwarded-For header works](https://developer.mozilla.org/en-US/docs/Web/HTTP/Headers/X-Forwarded-For),
|
||||
this is needed to parse the actual client's IP address to prevent
|
||||
IP spoofing.
|
||||
|
||||
:::note
|
||||
The `external_trusted_proxies` list automatically implicitly includes the
|
||||
following private CIDR ranges, even if they're not specified in the
|
||||
configuration file:
|
||||
|
||||
- `127.0.0.0/8`
|
||||
- `10.0.0.0/8`
|
||||
- `172.16.0.0/12`
|
||||
- `192.168.0.0/16`
|
||||
- `::1/128`
|
||||
- `fc00::/7`
|
||||
|
||||
This means any web requests originating from these IPs are automatically ignored
|
||||
from the `X-Forwarded-For` headers. If you're accessing Firezone from any IPs in
|
||||
this range (as seen by the Firezone web app), be sure to add them to the
|
||||
`default['firezone']['phoenix']['clients']` configuration option instead.
|
||||
:::
|
||||
|
||||
Read more about the configuration options
|
||||
[here](/docs/reference/configuration-file/).
|
||||
|
||||
### Proxy requirements
|
||||
|
||||
- All your proxies need to configure the `X-Forwarded-For` header as explained
|
||||
[here](https://developer.mozilla.org/en-US/docs/Web/HTTP/Headers/X-Forwarded-For)
|
||||
- Your proxy should also set the `X-Forwarded-Proto` to `https`.
|
||||
- Your proxy (or another downstream proxy) **must** terminate SSL since we
|
||||
enforce [secure cookies](https://developer.mozilla.org/en-US/docs/Web/HTTP/Cookies#restrict_access_to_cookies).
|
||||
- Firezone requires the use of WebSockets to establish realtime connections. We
|
||||
recommend following your proxy's specific documentation for supporting
|
||||
WebSockets as each proxy varies. In general, your proxy needs to be able to
|
||||
proxy HTTP 1.1 connections, and the Firezone web app expects the following
|
||||
headers to be set:
|
||||
- `Connection: upgrade`
|
||||
- `Upgrade: websocket`
|
||||
|
||||
## Security considerations
|
||||
|
||||
In addition to the headers above, we recommend adding the following headers for
|
||||
security purposes:
|
||||
|
||||
- `X-XSS-Protection: 1; mode=block`
|
||||
- `X-Content-Type-Options nosniff`
|
||||
- `Referrer-Policy no-referrer-when-downgrade`
|
||||
- `Content-Security-Policy: default-src 'self' ws: wss: http: https: data: blob:
|
||||
'unsafe-inline'; frame-ancestors 'self';`
|
||||
- `Permissions-Policy: interest-cohort=()`
|
||||
|
||||
Since the upstream Firezone web app expects plain HTTP traffic, any requests the
|
||||
proxy forwards is sent over HTTP and thus is **not encrypted**. In most cases,
|
||||
the reverse proxy is installed in a trusted network, and this is not an issue.
|
||||
But the connection between your trusted proxy and the Firezone web app spans
|
||||
an untrusted network (such as the Internet), you may want to leave the bundled
|
||||
`nginx` proxy enabled for SSL termination, and set up your custom
|
||||
reverse proxy to proxy to that instead.
|
||||
|
||||
## Example configurations
|
||||
|
||||
- [Apache](/docs/reference/reverse-proxy-templates/apache/)
|
||||
- [Traefik](/docs/reference/reverse-proxy-templates/traefik/)
|
||||
- [HAProxy](/docs/reference/reverse-proxy-templates/haproxy/)
|
||||
|
||||
These configurations are written to be as simple as possible. They're designed
|
||||
to function as a simple template which you can customize further to suit your
|
||||
needs.
|
||||
|
||||
If you have a working configuration for a different reverse proxy or a different
|
||||
version of an existing one we appreciate any
|
||||
[contribution](https://github.com/firezone/firezone/) to expand the examples for
|
||||
the community.
|
||||
@@ -1,45 +0,0 @@
|
||||
---
|
||||
title: Configure
|
||||
sidebar_position: 5
|
||||
---
|
||||
|
||||
# Configure Firezone
|
||||
|
||||
There are two types of configuration in Firezone:
|
||||
|
||||
- [Runtime configuration](#runtime-configuration): Application configuration
|
||||
related to day-to-day operation of Firezone.
|
||||
- [Deployment configuration](#deployment-configuration): Deployment or
|
||||
infrastructure-related configuration relevant to running Firezone on-prem.
|
||||
|
||||
## Runtime configuration
|
||||
|
||||
Most day-to-day configuration of Firezone can be done via the Web UI or
|
||||
[REST API](/docs/reference/rest-api/configurations).
|
||||
This type of configuration can be expected to be changed **with no downtime**
|
||||
in a production deployment.
|
||||
|
||||
We're actively working to move more configuration variables to
|
||||
this type of configuration, so expect more ENV vars to transition to runtime
|
||||
configuration in the future.
|
||||
|
||||
## Deployment configuration
|
||||
|
||||
Deployment-related and infrastructure configuration require restarting Firezone
|
||||
services after change.
|
||||
|
||||
<Tabs>
|
||||
<TabItem value="docker" label="Docker" default>
|
||||
|
||||
Docker-based deployments are configured through environment
|
||||
variables passed to the `firezone` container. These can be
|
||||
specified either in a `.env` file in the current directory,
|
||||
the `docker-compose.yml` file, or passed to the `docker run`
|
||||
call directly. See the [env var reference](../../reference/env-vars)
|
||||
for a complete listing.
|
||||
|
||||
See [Docker's documentation
|
||||
](https://docs.docker.com/compose/envvars-precedence/) for more information.
|
||||
|
||||
</TabItem>
|
||||
</Tabs>
|
||||
@@ -1,180 +0,0 @@
|
||||
---
|
||||
title: Docker
|
||||
sidebar_position: 2
|
||||
description: Install Firezone via Docker to manage secure remote
|
||||
access to private networks and resources.
|
||||
---
|
||||
|
||||
# Install Firezone with Docker
|
||||
|
||||
As of 0.6.0, Docker is now the **preferred method** for
|
||||
deploying Firezone. Docker offers a number of benefits over the old
|
||||
[Omnibus method](../omnibus):
|
||||
|
||||
- **Simpler, more robust upgrades**: In most cases, simply pull the latest `firezone/firezone`
|
||||
image and restart the container.
|
||||
- **Simpler configuration**: Most day-to-day configuration of Firezone can now
|
||||
be done in the web UI instead of the `/etc/firezone/firezone.rb` configuration
|
||||
file. All other configuration variables can be specified as ENV vars to the
|
||||
Firezone container.
|
||||
- **Smaller footprint**: The Firezone image weighs in at a couple dozen
|
||||
megabytes versus hundreds of megabytes for the Omnibus package.
|
||||
- **Portability**: Firezone now runs on any platform that supports Docker.
|
||||
- **Security**: Containerization providers better security isolation than
|
||||
simply running as an unprivileged local user.
|
||||
|
||||
## Step 1: Prerequisites
|
||||
|
||||
- Ensure you're on a [supported platform](supported-platforms) with [
|
||||
docker-compose](https://docs.docker.com/compose/install/) **version 2
|
||||
or higher** installed.
|
||||
- Ensure port forwarding is enabled on your firewall.
|
||||
The default Firezone configuration requires the following ports to be open:
|
||||
- `80/tcp` (optional): For automatically issuing SSL certificates.
|
||||
- `443/tcp`: To access the web UI.
|
||||
- `51820/udp`: VPN traffic listen port.
|
||||
|
||||
:::caution
|
||||
Before deploying Firezone in **production**, you'll need a valid DNS record
|
||||
pointing to this instance. See [Prepare to Deploy](../#prepare-to-deploy)
|
||||
if you haven't done this already.
|
||||
:::
|
||||
|
||||
## Step 2: Install server
|
||||
|
||||
After prerequisites are satisfied, you're ready to install the Firezone Server.
|
||||
|
||||
### Option 1: Automatic install
|
||||
|
||||
The easiest way to deploy Firezone with Docker is the automatic install script:
|
||||
|
||||
<InstallBlock />
|
||||
|
||||
This will ask you a few questions regarding initial configuration, then proceed
|
||||
to download a sample docker-compose.yml file, configure it with your responses,
|
||||
and then print instructions for accessing the Web UI.
|
||||
|
||||
Firezone files will be installed in `$HOME/.firezone` by default.
|
||||
|
||||
### Option 2: Manual install
|
||||
|
||||
If the automatic install fails, or you'd just like more control over the
|
||||
installation process, follow the steps below to install manually.
|
||||
|
||||
1. Download the docker compose template to a local working directory:
|
||||
**For Linux**:
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
curl -fsSL https://raw.githubusercontent.com/firezone/firezone/master/docker-compose.prod.yml -o docker-compose.yml
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
**For macOS, Windows (non-production only)**:
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
curl -fsSL https://raw.githubusercontent.com/firezone/firezone/master/docker-compose.desktop.yml -o docker-compose.yml
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
1. Generate required secrets:
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
docker run --rm firezone/firezone bin/gen-env > .env
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
1. At a minimum, change the `DEFAULT_ADMIN_EMAIL` and `EXTERNAL_URL` variables.
|
||||
Optionally modify other secrets as needed.
|
||||
1. Migrate the database:
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
docker compose run --rm firezone bin/migrate
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
1. Create the first admin:
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
docker compose run --rm firezone bin/create-or-reset-admin
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
1. Bring the services up: `docker compose up -d`
|
||||
|
||||
You should now be able to access the Firezone web portal at the `EXTERNAL_URL`
|
||||
variable you defined above.
|
||||
|
||||
## Step 3 (optional): Enable on boot
|
||||
|
||||
If you'd like Firezone to start automatically on boot, first ensure Docker is enabled at startup:
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
sudo systemctl enable docker
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Then, make sure your Firezone services have the `restart: always` or `restart: unless-stopped` option
|
||||
specified in the `docker-compose.yml` file. This is the default used in the docker-compose.prod.yml
|
||||
production template file.
|
||||
|
||||
## Step 4 (optional): Enable IPv6
|
||||
|
||||
By default, Firezone ships with IPv6 connectivity enabled inside the tunnel but not routable
|
||||
to the public internet. To enable IPv6 support in Docker-deployed Firezone, follow the steps below.
|
||||
|
||||
1. Enable IPv6 support within Docker by adding the following to `/etc/docker/daemon.json`:
|
||||
|
||||
```json
|
||||
{
|
||||
"ipv6": true,
|
||||
"ip6tables": true,
|
||||
"experimental": true,
|
||||
"fixed-cidr-v6": "2001:db8:1::/64"
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
This enables IPv6 NAT and configures IPv6 forwarding for Docker containers.
|
||||
|
||||
1. Enable router advertisements on boot for your default egress interface:
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
egress=`ip route show default 0.0.0.0/0 | grep -oP '(?<=dev ).*' | cut -f1 -d' ' | tr -d '\n'`
|
||||
sudo bash -c "echo net.ipv6.conf.${egress}.accept_ra=2 >> /etc/sysctl.conf"
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
1. Reboot
|
||||
|
||||
You should now be able to ping google from within a docker container:
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
docker run --rm -t busybox ping6 -c 4 google.com
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
You shouldn't need to manually add any `iptables` rules to enable IPv6 SNAT/masquerading for
|
||||
tunneled traffic; Firezone handles this for you by default on start.
|
||||
|
||||
## Step 5: Install client apps
|
||||
|
||||
:::note
|
||||
Firezone currently uses WireGuard's
|
||||
[open-source client apps](https://www.wireguard.com/install/).
|
||||
:::
|
||||
|
||||
Once successfully deployed, users and devices can be added to
|
||||
connect to the VPN server:
|
||||
|
||||
- [Add Users](../../user-guides/add-users):
|
||||
Add users to grant them access to your network.
|
||||
- [Client Instructions](../../user-guides/client-instructions):
|
||||
Instructions to establish a VPN session.
|
||||
|
||||
import SupportOptions from "@site/src/partials/_support_options.mdx";
|
||||
<SupportOptions />;
|
||||
|
||||
## Post Setup
|
||||
|
||||
Congrats! You have completed the setup, but there's a lot more you can do with
|
||||
Firezone:
|
||||
|
||||
- [Integrate your identity provider](../../authenticate/)
|
||||
for authenticating clients
|
||||
- Using Firezone as a NAT gateway to
|
||||
[establish a static IP for your team](../../user-guides/use-cases/nat-gateway)
|
||||
- Create tunnels between multiple peers with
|
||||
[reverse tunnels](../../user-guides/use-cases/reverse-tunnel)
|
||||
- Only route certain traffic through Firezone with
|
||||
[split tunneling](../../user-guides/use-cases/split-tunnel)
|
||||
@@ -1,33 +0,0 @@
|
||||
---
|
||||
title: Supported Platforms
|
||||
sidebar_position: 1
|
||||
---
|
||||
|
||||
Firezone currently supports the following platforms for Docker-based
|
||||
deployments.
|
||||
|
||||
| OS | Architecture(s) | Runtime | Status | Notes |
|
||||
| --- | --- | --- | --- | --- |
|
||||
| Linux | `amd64` `arm64` | Docker Server | **Fully-supported** | `wireguard` kernel module needed for kernels < `5.6`. |
|
||||
| Linux | `amd64` `arm64` | Docker Desktop | Works, but unsupported. | Not recommended for production deployments. See [caveats](#docker-desktop-caveats). |
|
||||
| macOS | `amd64` `arm64` | Docker Desktop | Works. but unsupported. | Not recommended for production deployments. See [caveats](#non-linux-platform-caveats). |
|
||||
| Windows | `amd64` `arm64` | Docker Desktop | **Untested** | Not recommended for production deployments. See [caveats](#non-linux-platform-caveats). |
|
||||
|
||||
## Docker Desktop caveats
|
||||
|
||||
Docker Desktop [rewrites the source address
|
||||
](https://www.docker.com/blog/how-docker-desktop-networking-works-under-the-hood/)
|
||||
for packets flowing out of container networks under some conditions. This can
|
||||
cause routing loops and other hard to debug connectivity issues with Firezone.
|
||||
We recommend **only** using Docker Server for Linux for production deployments.
|
||||
|
||||
## Non-Linux platform caveats
|
||||
|
||||
Only Docker for Linux supports the host networking mode, so macOS and Windows
|
||||
platforms will be able unable to properly attribute client source address
|
||||
for HTTP requests. This means any IP-based throttling or logging in your
|
||||
chosen proxy (`caddy` by default) will be ineffective, since the source
|
||||
IP will always be the Docker-side host IP (typically `172.X.0.1`).
|
||||
|
||||
Egress rules operate on the tunneled client IP address and aren't affected
|
||||
by this limitation.
|
||||
@@ -1,57 +0,0 @@
|
||||
---
|
||||
title: Security Considerations
|
||||
sidebar_position: 6
|
||||
---
|
||||
|
||||
# Security considerations
|
||||
|
||||
**Disclaimer**: Firezone is still beta software. The codebase has not yet
|
||||
received a formal security audit. For highly sensitive and mission-critical
|
||||
production deployments, we recommend disabling local authentication as
|
||||
detailed [below](#production-deployments).
|
||||
|
||||
## List of services and ports
|
||||
|
||||
Shown below is a table of default ports used by Firezone services.
|
||||
|
||||
<Tabs>
|
||||
<TabItem label="Docker" value="docker" default>
|
||||
|
||||
| Service | Port | Listen address | Description |
|
||||
| ---------- | ----------- | -------------- | ----------------------------------------------------------------------------- |
|
||||
| Caddy | `443/tcp` | `all` | Public HTTPS port for administering Firezone and facilitating authentication. |
|
||||
| Caddy | `80/tcp` | `all` | Public HTTP port used for ACME. Disabled when ACME is disabled. |
|
||||
| WireGuard | `51820/udp` | `all` | Public WireGuard port used for VPN sessions. |
|
||||
| Postgresql | `5432/tcp` | `-` | Containerized port used for bundled Postgresql server. |
|
||||
| Phoenix | `13000/tcp` | `-` | Containerized port used by upstream elixir app server. |
|
||||
|
||||
</TabItem>
|
||||
<TabItem label="Omnibus" value="omnibus">
|
||||
|
||||
| Service | Port | Listen address | Description |
|
||||
| ---------- | ----------- | -------------- | ----------------------------------------------------------------------------- |
|
||||
| Nginx | `443/tcp` | `all` | Public HTTPS port for administering Firezone and facilitating authentication. |
|
||||
| Nginx | `80/tcp` | `all` | Public HTTP port used for ACME. Disabled when ACME is disabled. |
|
||||
| WireGuard | `51820/udp` | `all` | Public WireGuard port used for VPN sessions. |
|
||||
| Postgresql | `15432/tcp` | `127.0.0.1` | Local-only port used for bundled Postgresql server. |
|
||||
| Phoenix | `13000/tcp` | `127.0.0.1` | Local-only port used by upstream elixir app server. |
|
||||
|
||||
</TabItem>
|
||||
</Tabs>
|
||||
|
||||
## Production deployments
|
||||
|
||||
For production deployments of Firezone, we recommend you disable local authentication
|
||||
altogether by setting `default['firezone']['authentication']['local']['enabled'] = false`
|
||||
(Omnibus-based deployments) or `LOCAL_AUTH_ENABLED=false` (Docker-based deployments).
|
||||
Local authentication can also be disabled on the `/settings/security` page.
|
||||
|
||||
:::caution
|
||||
Ensure you've set up a working [OIDC](/docs/authenticate/oidc/) or [SAML](/docs/authenticate/saml/)-based
|
||||
authentication provider before disabling the local authentication method.
|
||||
:::
|
||||
|
||||
## Reporting security issues
|
||||
|
||||
To report any security-related bugs, see [our security bug reporting policy
|
||||
](https://github.com/firezone/firezone/blob/master/SECURITY.md).
|
||||
@@ -1,11 +0,0 @@
|
||||
---
|
||||
title: Reference
|
||||
sidebar_position: 6
|
||||
---
|
||||
|
||||
```mdx-code-block
|
||||
import DocCardList from '@theme/DocCardList';
|
||||
import {useCurrentSidebarCategory} from '@docusaurus/theme-common';
|
||||
|
||||
<DocCardList items={useCurrentSidebarCategory().items}/>
|
||||
```
|
||||
@@ -1,17 +0,0 @@
|
||||
---
|
||||
title: Audit Logs
|
||||
sidebar_position: 2
|
||||
---
|
||||
|
||||
# Audit logs
|
||||
|
||||
Firezone maintains two types of logs tied to user identity: configuration logs
|
||||
and network activity logs.
|
||||
|
||||
Configuration logs track events related to the configuration of Firezone
|
||||
itself, either by admins or users. Network activity logs track connections to
|
||||
protected resources made by users of your network.
|
||||
|
||||
Logged events are recorded as JSON objects and stored in the database. These
|
||||
are accessible via a REST API or the Firezone portal, and exportable to CSV
|
||||
format.
|
||||
@@ -1,186 +0,0 @@
|
||||
---
|
||||
title: Configuration File
|
||||
sidebar_position: 2
|
||||
---
|
||||
|
||||
# Omnibus configuration options
|
||||
|
||||
:::warning
|
||||
This reference is written for Omnibus-based deployments of Firezone. For
|
||||
Docker-based deployments visit the [Environment Variables](../env-vars) page.
|
||||
:::
|
||||
|
||||
To configure Omnibus-based deployments of Firezone:
|
||||
|
||||
1. Edit `/etc/firezone/firezone.rb` with your changes.
|
||||
1. Run `sudo firezone-ctl reconfigure` to process the changes and restart affected services.
|
||||
|
||||
Read more about configuring Firezone in the [configure guide](/docs/deploy/configure).
|
||||
|
||||
## Configuration file reference
|
||||
|
||||
Shown below is a complete listing of the configuration options available in
|
||||
`/etc/firezone/firezone.rb`.
|
||||
|
||||
<!-- markdownlint-disable MD033 -->
|
||||
<!-- markdownlint-disable MD034 -->
|
||||
|
||||
| Option | Description | Default Value |
|
||||
| -------------------------------------------------------------------- | ---------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- | ------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------ |
|
||||
| `default['firezone']['external_url']` | URL used to access the web portal of this Firezone instance. | <code>"https://#{node['fqdn'] || node['hostname']}"</code> |
|
||||
| `default['firezone']['config_directory']` | Top-level directory for Firezone configuration. | `'/etc/firezone'` |
|
||||
| `default['firezone']['install_directory']` | Top-level directory to install Firezone to. | `'/opt/firezone'` |
|
||||
| `default['firezone']['app_directory']` | Top-level directory to install the Firezone web application. | `"#{node['firezone']['install_directory']}/embedded/service/firezone"` |
|
||||
| `default['firezone']['log_directory']` | Top-level directory for Firezone logs. | `'/var/log/firezone'` |
|
||||
| `default['firezone']['var_directory']` | Top-level directory for Firezone runtime files. | `'/var/opt/firezone'` |
|
||||
| `default['firezone']['user']` | Name of unprivileged Linux user most services and files will belong to. | `'firezone'` |
|
||||
| `default['firezone']['group']` | Name of Linux group most services and files will belong to. | `'firezone'` |
|
||||
| `default['firezone']['admin_email']` | Email address for initial Firezone user. | `"firezone@localhost"` |
|
||||
| `default['firezone']['max_devices_per_user']` | Maximum number of devices a user can have. | `10` |
|
||||
| `default['firezone']['allow_unprivileged_device_management']` | Allows non-admin users to create and delete devices. | `true` |
|
||||
| `default['firezone']['allow_unprivileged_device_configuration']` | Allows non-admin users to modify device configurations. When disabled, prevents unprivileged users from changing all device fields except for `name` and `description`. | `true` |
|
||||
| `default['firezone']['egress_interface']` | Interface name where tunneled traffic will exit. If nil, the default route interface will be used. | `nil` |
|
||||
| `default['firezone']['fips_enabled']` | Enable or disable OpenSSL FIPs mode. | `nil` |
|
||||
| `default['firezone']['logging']['enabled']` | Enable or disable logging across Firezone. Set to `false` to disable logging entirely. | `true` |
|
||||
| `default['enterprise']['name']` | Name used by the Chef 'enterprise' cookbook. | `'firezone'` |
|
||||
| `default['firezone']['install_path']` | Install path used by Chef 'enterprise' cookbook. Should be set to the same as the `install_directory` above. | `node['firezone']['install_directory']` |
|
||||
| `default['firezone']['sysvinit_id']` | An identifier used in `/etc/inittab`. Must be a unique sequence of 1-4 characters. | `'SUP'` |
|
||||
| `default['firezone']['authentication']['local']['enabled']` | Enable or disable local email/password authentication. | `true` |
|
||||
| `default['firezone']['authentication']['disable_vpn_on_oidc_error']` | Disable a user's VPN if an error is detected trying to refresh their OIDC token. | `false` |
|
||||
| `default['firezone']['authentication']['oidc']` | OpenID Connect config, in the format of `{"provider" => [config...]}` - See [OpenIDConnect documentation](https://hexdocs.pm/openid_connect/readme.html) for config examples. | `{}` |
|
||||
| `default['firezone']['nginx']['enabled']` | Enable or disable the bundled nginx server. | `true` |
|
||||
| `default['firezone']['nginx']['ssl_port']` | HTTPS listen port. | `443` |
|
||||
| `default['firezone']['nginx']['directory']` | Directory to store Firezone-related nginx virtual host configuration. | `"#{node['firezone']['var_directory']}/nginx/etc"` |
|
||||
| `default['firezone']['nginx']['log_directory']` | Directory to store Firezone-related nginx log files. | `"#{node['firezone']['log_directory']}/nginx"` |
|
||||
| `default['firezone']['nginx']['log_rotation']['file_maxbytes']` | File size at which to rotate Nginx log files. | `104857600` |
|
||||
| `default['firezone']['nginx']['log_rotation']['num_to_keep']` | Number of Firezone nginx log files to keep before discarding. | `10` |
|
||||
| `default['firezone']['nginx']['log_x_forwarded_for']` | Whether to log Firezone nginx `x-forwarded-for` header. | `true` |
|
||||
| `default['firezone']['nginx']['hsts_header']['enabled']` | Enable or disable [HSTS](https://www.nginx.com/blog/http-strict-transport-security-hsts-and-nginx/). | `true` |
|
||||
| `default['firezone']['nginx']['hsts_header']['include_subdomains']` | Enable or disable `includeSubDomains` for the HSTS header. | `true` |
|
||||
| `default['firezone']['nginx']['hsts_header']['max_age']` | Max age for the HSTS header. | `31536000` |
|
||||
| `default['firezone']['nginx']['redirect_to_canonical']` | Whether to redirect URLs to the canonical FQDN specified above | `false` |
|
||||
| `default['firezone']['nginx']['cache']['enabled']` | Enable or disable the Firezone nginx cache. | `false` |
|
||||
| `default['firezone']['nginx']['cache']['directory']` | Directory for Firezone nginx cache. | `"#{node['firezone']['var_directory']}/nginx/cache"` |
|
||||
| `default['firezone']['nginx']['user']` | Firezone nginx user. | `node['firezone']['user']` |
|
||||
| `default['firezone']['nginx']['group']` | Firezone nginx group. | `node['firezone']['group']` |
|
||||
| `default['firezone']['nginx']['dir']` | Top-level nginx configuration directory. | `node['firezone']['nginx']['directory']` |
|
||||
| `default['firezone']['nginx']['log_dir']` | Top-level nginx log directory. | `node['firezone']['nginx']['log_directory']` |
|
||||
| `default['firezone']['nginx']['pid']` | Location for nginx pid file. | `"#{node['firezone']['nginx']['directory']}/nginx.pid"` |
|
||||
| `default['firezone']['nginx']['daemon_disable']` | Disable nginx daemon mode so we can monitor it instead. | `true` |
|
||||
| `default['firezone']['nginx']['gzip']` | Turn nginx gzip compression on or off. | `'on'` |
|
||||
| `default['firezone']['nginx']['gzip_static']` | Turn nginx gzip compression on or off for static files. | `'off'` |
|
||||
| `default['firezone']['nginx']['gzip_http_version']` | HTTP version to use for serving static files. | `'1.0'` |
|
||||
| `default['firezone']['nginx']['gzip_comp_level']` | nginx gzip compression level. | `'2'` |
|
||||
| `default['firezone']['nginx']['gzip_proxied']` | Enables or disables gzipping of responses for proxied requests depending on the request and response. | `'any'` |
|
||||
| `default['firezone']['nginx']['gzip_vary']` | Enables or disables inserting the “Vary: Accept-Encoding” response header. | `'off'` |
|
||||
| `default['firezone']['nginx']['gzip_buffers']` | Sets the number and size of buffers used to compress a response. If `nil`, nginx default is used. | `nil` |
|
||||
| `default['firezone']['nginx']['gzip_types']` | MIME types to enable gzip compression for. | `['text/plain', 'text/css','application/x-javascript', 'text/xml', 'application/xml', 'application/rss+xml', 'application/atom+xml', 'text/javascript', 'application/javascript', 'application/json']` |
|
||||
| `default['firezone']['nginx']['gzip_min_length']` | Minimum file length to enable file gzip compression for. | `1000` |
|
||||
| `default['firezone']['nginx']['gzip_disable']` | User-agent matcher to disable gzip compression for. | `'MSIE [1-6]\.'` |
|
||||
| `default['firezone']['nginx']['keepalive']` | Activates cache for connection to upstream servers. | `'on'` |
|
||||
| `default['firezone']['nginx']['keepalive_timeout']` | Timeout in seconds for keepalive connection to upstream servers. | `65` |
|
||||
| `default['firezone']['nginx']['worker_processes']` | Number of nginx worker processes. | `node['cpu'] && node['cpu']['total'] ? node['cpu']['total'] : 1` |
|
||||
| `default['firezone']['nginx']['worker_connections']` | Max number of simultaneous connections that can be opened by a worker process. | `1024` |
|
||||
| `default['firezone']['nginx']['worker_rlimit_nofile']` | Changes the limit on the maximum number of open files for worker processes. Uses nginx default if nil. | `nil` |
|
||||
| `default['firezone']['nginx']['multi_accept']` | Whether workers should accept one connection at a time or multiple. | `true` |
|
||||
| `default['firezone']['nginx']['event']` | Specifies the connection processing method to use inside nginx events context. | `'epoll'` |
|
||||
| `default['firezone']['nginx']['server_tokens']` | Enables or disables emitting nginx version on error pages and in the “Server” response header field. | `nil` |
|
||||
| `default['firezone']['nginx']['server_names_hash_bucket_size']` | Sets the bucket size for the server names hash tables. | `64` |
|
||||
| `default['firezone']['nginx']['sendfile']` | Enables or disables the use of nginx's `sendfile()`. | `'on'` |
|
||||
| `default['firezone']['nginx']['access_log_options']` | Sets nginx access log options. | `nil` |
|
||||
| `default['firezone']['nginx']['error_log_options']` | Sets nginx error log options. | `nil` |
|
||||
| `default['firezone']['nginx']['disable_access_log']` | Disables nginx access log. | `false` |
|
||||
| `default['firezone']['nginx']['types_hash_max_size']` | nginx types hash max size. | `2048` |
|
||||
| `default['firezone']['nginx']['types_hash_bucket_size']` | nginx types hash bucket size. | `64` |
|
||||
| `default['firezone']['nginx']['proxy_read_timeout']` | nginx proxy read timeout. Set to `nil` to use nginx default. | `nil` |
|
||||
| `default['firezone']['nginx']['client_body_buffer_size']` | nginx client body buffer size. Set to `nil` to use nginx default. | `nil` |
|
||||
| `default['firezone']['nginx']['client_max_body_size']` | nginx client max body size. | `'250m'` |
|
||||
| `default['firezone']['nginx']['default']['modules']` | Specify additional nginx modules. | `[]` |
|
||||
| `default['firezone']['nginx']['enable_rate_limiting']` | Enable or disable nginx rate limiting. | `true` |
|
||||
| `default['firezone']['nginx']['rate_limiting_zone_name']` | Nginx rate limiting zone name. | `'firezone'` |
|
||||
| `default['firezone']['nginx']['rate_limiting_backoff']` | Nginx rate limiting backoff. | `'10m'` |
|
||||
| `default['firezone']['nginx']['rate_limit']` | Nginx rate limit. | `'10r/s'` |
|
||||
| `default['firezone']['nginx']['ipv6']` | Allow nginx to listen for HTTP requests for IPv6 in addition to IPv4. | `true` |
|
||||
| `default['firezone']['postgresql']['enabled']` | Enable or disable bundled Postgresql. Set to `false` and fill in the `database` options below to use your own Postgresql instance. | `true` |
|
||||
| `default['firezone']['postgresql']['username']` | Username for Postgresql. | `node['firezone']['user']` |
|
||||
| `default['firezone']['postgresql']['data_directory']` | Postgresql data directory. | `"#{node['firezone']['var_directory']}/postgresql/13.3/data"` |
|
||||
| `default['firezone']['postgresql']['log_directory']` | Postgresql log directory. | `"#{node['firezone']['log_directory']}/postgresql"` |
|
||||
| `default['firezone']['postgresql']['log_rotation']['file_maxbytes']` | Postgresql log file maximum size before it's rotated. | `104857600` |
|
||||
| `default['firezone']['postgresql']['log_rotation']['num_to_keep']` | Number of Postgresql log files to keep. | `10` |
|
||||
| `default['firezone']['postgresql']['checkpoint_completion_target']` | Postgresql checkpoint completion target. | `0.5` |
|
||||
| `default['firezone']['postgresql']['checkpoint_segments']` | Number of Postgresql checkpoint segments. | `3` |
|
||||
| `default['firezone']['postgresql']['checkpoint_timeout']` | Postgresql checkpoint timeout. | `'5min'` |
|
||||
| `default['firezone']['postgresql']['checkpoint_warning']` | Postgresql checkpoint warning time in seconds. | `'30s'` |
|
||||
| `default['firezone']['postgresql']['effective_cache_size']` | Postgresql effective cache size. | `'128MB'` |
|
||||
| `default['firezone']['postgresql']['listen_address']` | Postgresql listen address. | `'127.0.0.1'` |
|
||||
| `default['firezone']['postgresql']['max_connections']` | Postgresql max connections. | `350` |
|
||||
| `default['firezone']['postgresql']['md5_auth_cidr_addresses']` | Postgresql CIDRs to allow for md5 auth. | `['127.0.0.1/32', '::1/128']` |
|
||||
| `default['firezone']['postgresql']['port']` | Postgresql listen port. | `15432` |
|
||||
| `default['firezone']['postgresql']['shared_buffers']` | Postgresql shared buffers size. | `"#{(node['memory']['total'].to_i / 4) / 1024}MB"` |
|
||||
| `default['firezone']['postgresql']['shmmax']` | Postgresql shmmax in bytes. | `17179869184` |
|
||||
| `default['firezone']['postgresql']['shmall']` | Postgresql shmall in bytes. | `4194304` |
|
||||
| `default['firezone']['postgresql']['work_mem']` | Postgresql working memory size. | `'8MB'` |
|
||||
| `default['firezone']['database']['user']` | Specifies the username Firezone will use to connect to the DB. | `node['firezone']['postgresql']['username']` |
|
||||
| `default['firezone']['database']['password']` | If using an external DB, specifies the password Firezone will use to connect to the DB. | `'change_me'` |
|
||||
| `default['firezone']['database']['name']` | Database that Firezone will use. Will be created if it doesn't exist. | `'firezone'` |
|
||||
| `default['firezone']['database']['host']` | Database host that Firezone will connect to. | `node['firezone']['postgresql']['listen_address']` |
|
||||
| `default['firezone']['database']['port']` | Database port that Firezone will connect to. | `node['firezone']['postgresql']['port']` |
|
||||
| `default['firezone']['database']['pool']` | Database pool size Firezone will use. | `[10, Etc.nprocessors].max` |
|
||||
| `default['firezone']['database']['ssl']` | Whether to connect to the database over SSL. | `false` |
|
||||
| `default['firezone']['database']['ssl_opts']` | Hash of options to send to the `:ssl_opts` option when connecting over SSL. See [Ecto.Adapters.Postgres documentation](https://hexdocs.pm/ecto_sql/Ecto.Adapters.Postgres.html#module-connection-options). | `{}` |
|
||||
| `default['firezone']['database']['parameters']` | Hash of parameters to send to the `:parameters` option when connecting to the database. See [Ecto.Adapters.Postgres documentation](https://hexdocs.pm/ecto_sql/Ecto.Adapters.Postgres.html#module-connection-options). | `{}` |
|
||||
| `default['firezone']['database']['extensions']` | Database extensions to enable. | `{ 'plpgsql' => true, 'pg_trgm' => true }` |
|
||||
| `default['firezone']['phoenix']['enabled']` | Enable or disable the Firezone web application. | `true` |
|
||||
| `default['firezone']['phoenix']['listen_address']` | Firezone web application listen address. This will be the upstream listen address that nginx proxies. | `'127.0.0.1'` |
|
||||
| `default['firezone']['phoenix']['port']` | Firezone web application listen port. This will be the upstream port that nginx proxies. | `13000` |
|
||||
| `default['firezone']['phoenix']['log_directory']` | Firezone web application log directory. | `"#{node['firezone']['log_directory']}/phoenix"` |
|
||||
| `default['firezone']['phoenix']['log_rotation']['file_maxbytes']` | Firezone web application log file size. | `104857600` |
|
||||
| `default['firezone']['phoenix']['log_rotation']['num_to_keep']` | Number of Firezone web application log files to keep. | `10` |
|
||||
| `default['firezone']['phoenix']['crash_detection']['enabled']` | Enable or disable bringing down the Firezone web application when a crash is detected. | `true` |
|
||||
| `default['firezone']['phoenix']['external_trusted_proxies']` | List of trusted reverse proxies formatted as an Array of IPs and/or CIDRs. | `[]` |
|
||||
| `default['firezone']['phoenix']['private_clients']` | List of private network HTTP clients, formatted an Array of IPs and/or CIDRs. | `[]` |
|
||||
| `default['firezone']['wireguard']['enabled']` | Enable or disable bundled WireGuard management. | `true` |
|
||||
| `default['firezone']['wireguard']['log_directory']` | Log directory for bundled WireGuard management. | `"#{node['firezone']['log_directory']}/wireguard"` |
|
||||
| `default['firezone']['wireguard']['log_rotation']['file_maxbytes']` | WireGuard log file max size. | `104857600` |
|
||||
| `default['firezone']['wireguard']['log_rotation']['num_to_keep']` | Number of WireGuard log files to keep. | `10` |
|
||||
| `default['firezone']['wireguard']['interface_name']` | WireGuard interface name. **Changing this parameter may cause a temporary loss in VPN connectivity**. | `'wg-firezone'` |
|
||||
| `default['firezone']['wireguard']['port']` | WireGuard listen port. | `51820` |
|
||||
| `default['firezone']['wireguard']['persistent_keepalive']` | Default PersistentKeepalive setting for generated device configurations. A value of 0 disables. | `0` |
|
||||
| `default['firezone']['wireguard']['ipv4']['enabled']` | Enable or disable IPv4 for WireGuard network. | `true` |
|
||||
| `default['firezone']['wireguard']['ipv4']['masquerade']` | Enable or disable masquerade for packets leaving the IPv4 tunnel. | `true` |
|
||||
| `default['firezone']['wireguard']['ipv4']['network']` | WireGuard network IPv4 address pool. | `'10.3.2.0/24'` |
|
||||
| `default['firezone']['wireguard']['ipv4']['address']` | WireGuard interface IPv4 address. Must be within WireGuard address pool. | `'10.3.2.1'` |
|
||||
| `default['firezone']['wireguard']['ipv6']['enabled']` | Enable or disable IPv6 for WireGuard network. | `true` |
|
||||
| `default['firezone']['wireguard']['ipv6']['masquerade']` | Enable or disable masquerade for packets leaving the IPv6 tunnel. | `true` |
|
||||
| `default['firezone']['wireguard']['ipv6']['network']` | WireGuard network IPv6 address pool. | `'fd00::3:2:0/120'` |
|
||||
| `default['firezone']['wireguard']['ipv6']['address']` | WireGuard interface IPv6 address. Must be within IPv6 address pool. | `'fd00::3:2:1'` |
|
||||
| `default['firezone']['runit']['svlogd_bin']` | Runit svlogd bin location. | `"#{node['firezone']['install_directory']}/embedded/bin/svlogd"` |
|
||||
| `default['firezone']['ssl']['directory']` | SSL directory for storing generated certs. | `'/var/opt/firezone/ssl'` |
|
||||
| `default['firezone']['ssl']['email_address']` | Email address to use for self-signed certs and ACME protocol renewal notices. | `'you@example.com'` |
|
||||
| `default['firezone']['ssl']['acme']['enabled']` | Enable ACME for automatic SSL cert provisioning. | `false` |
|
||||
| `default['firezone']['ssl']['acme']['server']` | ACME server to use for certificate issuance/renewal. Can be any [valid acme.sh server](https://github.com/acmesh-official/acme.sh/wiki/Server) | `letsencrypt` |
|
||||
| `default['firezone']['ssl']['acme']['keylength']` | Specify the key type and length for SSL certificates. See [here](https://github.com/acmesh-official/acme.sh#10-issue-ecc-certificates) | `ec-256` |
|
||||
| `default['firezone']['ssl']['certificate']` | Path to the certificate file for your FQDN. Overrides ACME setting above if specified. If both ACME and this are `nil` a self-signed cert will be generated. | `nil` |
|
||||
| `default['firezone']['ssl']['certificate_key']` | Path to the certificate file. | `nil` |
|
||||
| `default['firezone']['ssl']['ssl_dhparam']` | nginx ssl dh_param. | `nil` |
|
||||
| `default['firezone']['ssl']['country_name']` | Country name for self-signed cert. | `'US'` |
|
||||
| `default['firezone']['ssl']['state_name']` | State name for self-signed cert. | `'CA'` |
|
||||
| `default['firezone']['ssl']['locality_name']` | Locality name for self-signed cert. | `'San Francisco'` |
|
||||
| `default['firezone']['ssl']['company_name']` | Company name self-signed cert. | `'My Company'` |
|
||||
| `default['firezone']['ssl']['organizational_unit_name']` | Organizational unit name for self-signed cert. | `'Operations'` |
|
||||
| `default['firezone']['ssl']['ciphers']` | SSL ciphers for nginx to use. | `'ECDHE-RSA-AES128-GCM-SHA256:ECDHE-ECDSA-AES128-GCM-SHA256:ECDHE-RSA-AES256-GCM-SHA384:ECDHE-ECDSA-AES256-GCM-SHA384:DHE-RSA-AES128-GCM-SHA256:DHE-DSS-AES128-GCM-SHA256:kEDH+AESGCM:ECDHE-RSA-AES128-SHA256:ECDHE-ECDSA-AES128-SHA256:ECDHE-RSA-AES128-SHA:ECDHE-ECDSA-AES128-SHA:ECDHE-RSA-AES256-SHA384:ECDHE-ECDSA-AES256-SHA384:ECDHE-RSA-AES256-SHA:ECDHE-ECDSA-AES256-SHA:DHE-RSA-AES128-SHA256:DHE-RSA-AES128-SHA:DHE-DSS-AES128-SHA256:DHE-RSA-AES256-SHA256:DHE-DSS-AES256-SHA:DHE-RSA-AES256-SHA:AES128-GCM-SHA256:AES256-GCM-SHA384:AES128-SHA:AES256-SHA:AES:CAMELLIA:DES-CBC3-SHA:!aNULL:!eNULL:!EXPORT:!DES:!RC4:!MD5:!PSK:!aECDH:!EDH-DSS-DES-CBC3-SHA:!EDH-RSA-DES-CBC3-SHA:!KRB5-DES-CBC3-SHA'` |
|
||||
| `default['firezone']['ssl']['fips_ciphers']` | SSL ciphers for FIPs mode. | `'FIPS@STRENGTH:!aNULL:!eNULL'` |
|
||||
| `default['firezone']['ssl']['protocols']` | TLS protocols to use. | `'TLSv1 TLSv1.1 TLSv1.2'` |
|
||||
| `default['firezone']['ssl']['session_cache']` | SSL session cache. | `'shared:SSL:4m'` |
|
||||
| `default['firezone']['ssl']['session_timeout']` | SSL session timeout. | `'5m'` |
|
||||
| `default['firezone']['robots_allow']` | nginx robots allow. | `'/'` |
|
||||
| `default['firezone']['robots_disallow']` | nginx robots disallow. | `nil` |
|
||||
| `default['firezone']['outbound_email']['from']` | Outbound email from address. | `nil` |
|
||||
| `default['firezone']['outbound_email']['provider']` | Outbound email service provider. | `nil` |
|
||||
| `default['firezone']['outbound_email']['configs']` | Outbound email provider configs. | see `omnibus/cookbooks/firezone/attributes/default.rb` |
|
||||
| `default['firezone']['telemetry']['enabled']` | Enable or disable anonymized product telemetry. | `true` |
|
||||
| `default['firezone']['connectivity_checks']['enabled']` | Enable or disable the Firezone connectivity checks service. | `true` |
|
||||
| `default['firezone']['connectivity_checks']['interval']` | Interval between connectivity checks in seconds. | `3_600` |
|
||||
|
||||
<!-- markdownlint-enable MD033 -->
|
||||
<!-- markdownlint-enable MD034 -->
|
||||
@@ -1,147 +0,0 @@
|
||||
---
|
||||
title: Environment Variables
|
||||
sidebar_position: 1
|
||||
---
|
||||
|
||||
Most day-to-day config of Firezone can be done via the Firezone Web UI,
|
||||
but for zero-touch deployments we allow to override most of configuration options
|
||||
using environment variables.
|
||||
|
||||
Read more about configuring Firezone in our [configure guide](/docs/deploy/configure).
|
||||
|
||||
## Errors
|
||||
|
||||
Firezone will not boot if the configuration is invalid, providing a detailed error message
|
||||
and a link to the documentation for the configuration key with samples how to set it.
|
||||
|
||||
## Naming
|
||||
|
||||
If environment variables are used, the configuration key must be in uppercase.
|
||||
The database variables are the same as the configuration keys.
|
||||
|
||||
## Precedence
|
||||
|
||||
The configuration precedence is as follows:
|
||||
|
||||
1. Environment variables
|
||||
2. Database values
|
||||
3. Default values
|
||||
|
||||
It means that if environment variable is set, it will be used, regardless of the database value,
|
||||
and UI to edit database value will be disabled.
|
||||
|
||||
## Environment Variable Listing
|
||||
|
||||
We recommend setting these in your Docker ENV file (`$HOME/.firezone/.env` by
|
||||
default). Required fields in **bold**.
|
||||
|
||||
### WebServer
|
||||
|
||||
| Env Key | Description | Format | Default |
|
||||
| -------------------------------- | ----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- | ----------------- | ------- |
|
||||
| **EXTERNAL_URL** | The external URL the web UI will be accessible at.<br /> <br />Must be a valid and public FQDN for ACME SSL issuance to function.<br /> <br />You can add a path suffix if you want to serve firezone from a non-root path, eg: `https://firezone.mycorp.com/vpn/`. | string | |
|
||||
| PHOENIX_SECURE_COOKIES | Enable or disable requiring secure cookies. Required for HTTPS. | boolean | true |
|
||||
| PHOENIX_HTTP_PORT | Internal port to listen on for the Phoenix web server. | integer | 13000 |
|
||||
| PHOENIX_HTTP_PROTOCOL_OPTIONS | Allows to override Cowboy HTTP server options.<br /> <br />Keep in mind though changing those limits can pose a security risk. Other times, browsers and proxies along the way may have equally strict limits, which means the request will still fail or the URL will be pruned.<br /> <br />You can see all supported options at https://ninenines.eu/docs/en/cowboy/2.5/manual/cowboy_http/. | JSON-encoded map | `{}` |
|
||||
| PHOENIX_EXTERNAL_TRUSTED_PROXIES | List of trusted reverse proxies.<br /> <br />This is used to determine the correct IP address of the client when the application is behind a reverse proxy by skipping a trusted proxy IP from a list of possible source IPs. | JSON-encoded list | `"[]"` |
|
||||
| PHOENIX_PRIVATE_CLIENTS | List of trusted clients.<br /> <br />This is used to determine the correct IP address of the client when the application is behind a reverse proxy by picking a trusted client IP from a list of possible source IPs. | JSON-encoded list | `"[]"` |
|
||||
|
||||
### Database
|
||||
|
||||
| Env Key | Description | Format | Default |
|
||||
| -------------------- | ----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- | ---------------- | --------- |
|
||||
| DATABASE_HOST | PostgreSQL host. | string | postgres |
|
||||
| DATABASE_PORT | PostgreSQL port. | integer | 5432 |
|
||||
| DATABASE_NAME | Name of the PostgreSQL database. | string | firezone |
|
||||
| DATABASE_USER | User that will be used to access the PostgreSQL database. | string | postgres |
|
||||
| DATABASE_PASSWORD | Password that will be used to access the PostgreSQL database. | string | |
|
||||
| DATABASE_POOL_SIZE | Size of the connection pool to the PostgreSQL database. | integer | generated |
|
||||
| DATABASE_SSL_ENABLED | Whether to connect to the database over SSL.<br /> <br />If this field is set to `true`, the `database_ssl_opts` config must be set too with at least `cacertfile` option present. | boolean | false |
|
||||
| DATABASE_SSL_OPTS | SSL options for connecting to the PostgreSQL database.<br /> <br />Typically, to enabled SSL you want following options: <br /> - `cacertfile` - path to the CA certificate file;<br /> - `verify` - set to `verify_peer` to verify the server certificate;<br /> - `fail_if_no_peer_cert` - set to `true` to require the server to present a certificate;<br /> - `server_name_indication` - specify the hostname to be used in TLS Server Name Indication extension.<br /> <br />See [Ecto.Adapters.Postgres documentation](https://hexdocs.pm/ecto_sql/Ecto.Adapters.Postgres.html#module-connection-options). For list of all supported options, see the [`ssl`](http://erlang.org/doc/man/ssl.html#type-tls_client_option) module documentation. | JSON-encoded map | `{}` |
|
||||
|
||||
### Admin Setup
|
||||
|
||||
Options responsible for initial admin provisioning and resetting the admin password.
|
||||
|
||||
For more details see [troubleshooting guide](/docs/administer/troubleshoot/#admin-login-isnt-working).
|
||||
|
||||
| Env Key | Description | Format | Default |
|
||||
| ---------------------- | --------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- | ------- | ------- |
|
||||
| RESET_ADMIN_ON_BOOT | Set this variable to `true` to create or reset the admin password every time Firezone starts. By default, the admin password is only set when Firezone is installed.<br /> <br />Note: This **will not** change the status of local authentication. | boolean | false |
|
||||
| DEFAULT_ADMIN_EMAIL | Primary administrator email. | string | |
|
||||
| DEFAULT_ADMIN_PASSWORD | Default password that will be used for creating or resetting the primary administrator account. | string | |
|
||||
|
||||
### Secrets and Encryption
|
||||
|
||||
Your secrets should be generated during installation automatically and persisted to `.env` file.
|
||||
|
||||
All secrets should be a **base64-encoded string**.
|
||||
|
||||
| Env Key | Description | Format | Default |
|
||||
| --------------------------- | ------------------------------------------------------------------ | ------ | ------- |
|
||||
| **GUARDIAN_SECRET_KEY** | Secret key used for signing JWTs. | string | |
|
||||
| **DATABASE_ENCRYPTION_KEY** | Secret key used for encrypting sensitive data in the database. | string | |
|
||||
| **SECRET_KEY_BASE** | Primary secret key base for the Phoenix application. | string | |
|
||||
| **LIVE_VIEW_SIGNING_SALT** | Signing salt for Phoenix LiveView connection tokens. | string | |
|
||||
| **COOKIE_SIGNING_SALT** | Signing salt for cookies issued by the Phoenix web application. | string | |
|
||||
| **COOKIE_ENCRYPTION_SALT** | Encryption salt for cookies issued by the Phoenix web application. | string | |
|
||||
|
||||
### Devices
|
||||
|
||||
| Env Key | Description | Format | Default |
|
||||
| --------------------------------------- | -------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- | --------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- | ----------------- |
|
||||
| ALLOW_UNPRIVILEGED_DEVICE_MANAGEMENT | Enable or disable management of devices on unprivileged accounts. | boolean | true |
|
||||
| ALLOW_UNPRIVILEGED_DEVICE_CONFIGURATION | Enable or disable configuration of device network settings for unprivileged users. | boolean | true |
|
||||
| VPN_SESSION_DURATION | Optionally require users to periodically authenticate to the Firezone web UI in order to keep their VPN sessions active. | integer | 0 |
|
||||
| DEFAULT_CLIENT_PERSISTENT_KEEPALIVE | Interval for WireGuard [persistent keepalive](https://www.wireguard.com/quickstart/#nat-and-firewall-traversal-persistence).<br /> <br />If you experience NAT or firewall traversal problems, you can enable this to send a keepalive packet every 25 seconds. Otherwise, keep it disabled with a 0 default value. | integer | 25 |
|
||||
| DEFAULT_CLIENT_MTU | WireGuard interface MTU for devices. 1280 is a safe bet for most networks. Leave this blank to omit this field from generated configs. | integer | 1280 |
|
||||
| DEFAULT_CLIENT_ENDPOINT | IPv4, IPv6 address, or FQDN that devices will be configured to connect to. Defaults to this server's FQDN. | one of `IP with port`, `string` | generated |
|
||||
| DEFAULT_CLIENT_DNS | Comma-separated list of DNS servers to use for devices.<br /> <br />It can be either an IP address or a FQDN if you intend to use a DNS-over-TLS server.<br /> <br />Leave this blank to omit the `DNS` section from generated configs. | {:array, ",", {:one_of, [Domain.Types.IP, :string]}, [validate_unique: true]} | `[]` |
|
||||
| DEFAULT_CLIENT_ALLOWED_IPS | Configures the default AllowedIPs setting for devices.<br /> <br />AllowedIPs determines which destination IPs get routed through Firezone.<br /> <br />Specify a comma-separated list of IPs or CIDRs here to achieve split tunneling, or use `0.0.0.0/0, ::/0` to route all device traffic through this Firezone server. | {:array, ",", {:one_of, [Domain.Types.CIDR, Domain.Types.IP]}, [validate_unique: true]} | `0.0.0.0/0, ::/0` |
|
||||
|
||||
### Authorization
|
||||
|
||||
| Env Key | Description | Format | Default |
|
||||
| ------------------------- | ---------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- | ----------------- | ----------------------------- |
|
||||
| LOCAL_AUTH_ENABLED | Enable or disable the local authentication method for all users. | boolean | true |
|
||||
| DISABLE_VPN_ON_OIDC_ERROR | Enable or disable auto disabling VPN connection on OIDC refresh error. | boolean | false |
|
||||
| SAML_ENTITY_ID | Entity ID for SAML authentication. | string | urn:firezone.dev:firezone-app |
|
||||
| SAML_KEYFILE_PATH | Path to the SAML keyfile inside the container. Should be either a PEM or DER-encoded private key, with file extension `.pem` or `.key`. | string | /var/firezone/saml.key |
|
||||
| SAML_CERTFILE_PATH | Path to the SAML certificate file inside the container. Should be either a PEM or DER-encoded certificate, with file extension `.crt` or `.pem`. | string | /var/firezone/saml.crt |
|
||||
| OPENID_CONNECT_PROVIDERS | List of OpenID Connect identity providers configurations.<br /> <br />For example:<br /> <br />`[ { "auto_create_users": false, "id": "google", "label": "google", "client_id": "test-id", "client_secret": "test-secret", "discovery_document_uri": "https://accounts.google.com/.well-known/openid-configuration", "redirect_uri": "https://invalid", "response_type": "response-type", "scope": "oauth email profile" } ]`<br /> <br />For more details see https://docs.firezone.dev/authenticate/oidc/. | JSON-encoded list | `"[]"` |
|
||||
| SAML_IDENTITY_PROVIDERS | List of SAML identity providers configurations.<br /> <br />For example:<br /> <br />`[ { "auto_create_users": false, "base_url": "https://saml", "id": "okta", "label": "okta", "metadata": "<?xml version="1.0"?>...", "sign_metadata": false, "sign_requests": false, "signed_assertion_in_resp": false, "signed_envelopes_in_resp": false } ]`<br /> <br />For more details see https://docs.firezone.dev/authenticate/saml/. | JSON-encoded list | `"[]"` |
|
||||
|
||||
### WireGuard
|
||||
|
||||
| Env Key | Description | Format | Default |
|
||||
| ---------------------- | --------------------------------------------------------------- | ------- | ------- |
|
||||
| WIREGUARD_PORT | A port on which WireGuard will listen for incoming connections. | integer | 51820 |
|
||||
| WIREGUARD_IPV4_ENABLED | Enable or disable IPv4 support for WireGuard. | boolean | true |
|
||||
| WIREGUARD_IPV6_ENABLED | Enable or disable IPv6 support for WireGuard. | boolean | true |
|
||||
|
||||
### Outbound Emails
|
||||
|
||||
| Env Key | Description | Format | Default |
|
||||
| --------------------------- | ------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------ | ----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- | ------------------------------- |
|
||||
| OUTBOUND_EMAIL_FROM | From address to use for sending outbound emails. If not set, sending email will be disabled (default). | string | generated |
|
||||
| OUTBOUND_EMAIL_ADAPTER | Method to use for sending outbound email. | One of `Elixir.Swoosh.Adapters.AmazonSES`, `Elixir.Swoosh.Adapters.CustomerIO`, `Elixir.Swoosh.Adapters.Dyn`, `Elixir.Swoosh.Adapters.ExAwsAmazonSES`, `Elixir.Swoosh.Adapters.Gmail`, `Elixir.Swoosh.Adapters.MailPace`, `Elixir.Swoosh.Adapters.Mailgun`, `Elixir.Swoosh.Adapters.Mailjet`, `Elixir.Swoosh.Adapters.Mandrill`, `Elixir.Swoosh.Adapters.Postmark`, `Elixir.Swoosh.Adapters.ProtonBridge`, `Elixir.Swoosh.Adapters.SMTP`, `Elixir.Swoosh.Adapters.SMTP2GO`, `Elixir.Swoosh.Adapters.Sendgrid`, `Elixir.Swoosh.Adapters.Sendinblue`, `Elixir.Swoosh.Adapters.Sendmail`, `Elixir.Swoosh.Adapters.SocketLabs`, `Elixir.Swoosh.Adapters.SparkPost`, `Elixir.Web.Mailer.NoopAdapter` | `Elixir.Web.Mailer.NoopAdapter` |
|
||||
| OUTBOUND_EMAIL_ADAPTER_OPTS | Adapter configuration, for list of options see [Swoosh Adapters](https://github.com/swoosh/swoosh#adapters). | JSON-encoded map | `{}` |
|
||||
|
||||
### Connectivity Checks
|
||||
|
||||
| Env Key | Description | Format | Default |
|
||||
| ---------------------------- | ------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------ | ------- | ------- |
|
||||
| CONNECTIVITY_CHECKS_ENABLED | Enable / disable periodic checking for egress connectivity. Determines the instance's public IP to populate `Endpoint` fields. | boolean | true |
|
||||
| CONNECTIVITY_CHECKS_INTERVAL | Periodicity in seconds to check for egress connectivity. | integer | 43200 |
|
||||
|
||||
### Telemetry
|
||||
|
||||
| Env Key | Description | Format | Default |
|
||||
| ----------------- | ------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- | ------- | ------- |
|
||||
| TELEMETRY_ENABLED | Enable or disable the Firezone telemetry collection.<br /> <br />For more details see https://docs.firezone.dev/reference/telemetry/. | boolean | true |
|
||||
|
||||
### Other
|
||||
|
||||
| Env Key | Description | Format | Default |
|
||||
| ------- | --------------------------------------------------------------- | ---------------------------- | ------- |
|
||||
| LOGO | The path to a logo image file to replace default Firezone logo. | {:embed, Domain.Config.Logo} | `` |
|
||||
@@ -1,37 +0,0 @@
|
||||
---
|
||||
title: File and Directory Locations
|
||||
sidebar_position: 3
|
||||
---
|
||||
|
||||
Here you'll find a listing of files and directories related to a typical
|
||||
Firezone installation. These can change depending on how you've configured
|
||||
your installation.
|
||||
|
||||
<Tabs>
|
||||
<TabItem label="Docker" value="docker" default>
|
||||
|
||||
| Default path | Description |
|
||||
| ----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- | ------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- |
|
||||
| `$HOME/.firezone/.env` | Firezone secrets used for encryption, cookies, and sessions. **Losing this file will result in irrecoverable data loss**. |
|
||||
| `$HOME/.firezone/docker-compose.yml` | Docker Compose file used to manage Firezone services. |
|
||||
| `$HOME/.firezone/firezone` | Top-level directory containing Firezone-related persisted data |
|
||||
| `$HOME/.firezone/caddy` | Caddy persisted files. |
|
||||
| Default Docker named volume location, typically `/var/lib/docker/volumes/firezone_postgres-data` for Linux. | Postgres DB files. |
|
||||
|
||||
</TabItem>
|
||||
<TabItem label="Omnibus" value="omnibus">
|
||||
|
||||
| Path | Description |
|
||||
| ----------------------------------------------------- | ---------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- |
|
||||
| `/var/opt/firezone` | Top-level directory containing data and generated configuration for Firezone bundled services. |
|
||||
| `/opt/firezone` | Top-level directory containing built libraries, binaries and runtime files needed by Firezone. |
|
||||
| `/usr/bin/firezone-ctl` | `firezone-ctl` utility for managing your Firezone installation. |
|
||||
| `/etc/systemd/system/firezone-runsvdir-start.service` | systemd unit file for starting the Firezone runsvdir supervisor process. |
|
||||
| `/etc/firezone` | Firezone configuration files. |
|
||||
|
||||
</TabItem>
|
||||
</Tabs>
|
||||
|
||||
## Backup and restore
|
||||
|
||||
See our [backup guide](/docs/administer/backup).
|
||||
@@ -1,15 +0,0 @@
|
||||
---
|
||||
title: Firewall Templates
|
||||
sidebar_position: 9
|
||||
---
|
||||
|
||||
Firewall templates to secure the Firezone server itself are available from here.
|
||||
If the server is not running any services other than Firezone, the firewall
|
||||
template should work as-is.
|
||||
|
||||
```mdx-code-block
|
||||
import DocCardList from '@theme/DocCardList';
|
||||
import {useCurrentSidebarCategory} from '@docusaurus/theme-common';
|
||||
|
||||
<DocCardList items={useCurrentSidebarCategory().items}/>
|
||||
```
|
||||
@@ -1,339 +0,0 @@
|
||||
---
|
||||
title: nftables Firewall Template
|
||||
sidebar_position: 1
|
||||
---
|
||||
|
||||
The following nftables firewall template can be used to secure the server
|
||||
running Firezone. The template does make some assumptions; you may need to
|
||||
adjust the rules to suit your use case:
|
||||
|
||||
* The WireGuard interface is named `wg-firezone`. If this is not correct,
|
||||
change the `DEV_WIREGUARD` variable to match the
|
||||
`default['firezone']['wireguard']['interface_name']` configuration option.
|
||||
* The port WireGuard is listening on is `51820`. If you are not using the
|
||||
default port change the `WIREGUARD_PORT` variable.
|
||||
* Only the following inbound traffic will be allowed to the server:
|
||||
* SSH (TCP dport 22)
|
||||
* HTTP (TCP dport 80)
|
||||
* HTTPS (TCP dport 443)
|
||||
* WireGuard (UDP dport `WIREGUARD_PORT`)
|
||||
* UDP traceroute (UDP dport 33434-33524, rate limited to 500/second)
|
||||
* ICMP and ICMPv6 (ping/ping responses rate limited to 2000/second)
|
||||
* Only the following outbound traffic will be allowed from the server:
|
||||
* DNS (UDP and TCP dport 53)
|
||||
* HTTP (TCP dport 80)
|
||||
* NTP (UDP port 123)
|
||||
* HTTPS (TCP dport 443)
|
||||
* SMTP submission (TCP dport 587)
|
||||
* UDP traceroute (UDP dport 33434-33524, rate limited to 500/second)
|
||||
* Unmatched traffic will be logged. The rules used for logging are separated
|
||||
from the rules to drop traffic and are rate limited. Removing the relevant
|
||||
logging rules will not affect traffic.
|
||||
|
||||
## Firezone-managed rules
|
||||
|
||||
Firezone configures its own nftables rules to permit/reject traffic to destinations
|
||||
configured in the web interface and to handle outbound NAT for client traffic.
|
||||
|
||||
Applying the below firewall template on an already running server (not at boot time)
|
||||
will result in the Firezone rules being cleared. This may have security implications.
|
||||
|
||||
To work around this restart the `phoenix` service:
|
||||
|
||||
```shell
|
||||
firezone-ctl restart phoenix
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
## Base firewall template
|
||||
|
||||
```shell
|
||||
#!/usr/sbin/nft -f
|
||||
|
||||
## Clear/flush all existing rules
|
||||
flush ruleset
|
||||
|
||||
################################ VARIABLES ################################
|
||||
## Internet/WAN interface name
|
||||
define DEV_WAN = eth0
|
||||
|
||||
## WireGuard interface name
|
||||
define DEV_WIREGUARD = wg-firezone
|
||||
|
||||
## WireGuard listen port
|
||||
define WIREGUARD_PORT = 51820
|
||||
############################## VARIABLES END ##############################
|
||||
|
||||
# Main inet family filtering table
|
||||
table inet filter {
|
||||
|
||||
# Rules for forwarded traffic
|
||||
# This chain is processed before the Firezone forward chain
|
||||
chain forward {
|
||||
type filter hook forward priority filter - 5; policy accept
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
# Rules for input traffic
|
||||
chain input {
|
||||
type filter hook input priority filter; policy drop
|
||||
|
||||
## Permit inbound traffic to loopback interface
|
||||
iif lo \
|
||||
accept \
|
||||
comment "Permit all traffic in from loopback interface"
|
||||
|
||||
## Permit established and related connections
|
||||
ct state established,related \
|
||||
accept \
|
||||
comment "Permit established/related connections"
|
||||
|
||||
## Permit inbound WireGuard traffic
|
||||
iif $DEV_WAN udp dport $WIREGUARD_PORT \
|
||||
counter \
|
||||
accept \
|
||||
comment "Permit inbound WireGuard traffic"
|
||||
|
||||
## Log and drop new TCP non-SYN packets
|
||||
tcp flags != syn ct state new \
|
||||
limit rate 100/minute burst 150 packets \
|
||||
log prefix "IN - New !SYN: " \
|
||||
comment "Rate limit logging for new connections that do not have the SYN TCP flag set"
|
||||
tcp flags != syn ct state new \
|
||||
counter \
|
||||
drop \
|
||||
comment "Drop new connections that do not have the SYN TCP flag set"
|
||||
|
||||
## Log and drop TCP packets with invalid fin/syn flag set
|
||||
tcp flags & (fin|syn) == (fin|syn) \
|
||||
limit rate 100/minute burst 150 packets \
|
||||
log prefix "IN - TCP FIN|SIN: " \
|
||||
comment "Rate limit logging for TCP packets with invalid fin/syn flag set"
|
||||
tcp flags & (fin|syn) == (fin|syn) \
|
||||
counter \
|
||||
drop \
|
||||
comment "Drop TCP packets with invalid fin/syn flag set"
|
||||
|
||||
## Log and drop TCP packets with invalid syn/rst flag set
|
||||
tcp flags & (syn|rst) == (syn|rst) \
|
||||
limit rate 100/minute burst 150 packets \
|
||||
log prefix "IN - TCP SYN|RST: " \
|
||||
comment "Rate limit logging for TCP packets with invalid syn/rst flag set"
|
||||
tcp flags & (syn|rst) == (syn|rst) \
|
||||
counter \
|
||||
drop \
|
||||
comment "Drop TCP packets with invalid syn/rst flag set"
|
||||
|
||||
## Log and drop invalid TCP flags
|
||||
tcp flags & (fin|syn|rst|psh|ack|urg) < (fin) \
|
||||
limit rate 100/minute burst 150 packets \
|
||||
log prefix "IN - FIN:" \
|
||||
comment "Rate limit logging for invalid TCP flags (fin|syn|rst|psh|ack|urg) < (fin)"
|
||||
tcp flags & (fin|syn|rst|psh|ack|urg) < (fin) \
|
||||
counter \
|
||||
drop \
|
||||
comment "Drop TCP packets with flags (fin|syn|rst|psh|ack|urg) < (fin)"
|
||||
|
||||
## Log and drop invalid TCP flags
|
||||
tcp flags & (fin|syn|rst|psh|ack|urg) == (fin|psh|urg) \
|
||||
limit rate 100/minute burst 150 packets \
|
||||
log prefix "IN - FIN|PSH|URG:" \
|
||||
comment "Rate limit logging for invalid TCP flags (fin|syn|rst|psh|ack|urg) == (fin|psh|urg)"
|
||||
tcp flags & (fin|syn|rst|psh|ack|urg) == (fin|psh|urg) \
|
||||
counter \
|
||||
drop \
|
||||
comment "Drop TCP packets with flags (fin|syn|rst|psh|ack|urg) == (fin|psh|urg)"
|
||||
|
||||
## Drop traffic with invalid connection state
|
||||
ct state invalid \
|
||||
limit rate 100/minute burst 150 packets \
|
||||
log flags all prefix "IN - Invalid: " \
|
||||
comment "Rate limit logging for traffic with invalid connection state"
|
||||
ct state invalid \
|
||||
counter \
|
||||
drop \
|
||||
comment "Drop traffic with invalid connection state"
|
||||
|
||||
## Permit IPv4 ping/ping responses but rate limit to 2000 PPS
|
||||
ip protocol icmp icmp type { echo-reply, echo-request } \
|
||||
limit rate 2000/second \
|
||||
counter \
|
||||
accept \
|
||||
comment "Permit inbound IPv4 echo (ping) limited to 2000 PPS"
|
||||
|
||||
## Permit all other inbound IPv4 ICMP
|
||||
ip protocol icmp \
|
||||
counter \
|
||||
accept \
|
||||
comment "Permit all other IPv4 ICMP"
|
||||
|
||||
## Permit IPv6 ping/ping responses but rate limit to 2000 PPS
|
||||
icmpv6 type { echo-reply, echo-request } \
|
||||
limit rate 2000/second \
|
||||
counter \
|
||||
accept \
|
||||
comment "Permit inbound IPv6 echo (ping) limited to 2000 PPS"
|
||||
|
||||
## Permit all other inbound IPv6 ICMP
|
||||
meta l4proto { icmpv6 } \
|
||||
counter \
|
||||
accept \
|
||||
comment "Permit all other IPv6 ICMP"
|
||||
|
||||
## Permit inbound traceroute UDP ports but limit to 500 PPS
|
||||
udp dport 33434-33524 \
|
||||
limit rate 500/second \
|
||||
counter \
|
||||
accept \
|
||||
comment "Permit inbound UDP traceroute limited to 500 PPS"
|
||||
|
||||
## Permit inbound SSH
|
||||
tcp dport ssh ct state new \
|
||||
counter \
|
||||
accept \
|
||||
comment "Permit inbound SSH connections"
|
||||
|
||||
## Permit inbound HTTP and HTTPS
|
||||
tcp dport { http, https } ct state new \
|
||||
counter \
|
||||
accept \
|
||||
comment "Permit inbound HTTP and HTTPS connections"
|
||||
|
||||
## Log any unmatched traffic but rate limit logging to a maximum of 60 messages/minute
|
||||
## The default policy will be applied to unmatched traffic
|
||||
limit rate 60/minute burst 100 packets \
|
||||
log prefix "IN - Drop: " \
|
||||
comment "Log any unmatched traffic"
|
||||
|
||||
## Count the unmatched traffic
|
||||
counter \
|
||||
comment "Count any unmatched traffic"
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
# Rules for output traffic
|
||||
chain output {
|
||||
type filter hook output priority filter; policy drop
|
||||
|
||||
## Permit outbound traffic to loopback interface
|
||||
oif lo \
|
||||
accept \
|
||||
comment "Permit all traffic out to loopback interface"
|
||||
|
||||
## Permit established and related connections
|
||||
ct state established,related \
|
||||
counter \
|
||||
accept \
|
||||
comment "Permit established/related connections"
|
||||
|
||||
## Permit outbound WireGuard traffic before dropping connections with bad state
|
||||
oif $DEV_WAN udp sport $WIREGUARD_PORT \
|
||||
counter \
|
||||
accept \
|
||||
comment "Permit WireGuard outbound traffic"
|
||||
|
||||
## Drop traffic with invalid connection state
|
||||
ct state invalid \
|
||||
limit rate 100/minute burst 150 packets \
|
||||
log flags all prefix "OUT - Invalid: " \
|
||||
comment "Rate limit logging for traffic with invalid connection state"
|
||||
ct state invalid \
|
||||
counter \
|
||||
drop \
|
||||
comment "Drop traffic with invalid connection state"
|
||||
|
||||
## Permit all other outbound IPv4 ICMP
|
||||
ip protocol icmp \
|
||||
counter \
|
||||
accept \
|
||||
comment "Permit all IPv4 ICMP types"
|
||||
|
||||
## Permit all other outbound IPv6 ICMP
|
||||
meta l4proto { icmpv6 } \
|
||||
counter \
|
||||
accept \
|
||||
comment "Permit all IPv6 ICMP types"
|
||||
|
||||
## Permit outbound traceroute UDP ports but limit to 500 PPS
|
||||
udp dport 33434-33524 \
|
||||
limit rate 500/second \
|
||||
counter \
|
||||
accept \
|
||||
comment "Permit outbound UDP traceroute limited to 500 PPS"
|
||||
|
||||
## Permit outbound HTTP and HTTPS connections
|
||||
tcp dport { http, https } ct state new \
|
||||
counter \
|
||||
accept \
|
||||
comment "Permit outbound HTTP and HTTPS connections"
|
||||
|
||||
## Permit outbound SMTP submission
|
||||
tcp dport submission ct state new \
|
||||
counter \
|
||||
accept \
|
||||
comment "Permit outbound SMTP submission"
|
||||
|
||||
## Permit outbound DNS requests
|
||||
udp dport 53 \
|
||||
counter \
|
||||
accept \
|
||||
comment "Permit outbound UDP DNS requests"
|
||||
tcp dport 53 \
|
||||
counter \
|
||||
accept \
|
||||
comment "Permit outbound TCP DNS requests"
|
||||
|
||||
## Permit outbound NTP requests
|
||||
udp dport 123 \
|
||||
counter \
|
||||
accept \
|
||||
comment "Permit outbound NTP requests"
|
||||
|
||||
## Log any unmatched traffic but rate limit logging to a maximum of 60 messages/minute
|
||||
## The default policy will be applied to unmatched traffic
|
||||
limit rate 60/minute burst 100 packets \
|
||||
log prefix "OUT - Drop: " \
|
||||
comment "Log any unmatched traffic"
|
||||
|
||||
## Count the unmatched traffic
|
||||
counter \
|
||||
comment "Count any unmatched traffic"
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
# Main NAT filtering table
|
||||
table inet nat {
|
||||
|
||||
# Rules for NAT traffic pre-routing
|
||||
chain prerouting {
|
||||
type nat hook prerouting priority dstnat; policy accept
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
# Rules for NAT traffic post-routing
|
||||
# This table is processed before the Firezone post-routing chain
|
||||
chain postrouting {
|
||||
type nat hook postrouting priority srcnat - 5; policy accept
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
## Usage
|
||||
|
||||
The firewall should be stored in the relevant location for the Linux distribution
|
||||
that is running. For Debian/Ubuntu this is `/etc/nftables.conf` and for RHEL this
|
||||
is `/etc/sysconfig/nftables.conf`.
|
||||
|
||||
`nftables.service` will need to be configured to start on boot (if not already) set:
|
||||
|
||||
```shell
|
||||
systemctl enable nftables.service
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
If making any changes to the firewall template the syntax can be validated by running
|
||||
the check command:
|
||||
|
||||
```shell
|
||||
nft -f /path/to/nftables.conf -c
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Be sure to validate the firewall works as expected as certain nftables features may
|
||||
not be available depending on the release running on the server.
|
||||
@@ -1,35 +0,0 @@
|
||||
---
|
||||
title: REST API
|
||||
sidebar_position: 10
|
||||
---
|
||||
|
||||
Welcome to Firezone's REST API v0 documentation.
|
||||
|
||||
## Getting started
|
||||
|
||||
To get started with the REST API, you'll first need an API token.
|
||||
This can be generated in the UI at `/settings/account` or via the CLI
|
||||
with:
|
||||
|
||||
```shell
|
||||
docker compose -f $HOME/.firezone/docker-compose.yml exec firezone bin/create-api-token
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
**Note**: The token is written to `STDOUT` by default. You may wish to redirect its output
|
||||
to a file instead:
|
||||
|
||||
```shell
|
||||
docker compose -f $HOME/.firezone/docker-compose.yml exec firezone bin/create-api-token > fz_token
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
:::caution
|
||||
API tokens generated from the CLI are owned by the primary administrator specified by
|
||||
the `DEFAULT_ADMIN_EMAIL` environment variable.
|
||||
:::
|
||||
|
||||
```mdx-code-block
|
||||
import DocCardList from '@theme/DocCardList';
|
||||
import {useCurrentSidebarCategory} from '@docusaurus/theme-common';
|
||||
|
||||
<DocCardList items={useCurrentSidebarCategory().items}/>
|
||||
```
|
||||
@@ -1,163 +0,0 @@
|
||||
---
|
||||
title: Configurations
|
||||
group: Configuration
|
||||
---
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
This endpoint allows an administrator to manage Configurations.
|
||||
|
||||
Updates here can be applied at runtime with little to no downtime of affected services.
|
||||
|
||||
## API Documentation
|
||||
### GET /v0/configuration
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
#### Example
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
$ curl -i \
|
||||
-X GET "https://{firezone_host}/v0/configuration" \
|
||||
-H 'Content-Type: application/json' \
|
||||
-H 'Authorization: Bearer {api_token}' \
|
||||
|
||||
HTTP/1.1 200
|
||||
Content-Type: application/json; charset=utf-8
|
||||
|
||||
{
|
||||
"data": {
|
||||
"allow_unprivileged_device_configuration": true,
|
||||
"allow_unprivileged_device_management": true,
|
||||
"default_client_allowed_ips": [
|
||||
"0.0.0.0/0",
|
||||
"::/0"
|
||||
],
|
||||
"default_client_dns": [
|
||||
"1.1.1.1",
|
||||
"1.0.0.1"
|
||||
],
|
||||
"default_client_endpoint": "localhost:51820",
|
||||
"default_client_mtu": 1280,
|
||||
"default_client_persistent_keepalive": 25,
|
||||
"disable_vpn_on_oidc_error": false,
|
||||
"id": "c4582e2b-cba3-4a4e-9f05-0f37666c41fe",
|
||||
"inserted_at": "2023-03-29T15:10:03.142320Z",
|
||||
"local_auth_enabled": true,
|
||||
"logo": {},
|
||||
"openid_connect_providers": [],
|
||||
"saml_identity_providers": [],
|
||||
"updated_at": "2023-03-29T15:10:03.142320Z",
|
||||
"vpn_session_duration": 0
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
### PATCH /v0/configuration
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
#### Example
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
$ curl -i \
|
||||
-X PUT "https://{firezone_host}/v0/configuration" \
|
||||
-H 'Content-Type: application/json' \
|
||||
-H 'Authorization: Bearer {api_token}' \
|
||||
--data-binary @- << EOF
|
||||
{
|
||||
"configuration": {
|
||||
"allow_unprivileged_device_configuration": false,
|
||||
"allow_unprivileged_device_management": false,
|
||||
"default_client_allowed_ips": [
|
||||
"1.1.1.1",
|
||||
"2.2.2.2"
|
||||
],
|
||||
"default_client_dns": [
|
||||
"1.1.1.1"
|
||||
],
|
||||
"default_client_endpoint": "new-endpoint",
|
||||
"default_client_mtu": 1100,
|
||||
"default_client_persistent_keepalive": 1,
|
||||
"disable_vpn_on_oidc_error": true,
|
||||
"local_auth_enabled": false,
|
||||
"openid_connect_providers": [
|
||||
{
|
||||
"auto_create_users": false,
|
||||
"client_id": "test-id",
|
||||
"client_secret": "test-secret",
|
||||
"discovery_document_uri": "https://accounts.google.com/.well-known/openid-configuration",
|
||||
"id": "google",
|
||||
"label": "google",
|
||||
"redirect_uri": "https://invalid",
|
||||
"response_type": "code",
|
||||
"scope": "email openid"
|
||||
}
|
||||
],
|
||||
"saml_identity_providers": [
|
||||
{
|
||||
"auto_create_users": false,
|
||||
"base_url": "https://saml",
|
||||
"id": "okta",
|
||||
"label": "okta",
|
||||
"metadata": "<?xml version=\"1.0\" encoding=\"UTF-8\"?>\n<md:EntityDescriptor entityID=\"http://www.okta.com/exk6ff6p62kFjUR3X5d7\"\n xmlns:md=\"urn:oasis:names:tc:SAML:2.0:metadata\">\n <md:IDPSSODescriptor WantAuthnRequestsSigned=\"false\" protocolSupportEnumeration=\"urn:oasis:names:tc:SAML:2.0:protocol\">\n <md:KeyDescriptor use=\"signing\">\n <ds:KeyInfo\n xmlns:ds=\"http://www.w3.org/2000/09/xmldsig#\">\n <ds:X509Data>\n <ds:X509Certificate>MIIDqDCCApCgAwIBAgIGAYMaIfiKMA0GCSqGSIb3DQEBCwUAMIGUMQswCQYDVQQGEwJVUzETMBEG\nA1UECAwKQ2FsaWZvcm5pYTEWMBQGA1UEBwwNU2FuIEZyYW5jaXNjbzENMAsGA1UECgwET2t0YTEU\nMBIGA1UECwwLU1NPUHJvdmlkZXIxFTATBgNVBAMMDGRldi04Mzg1OTk1NTEcMBoGCSqGSIb3DQEJ\nARYNaW5mb0Bva3RhLmNvbTAeFw0yMjA5MDcyMjQ1MTdaFw0zMjA5MDcyMjQ2MTdaMIGUMQswCQYD\nVQQGEwJVUzETMBEGA1UECAwKQ2FsaWZvcm5pYTEWMBQGA1UEBwwNU2FuIEZyYW5jaXNjbzENMAsG\nA1UECgwET2t0YTEUMBIGA1UECwwLU1NPUHJvdmlkZXIxFTATBgNVBAMMDGRldi04Mzg1OTk1NTEc\nMBoGCSqGSIb3DQEJARYNaW5mb0Bva3RhLmNvbTCCASIwDQYJKoZIhvcNAQEBBQADggEPADCCAQoC\nggEBAOmj276L3kHm57hNGYTocT6NS4mffPbcvsA2UuKIWfmpV8HLTcmS+NahLtuN841OnRnTn+2p\nfjlwa1mwJhCODbF3dcVYOkGTPUC4y2nvf1Xas6M7+0O2WIfrzdX/OOUs/ROMnB/O/MpBwMR2SQh6\nQ3V+9v8g3K9yfMvcifDbl6g9fTliDzqV7I9xF5eJykl+iCAKNaQgp3cO6TaIa5u2ZKtRAdzwnuJC\nBXMyzaoNs/vfnwzuFtzWP1PSS1Roan+8AMwkYA6BCr1YRIqZ0GSkr/qexFCTZdq0UnSN78fY6CCM\nRFw5wU0WM9nEpbWzkBBWsYHeTLo5JqR/mZukfjlPDlcCAwEAATANBgkqhkiG9w0BAQsFAAOCAQEA\nlUhwzCSnuqt4wlHxJONN4kxUBG8bPnjHxob6jBKK+onFDuSVWZ+7LZw67blz6xdxvlOLaQLi1fK2\nFifehbc7KbRLckcgNgg7Y8qfUKdP0/nS0JlyAvlnICQqaHTHwhIzQqTHtTZeeIJHtpWOX/OPRI0S\nbkygh2qjF8bYn3sX8bGNUQL8iiMxFnvwGrXaErPqlRqFJbWQDBXD+nYDIBw7WN3Jyb0Ydin2zrlh\ngp3Qooi0TnAir3ncw/UF/+sivCgd+6nX7HkbZtipkMbg7ZByyD9xrOQG2JXrP6PyzGCPwnGMt9pL\niiVMepeLNqKZ3UvhrR1uRN0KWu7lduIRhxldLA==</ds:X509Certificate>\n </ds:X509Data>\n </ds:KeyInfo>\n </md:KeyDescriptor>\n <md:NameIDFormat>urn:oasis:names:tc:SAML:1.1:nameid-format:unspecified</md:NameIDFormat>\n <md:NameIDFormat>urn:oasis:names:tc:SAML:1.1:nameid-format:emailAddress</md:NameIDFormat>\n <md:SingleSignOnService Binding=\"urn:oasis:names:tc:SAML:2.0:bindings:HTTP-POST\" Location=\"https://dev-83859955.okta.com/app/dev-83859955_firezonesaml_1/exk6ff6p62kFjUR3X5d7/sso/saml\"/>\n <md:SingleSignOnService Binding=\"urn:oasis:names:tc:SAML:2.0:bindings:HTTP-Redirect\" Location=\"https://dev-83859955.okta.com/app/dev-83859955_firezonesaml_1/exk6ff6p62kFjUR3X5d7/sso/saml\"/>\n </md:IDPSSODescriptor>\n</md:EntityDescriptor>\n",
|
||||
"sign_metadata": false,
|
||||
"sign_requests": false,
|
||||
"signed_assertion_in_resp": false,
|
||||
"signed_envelopes_in_resp": false
|
||||
}
|
||||
],
|
||||
"vpn_session_duration": 100
|
||||
}
|
||||
}'
|
||||
EOF
|
||||
|
||||
HTTP/1.1 200
|
||||
Content-Type: application/json; charset=utf-8
|
||||
|
||||
{
|
||||
"data": {
|
||||
"allow_unprivileged_device_configuration": false,
|
||||
"allow_unprivileged_device_management": false,
|
||||
"default_client_allowed_ips": [
|
||||
"1.1.1.1",
|
||||
"2.2.2.2"
|
||||
],
|
||||
"default_client_dns": [
|
||||
"1.1.1.1"
|
||||
],
|
||||
"default_client_endpoint": "new-endpoint",
|
||||
"default_client_mtu": 1100,
|
||||
"default_client_persistent_keepalive": 1,
|
||||
"disable_vpn_on_oidc_error": true,
|
||||
"id": "c4582e2b-cba3-4a4e-9f05-0f37666c41fe",
|
||||
"inserted_at": "2023-03-29T15:10:03.142320Z",
|
||||
"local_auth_enabled": false,
|
||||
"logo": {},
|
||||
"openid_connect_providers": [
|
||||
{
|
||||
"auto_create_users": false,
|
||||
"client_id": "test-id",
|
||||
"client_secret": "test-secret",
|
||||
"discovery_document_uri": "https://accounts.google.com/.well-known/openid-configuration",
|
||||
"id": "google",
|
||||
"label": "google",
|
||||
"redirect_uri": "https://invalid",
|
||||
"response_type": "code",
|
||||
"scope": "email openid"
|
||||
}
|
||||
],
|
||||
"saml_identity_providers": [
|
||||
{
|
||||
"auto_create_users": false,
|
||||
"base_url": "https://saml",
|
||||
"id": "okta",
|
||||
"label": "okta",
|
||||
"metadata": "<?xml version=\"1.0\" encoding=\"UTF-8\"?>\n<md:EntityDescriptor entityID=\"http://www.okta.com/exk6ff6p62kFjUR3X5d7\"\n xmlns:md=\"urn:oasis:names:tc:SAML:2.0:metadata\">\n <md:IDPSSODescriptor WantAuthnRequestsSigned=\"false\" protocolSupportEnumeration=\"urn:oasis:names:tc:SAML:2.0:protocol\">\n <md:KeyDescriptor use=\"signing\">\n <ds:KeyInfo\n xmlns:ds=\"http://www.w3.org/2000/09/xmldsig#\">\n <ds:X509Data>\n <ds:X509Certificate>MIIDqDCCApCgAwIBAgIGAYMaIfiKMA0GCSqGSIb3DQEBCwUAMIGUMQswCQYDVQQGEwJVUzETMBEG\nA1UECAwKQ2FsaWZvcm5pYTEWMBQGA1UEBwwNU2FuIEZyYW5jaXNjbzENMAsGA1UECgwET2t0YTEU\nMBIGA1UECwwLU1NPUHJvdmlkZXIxFTATBgNVBAMMDGRldi04Mzg1OTk1NTEcMBoGCSqGSIb3DQEJ\nARYNaW5mb0Bva3RhLmNvbTAeFw0yMjA5MDcyMjQ1MTdaFw0zMjA5MDcyMjQ2MTdaMIGUMQswCQYD\nVQQGEwJVUzETMBEGA1UECAwKQ2FsaWZvcm5pYTEWMBQGA1UEBwwNU2FuIEZyYW5jaXNjbzENMAsG\nA1UECgwET2t0YTEUMBIGA1UECwwLU1NPUHJvdmlkZXIxFTATBgNVBAMMDGRldi04Mzg1OTk1NTEc\nMBoGCSqGSIb3DQEJARYNaW5mb0Bva3RhLmNvbTCCASIwDQYJKoZIhvcNAQEBBQADggEPADCCAQoC\nggEBAOmj276L3kHm57hNGYTocT6NS4mffPbcvsA2UuKIWfmpV8HLTcmS+NahLtuN841OnRnTn+2p\nfjlwa1mwJhCODbF3dcVYOkGTPUC4y2nvf1Xas6M7+0O2WIfrzdX/OOUs/ROMnB/O/MpBwMR2SQh6\nQ3V+9v8g3K9yfMvcifDbl6g9fTliDzqV7I9xF5eJykl+iCAKNaQgp3cO6TaIa5u2ZKtRAdzwnuJC\nBXMyzaoNs/vfnwzuFtzWP1PSS1Roan+8AMwkYA6BCr1YRIqZ0GSkr/qexFCTZdq0UnSN78fY6CCM\nRFw5wU0WM9nEpbWzkBBWsYHeTLo5JqR/mZukfjlPDlcCAwEAATANBgkqhkiG9w0BAQsFAAOCAQEA\nlUhwzCSnuqt4wlHxJONN4kxUBG8bPnjHxob6jBKK+onFDuSVWZ+7LZw67blz6xdxvlOLaQLi1fK2\nFifehbc7KbRLckcgNgg7Y8qfUKdP0/nS0JlyAvlnICQqaHTHwhIzQqTHtTZeeIJHtpWOX/OPRI0S\nbkygh2qjF8bYn3sX8bGNUQL8iiMxFnvwGrXaErPqlRqFJbWQDBXD+nYDIBw7WN3Jyb0Ydin2zrlh\ngp3Qooi0TnAir3ncw/UF/+sivCgd+6nX7HkbZtipkMbg7ZByyD9xrOQG2JXrP6PyzGCPwnGMt9pL\niiVMepeLNqKZ3UvhrR1uRN0KWu7lduIRhxldLA==</ds:X509Certificate>\n </ds:X509Data>\n </ds:KeyInfo>\n </md:KeyDescriptor>\n <md:NameIDFormat>urn:oasis:names:tc:SAML:1.1:nameid-format:unspecified</md:NameIDFormat>\n <md:NameIDFormat>urn:oasis:names:tc:SAML:1.1:nameid-format:emailAddress</md:NameIDFormat>\n <md:SingleSignOnService Binding=\"urn:oasis:names:tc:SAML:2.0:bindings:HTTP-POST\" Location=\"https://dev-83859955.okta.com/app/dev-83859955_firezonesaml_1/exk6ff6p62kFjUR3X5d7/sso/saml\"/>\n <md:SingleSignOnService Binding=\"urn:oasis:names:tc:SAML:2.0:bindings:HTTP-Redirect\" Location=\"https://dev-83859955.okta.com/app/dev-83859955_firezonesaml_1/exk6ff6p62kFjUR3X5d7/sso/saml\"/>\n </md:IDPSSODescriptor>\n</md:EntityDescriptor>\n",
|
||||
"sign_metadata": false,
|
||||
"sign_requests": false,
|
||||
"signed_assertion_in_resp": false,
|
||||
"signed_envelopes_in_resp": false
|
||||
}
|
||||
],
|
||||
"updated_at": "2023-03-29T15:11:47.879874Z",
|
||||
"vpn_session_duration": 100
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
@@ -1,423 +0,0 @@
|
||||
---
|
||||
title: Devices
|
||||
group: Devices
|
||||
---
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
This endpoint allows an administrator to manage Devices.
|
||||
|
||||
## API Documentation
|
||||
### GET /v0/devices
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
#### Example
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
$ curl -i \
|
||||
-X GET "https://{firezone_host}/v0/devices" \
|
||||
-H 'Content-Type: application/json' \
|
||||
-H 'Authorization: Bearer {api_token}' \
|
||||
|
||||
HTTP/1.1 200
|
||||
Content-Type: application/json; charset=utf-8
|
||||
|
||||
{
|
||||
"data": [
|
||||
{
|
||||
"allowed_ips": [
|
||||
"0.0.0.0/0",
|
||||
"::/0"
|
||||
],
|
||||
"description": "factory description",
|
||||
"dns": [
|
||||
"1.1.1.1",
|
||||
"1.0.0.1"
|
||||
],
|
||||
"endpoint": "localhost:51820",
|
||||
"id": "61d5930b-2b35-44b3-87a9-904e81806728",
|
||||
"inserted_at": "2023-03-29T15:11:47.450107Z",
|
||||
"ipv4": "100.72.98.240",
|
||||
"ipv6": "fd00::39:bf15",
|
||||
"latest_handshake": null,
|
||||
"mtu": 1280,
|
||||
"name": "factory 4421",
|
||||
"persistent_keepalive": 25,
|
||||
"preshared_key": "32vztut9u6QJG2spTUMnvcb+twugGlT1ikM6AyiPDv8=",
|
||||
"public_key": "cGEIZje2ITjFDn96F3bItc5BCl8G1r4SWHH/6QUF4ek=",
|
||||
"remote_ip": null,
|
||||
"rx_bytes": null,
|
||||
"server_public_key": "is+0ov0/SZ9I+qyDD+adVoH9LreWHa85QQgpt6RUtA4=",
|
||||
"tx_bytes": null,
|
||||
"updated_at": "2023-03-29T15:11:47.450107Z",
|
||||
"use_default_allowed_ips": true,
|
||||
"use_default_dns": true,
|
||||
"use_default_endpoint": true,
|
||||
"use_default_mtu": true,
|
||||
"use_default_persistent_keepalive": true,
|
||||
"user_id": "56062619-2fe2-49de-898c-492d8da794c7"
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"allowed_ips": [
|
||||
"0.0.0.0/0",
|
||||
"::/0"
|
||||
],
|
||||
"description": "factory description",
|
||||
"dns": [
|
||||
"1.1.1.1",
|
||||
"1.0.0.1"
|
||||
],
|
||||
"endpoint": "localhost:51820",
|
||||
"id": "05db5d62-218e-4139-92f5-0510903ce4f8",
|
||||
"inserted_at": "2023-03-29T15:11:47.455712Z",
|
||||
"ipv4": "100.111.252.39",
|
||||
"ipv6": "fd00::2:456a",
|
||||
"latest_handshake": null,
|
||||
"mtu": 1280,
|
||||
"name": "factory 5411",
|
||||
"persistent_keepalive": 25,
|
||||
"preshared_key": "78O12m5lG+je3eAqlgJ9pd6d/+VeLjsswsljJFV0jU0=",
|
||||
"public_key": "ADOmUjeMl08RgKNhpRaaaHV3YmI9GOVh81zLVLOPk84=",
|
||||
"remote_ip": null,
|
||||
"rx_bytes": null,
|
||||
"server_public_key": "is+0ov0/SZ9I+qyDD+adVoH9LreWHa85QQgpt6RUtA4=",
|
||||
"tx_bytes": null,
|
||||
"updated_at": "2023-03-29T15:11:47.455712Z",
|
||||
"use_default_allowed_ips": true,
|
||||
"use_default_dns": true,
|
||||
"use_default_endpoint": true,
|
||||
"use_default_mtu": true,
|
||||
"use_default_persistent_keepalive": true,
|
||||
"user_id": "9d3e2da3-bce1-4a03-95cc-d8d0a9797a17"
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"allowed_ips": [
|
||||
"0.0.0.0/0",
|
||||
"::/0"
|
||||
],
|
||||
"description": "factory description",
|
||||
"dns": [
|
||||
"1.1.1.1",
|
||||
"1.0.0.1"
|
||||
],
|
||||
"endpoint": "localhost:51820",
|
||||
"id": "c865c545-36bd-473e-9c20-9b76766582b2",
|
||||
"inserted_at": "2023-03-29T15:11:47.461266Z",
|
||||
"ipv4": "100.116.252.229",
|
||||
"ipv6": "fd00::7:f039",
|
||||
"latest_handshake": null,
|
||||
"mtu": 1280,
|
||||
"name": "factory 5766",
|
||||
"persistent_keepalive": 25,
|
||||
"preshared_key": "Dlefj06JAOOCtKxoSlLmvmNXq2zql30FvwDFlEpEISQ=",
|
||||
"public_key": "hH9ifN5kI1RtnG54eUXGLEL7Pue9qgGvJ3Gvef7irzU=",
|
||||
"remote_ip": null,
|
||||
"rx_bytes": null,
|
||||
"server_public_key": "is+0ov0/SZ9I+qyDD+adVoH9LreWHa85QQgpt6RUtA4=",
|
||||
"tx_bytes": null,
|
||||
"updated_at": "2023-03-29T15:11:47.461266Z",
|
||||
"use_default_allowed_ips": true,
|
||||
"use_default_dns": true,
|
||||
"use_default_endpoint": true,
|
||||
"use_default_mtu": true,
|
||||
"use_default_persistent_keepalive": true,
|
||||
"user_id": "47a8eda4-433a-4ce3-a119-720b5d62ddac"
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"allowed_ips": [
|
||||
"0.0.0.0/0",
|
||||
"::/0"
|
||||
],
|
||||
"description": "factory description",
|
||||
"dns": [
|
||||
"1.1.1.1",
|
||||
"1.0.0.1"
|
||||
],
|
||||
"endpoint": "localhost:51820",
|
||||
"id": "93da8405-217e-40b3-a91b-45d8cd28c2d4",
|
||||
"inserted_at": "2023-03-29T15:11:47.467794Z",
|
||||
"ipv4": "100.70.183.42",
|
||||
"ipv6": "fd00::9:a393",
|
||||
"latest_handshake": null,
|
||||
"mtu": 1280,
|
||||
"name": "factory 1417",
|
||||
"persistent_keepalive": 25,
|
||||
"preshared_key": "3ipinU20+iTgqCZxSskRPRTBargqtoG73seKz8wZqiE=",
|
||||
"public_key": "gzAOiYTnq+rFRBDUbRuJhKXCbe+ULB9xjpCy9l0mBCA=",
|
||||
"remote_ip": null,
|
||||
"rx_bytes": null,
|
||||
"server_public_key": "is+0ov0/SZ9I+qyDD+adVoH9LreWHa85QQgpt6RUtA4=",
|
||||
"tx_bytes": null,
|
||||
"updated_at": "2023-03-29T15:11:47.467794Z",
|
||||
"use_default_allowed_ips": true,
|
||||
"use_default_dns": true,
|
||||
"use_default_endpoint": true,
|
||||
"use_default_mtu": true,
|
||||
"use_default_persistent_keepalive": true,
|
||||
"user_id": "d8c001ca-ee0f-457f-80a6-802592a7d4ca"
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"allowed_ips": [
|
||||
"0.0.0.0/0",
|
||||
"::/0"
|
||||
],
|
||||
"description": "factory description",
|
||||
"dns": [
|
||||
"1.1.1.1",
|
||||
"1.0.0.1"
|
||||
],
|
||||
"endpoint": "localhost:51820",
|
||||
"id": "16b319c1-4d8a-478a-88d2-f17056bf1b66",
|
||||
"inserted_at": "2023-03-29T15:11:47.473062Z",
|
||||
"ipv4": "100.101.38.171",
|
||||
"ipv6": "fd00::39:35af",
|
||||
"latest_handshake": null,
|
||||
"mtu": 1280,
|
||||
"name": "factory 4485",
|
||||
"persistent_keepalive": 25,
|
||||
"preshared_key": "WzNqj8NEQBvYCYjWv4qhuL8sT3n0LVIH52x1xx5U6EE=",
|
||||
"public_key": "eD1iqgs712xDZsplZHd7LrNs+WXYshMH99WFkJ0So8o=",
|
||||
"remote_ip": null,
|
||||
"rx_bytes": null,
|
||||
"server_public_key": "is+0ov0/SZ9I+qyDD+adVoH9LreWHa85QQgpt6RUtA4=",
|
||||
"tx_bytes": null,
|
||||
"updated_at": "2023-03-29T15:11:47.473062Z",
|
||||
"use_default_allowed_ips": true,
|
||||
"use_default_dns": true,
|
||||
"use_default_endpoint": true,
|
||||
"use_default_mtu": true,
|
||||
"use_default_persistent_keepalive": true,
|
||||
"user_id": "605c4532-d516-4b59-a7df-b0479d493cce"
|
||||
}
|
||||
]
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
### POST /v0/devices
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
#### Example
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
$ curl -i \
|
||||
-X POST "https://{firezone_host}/v0/devices" \
|
||||
-H 'Content-Type: application/json' \
|
||||
-H 'Authorization: Bearer {api_token}' \
|
||||
--data-binary @- << EOF
|
||||
{
|
||||
"device": {
|
||||
"allowed_ips": [
|
||||
"0.0.0.0/0",
|
||||
"::/0",
|
||||
"1.1.1.1"
|
||||
],
|
||||
"description": "create-description",
|
||||
"dns": [
|
||||
"9.9.9.8"
|
||||
],
|
||||
"endpoint": "9.9.9.9",
|
||||
"ipv4": "100.64.0.2",
|
||||
"ipv6": "fd00::2",
|
||||
"mtu": 999,
|
||||
"name": "create-name",
|
||||
"persistent_keepalive": 9,
|
||||
"preshared_key": "CHqFuS+iL3FTog5F4Ceumqlk0CU4Cl/dyUP/9F9NDnI=",
|
||||
"public_key": "CHqFuS+iL3FTog5F4Ceumqlk0CU4Cl/dyUP/9F9NDnI=",
|
||||
"use_default_allowed_ips": false,
|
||||
"use_default_dns": false,
|
||||
"use_default_endpoint": false,
|
||||
"use_default_mtu": false,
|
||||
"use_default_persistent_keepalive": false,
|
||||
"user_id": "95138a8e-c89f-41b4-b62c-a5b8c23a0b8c"
|
||||
}
|
||||
}'
|
||||
EOF
|
||||
|
||||
HTTP/1.1 201
|
||||
Content-Type: application/json; charset=utf-8
|
||||
Location: /v0/devices/3aefe1b8-d98b-4725-bed3-cad021a13480
|
||||
|
||||
{
|
||||
"data": {
|
||||
"allowed_ips": [
|
||||
"0.0.0.0/0",
|
||||
"::/0",
|
||||
"1.1.1.1"
|
||||
],
|
||||
"description": "create-description",
|
||||
"dns": [
|
||||
"9.9.9.8"
|
||||
],
|
||||
"endpoint": "9.9.9.9",
|
||||
"id": "3aefe1b8-d98b-4725-bed3-cad021a13480",
|
||||
"inserted_at": "2023-03-29T15:11:47.190722Z",
|
||||
"ipv4": "100.64.0.2",
|
||||
"ipv6": "fd00::2",
|
||||
"latest_handshake": null,
|
||||
"mtu": 999,
|
||||
"name": "create-name",
|
||||
"persistent_keepalive": 9,
|
||||
"preshared_key": "CHqFuS+iL3FTog5F4Ceumqlk0CU4Cl/dyUP/9F9NDnI=",
|
||||
"public_key": "CHqFuS+iL3FTog5F4Ceumqlk0CU4Cl/dyUP/9F9NDnI=",
|
||||
"remote_ip": null,
|
||||
"rx_bytes": null,
|
||||
"server_public_key": "is+0ov0/SZ9I+qyDD+adVoH9LreWHa85QQgpt6RUtA4=",
|
||||
"tx_bytes": null,
|
||||
"updated_at": "2023-03-29T15:11:47.190722Z",
|
||||
"use_default_allowed_ips": false,
|
||||
"use_default_dns": false,
|
||||
"use_default_endpoint": false,
|
||||
"use_default_mtu": false,
|
||||
"use_default_persistent_keepalive": false,
|
||||
"user_id": "95138a8e-c89f-41b4-b62c-a5b8c23a0b8c"
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
### GET /v0/devices/{id}
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
#### Example
|
||||
**URI Parameters:**
|
||||
|
||||
- `id`: `f85310b7-87b5-4c89-b391-d985f7789007`
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
$ curl -i \
|
||||
-X GET "https://{firezone_host}/v0/devices/{id}" \
|
||||
-H 'Content-Type: application/json' \
|
||||
-H 'Authorization: Bearer {api_token}' \
|
||||
|
||||
HTTP/1.1 200
|
||||
Content-Type: application/json; charset=utf-8
|
||||
|
||||
{
|
||||
"data": {
|
||||
"allowed_ips": [
|
||||
"0.0.0.0/0",
|
||||
"::/0"
|
||||
],
|
||||
"description": "factory description",
|
||||
"dns": [
|
||||
"1.1.1.1",
|
||||
"1.0.0.1"
|
||||
],
|
||||
"endpoint": "localhost:51820",
|
||||
"id": "f85310b7-87b5-4c89-b391-d985f7789007",
|
||||
"inserted_at": "2023-03-29T15:11:47.299345Z",
|
||||
"ipv4": "100.99.173.193",
|
||||
"ipv6": "fd00::17:d1a9",
|
||||
"latest_handshake": null,
|
||||
"mtu": 1280,
|
||||
"name": "factory 713",
|
||||
"persistent_keepalive": 25,
|
||||
"preshared_key": "qrcrAnUh7ryP69SwfseKdBNElOSjOC9/Wv7Z+EBxs50=",
|
||||
"public_key": "mLN9py6whsGt+Lg9jP4lX+Cqqlf02plODqWg2UqOmPI=",
|
||||
"remote_ip": null,
|
||||
"rx_bytes": null,
|
||||
"server_public_key": "is+0ov0/SZ9I+qyDD+adVoH9LreWHa85QQgpt6RUtA4=",
|
||||
"tx_bytes": null,
|
||||
"updated_at": "2023-03-29T15:11:47.299345Z",
|
||||
"use_default_allowed_ips": true,
|
||||
"use_default_dns": true,
|
||||
"use_default_endpoint": true,
|
||||
"use_default_mtu": true,
|
||||
"use_default_persistent_keepalive": true,
|
||||
"user_id": "5f5b582d-9153-46ac-99e5-37a6bc93ce13"
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
### PATCH /v0/devices/{id}
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
#### Example
|
||||
**URI Parameters:**
|
||||
|
||||
- `id`: `01272ce2-df59-4816-9d82-44830427d757`
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
$ curl -i \
|
||||
-X PUT "https://{firezone_host}/v0/devices/{id}" \
|
||||
-H 'Content-Type: application/json' \
|
||||
-H 'Authorization: Bearer {api_token}' \
|
||||
--data-binary @- << EOF
|
||||
{
|
||||
"device": {
|
||||
"allowed_ips": [
|
||||
"0.0.0.0/0",
|
||||
"::/0",
|
||||
"1.1.1.1"
|
||||
],
|
||||
"description": "create-description",
|
||||
"dns": [
|
||||
"9.9.9.8"
|
||||
],
|
||||
"endpoint": "9.9.9.9",
|
||||
"ipv4": "100.64.0.2",
|
||||
"ipv6": "fd00::2",
|
||||
"mtu": 999,
|
||||
"name": "create-name",
|
||||
"persistent_keepalive": 9,
|
||||
"preshared_key": "CHqFuS+iL3FTog5F4Ceumqlk0CU4Cl/dyUP/9F9NDnI=",
|
||||
"public_key": "CHqFuS+iL3FTog5F4Ceumqlk0CU4Cl/dyUP/9F9NDnI=",
|
||||
"use_default_allowed_ips": false,
|
||||
"use_default_dns": false,
|
||||
"use_default_endpoint": false,
|
||||
"use_default_mtu": false,
|
||||
"use_default_persistent_keepalive": false
|
||||
}
|
||||
}'
|
||||
EOF
|
||||
|
||||
HTTP/1.1 200
|
||||
Content-Type: application/json; charset=utf-8
|
||||
|
||||
{
|
||||
"data": {
|
||||
"allowed_ips": [
|
||||
"0.0.0.0/0",
|
||||
"::/0",
|
||||
"1.1.1.1"
|
||||
],
|
||||
"description": "create-description",
|
||||
"dns": [
|
||||
"9.9.9.8"
|
||||
],
|
||||
"endpoint": "9.9.9.9",
|
||||
"id": "01272ce2-df59-4816-9d82-44830427d757",
|
||||
"inserted_at": "2023-03-29T15:11:47.264313Z",
|
||||
"ipv4": "100.64.0.2",
|
||||
"ipv6": "fd00::2",
|
||||
"latest_handshake": null,
|
||||
"mtu": 999,
|
||||
"name": "create-name",
|
||||
"persistent_keepalive": 9,
|
||||
"preshared_key": "CHqFuS+iL3FTog5F4Ceumqlk0CU4Cl/dyUP/9F9NDnI=",
|
||||
"public_key": "CHqFuS+iL3FTog5F4Ceumqlk0CU4Cl/dyUP/9F9NDnI=",
|
||||
"remote_ip": null,
|
||||
"rx_bytes": null,
|
||||
"server_public_key": "is+0ov0/SZ9I+qyDD+adVoH9LreWHa85QQgpt6RUtA4=",
|
||||
"tx_bytes": null,
|
||||
"updated_at": "2023-03-29T15:11:47.276849Z",
|
||||
"use_default_allowed_ips": false,
|
||||
"use_default_dns": false,
|
||||
"use_default_endpoint": false,
|
||||
"use_default_mtu": false,
|
||||
"use_default_persistent_keepalive": false,
|
||||
"user_id": "3f7c9d0f-fa89-4619-9237-f0215db34e58"
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
### DELETE /v0/devices/{id}
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
#### Example
|
||||
**URI Parameters:**
|
||||
|
||||
- `id`: `29f86ac9-82e8-4691-aa44-ea396d3af476`
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
$ curl -i \
|
||||
-X DELETE "https://{firezone_host}/v0/devices/{id}" \
|
||||
-H 'Content-Type: application/json' \
|
||||
-H 'Authorization: Bearer {api_token}' \
|
||||
|
||||
HTTP/1.1 204
|
||||
```
|
||||
@@ -1,203 +0,0 @@
|
||||
---
|
||||
title: Rules
|
||||
group: Rules
|
||||
---
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
This endpoint allows an adminisrator to manage Rules.
|
||||
|
||||
## API Documentation
|
||||
### GET /v0/rules
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
#### Example
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
$ curl -i \
|
||||
-X GET "https://{firezone_host}/v0/rules" \
|
||||
-H 'Content-Type: application/json' \
|
||||
-H 'Authorization: Bearer {api_token}' \
|
||||
|
||||
HTTP/1.1 200
|
||||
Content-Type: application/json; charset=utf-8
|
||||
|
||||
{
|
||||
"data": [
|
||||
{
|
||||
"action": "drop",
|
||||
"destination": "10.3.2.1",
|
||||
"id": "2a136a17-4d29-4d8b-a6d4-f35ee3051105",
|
||||
"inserted_at": "2023-03-29T15:11:47.482818Z",
|
||||
"port_range": null,
|
||||
"port_type": null,
|
||||
"updated_at": "2023-03-29T15:11:47.482818Z",
|
||||
"user_id": null
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"action": "drop",
|
||||
"destination": "10.3.2.2",
|
||||
"id": "7a4961bf-6b2b-4217-b87b-ffd1deb448ac",
|
||||
"inserted_at": "2023-03-29T15:11:47.483506Z",
|
||||
"port_range": null,
|
||||
"port_type": null,
|
||||
"updated_at": "2023-03-29T15:11:47.483506Z",
|
||||
"user_id": null
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"action": "drop",
|
||||
"destination": "10.3.2.3",
|
||||
"id": "6dffbc74-ec58-43ca-8700-d0c572baa198",
|
||||
"inserted_at": "2023-03-29T15:11:47.484107Z",
|
||||
"port_range": null,
|
||||
"port_type": null,
|
||||
"updated_at": "2023-03-29T15:11:47.484107Z",
|
||||
"user_id": null
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"action": "drop",
|
||||
"destination": "10.3.2.4",
|
||||
"id": "9bba129d-cdad-4efe-8296-b78ba50f3ef4",
|
||||
"inserted_at": "2023-03-29T15:11:47.484759Z",
|
||||
"port_range": null,
|
||||
"port_type": null,
|
||||
"updated_at": "2023-03-29T15:11:47.484759Z",
|
||||
"user_id": null
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"action": "drop",
|
||||
"destination": "10.3.2.5",
|
||||
"id": "df142fde-922c-4a6d-a8e4-0b145a875624",
|
||||
"inserted_at": "2023-03-29T15:11:47.485540Z",
|
||||
"port_range": null,
|
||||
"port_type": null,
|
||||
"updated_at": "2023-03-29T15:11:47.485540Z",
|
||||
"user_id": null
|
||||
}
|
||||
]
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
### POST /v0/rules
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
#### Example
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
$ curl -i \
|
||||
-X POST "https://{firezone_host}/v0/rules" \
|
||||
-H 'Content-Type: application/json' \
|
||||
-H 'Authorization: Bearer {api_token}' \
|
||||
--data-binary @- << EOF
|
||||
{
|
||||
"rule": {
|
||||
"action": "accept",
|
||||
"destination": "1.1.1.1/24",
|
||||
"port_range": "1 - 2",
|
||||
"port_type": "udp",
|
||||
"user_id": "def4dacc-6367-4320-a0fb-4675b9b571cf"
|
||||
}
|
||||
}'
|
||||
EOF
|
||||
|
||||
HTTP/1.1 201
|
||||
Content-Type: application/json; charset=utf-8
|
||||
Location: /v0/rules/c52efbe6-5ed0-4514-97df-93f6013dd52b
|
||||
|
||||
{
|
||||
"data": {
|
||||
"action": "accept",
|
||||
"destination": "1.1.1.1/24",
|
||||
"id": "c52efbe6-5ed0-4514-97df-93f6013dd52b",
|
||||
"inserted_at": "2023-03-29T15:11:47.185000Z",
|
||||
"port_range": "1 - 2",
|
||||
"port_type": "udp",
|
||||
"updated_at": "2023-03-29T15:11:47.185000Z",
|
||||
"user_id": "def4dacc-6367-4320-a0fb-4675b9b571cf"
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
### GET /v0/rules/{id}
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
#### Example
|
||||
**URI Parameters:**
|
||||
|
||||
- `id`: `dd39b339-2ac4-4c83-96e5-9b29516dd85e`
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
$ curl -i \
|
||||
-X GET "https://{firezone_host}/v0/rules/{id}" \
|
||||
-H 'Content-Type: application/json' \
|
||||
-H 'Authorization: Bearer {api_token}' \
|
||||
|
||||
HTTP/1.1 200
|
||||
Content-Type: application/json; charset=utf-8
|
||||
|
||||
{
|
||||
"data": {
|
||||
"action": "drop",
|
||||
"destination": "10.10.10.0/24",
|
||||
"id": "dd39b339-2ac4-4c83-96e5-9b29516dd85e",
|
||||
"inserted_at": "2023-03-29T15:11:47.447659Z",
|
||||
"port_range": null,
|
||||
"port_type": null,
|
||||
"updated_at": "2023-03-29T15:11:47.447659Z",
|
||||
"user_id": null
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
### PATCH /v0/rules/{id}
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
#### Example
|
||||
**URI Parameters:**
|
||||
|
||||
- `id`: `720fdab6-32af-4487-bce5-e72fa76be829`
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
$ curl -i \
|
||||
-X PUT "https://{firezone_host}/v0/rules/{id}" \
|
||||
-H 'Content-Type: application/json' \
|
||||
-H 'Authorization: Bearer {api_token}' \
|
||||
--data-binary @- << EOF
|
||||
{
|
||||
"rule": {
|
||||
"action": "accept",
|
||||
"destination": "1.1.1.1/24",
|
||||
"port_range": "1 - 2",
|
||||
"port_type": "udp"
|
||||
}
|
||||
}'
|
||||
EOF
|
||||
|
||||
HTTP/1.1 200
|
||||
Content-Type: application/json; charset=utf-8
|
||||
|
||||
{
|
||||
"data": {
|
||||
"action": "accept",
|
||||
"destination": "1.1.1.1/24",
|
||||
"id": "720fdab6-32af-4487-bce5-e72fa76be829",
|
||||
"inserted_at": "2023-03-29T15:11:47.243306Z",
|
||||
"port_range": "1 - 2",
|
||||
"port_type": "udp",
|
||||
"updated_at": "2023-03-29T15:11:47.251589Z",
|
||||
"user_id": null
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
### DELETE /v0/rules/{id}
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
#### Example
|
||||
**URI Parameters:**
|
||||
|
||||
- `id`: `f5f10a6e-cfdd-47ea-ae23-264195b3503c`
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
$ curl -i \
|
||||
-X DELETE "https://{firezone_host}/v0/rules/{id}" \
|
||||
-H 'Content-Type: application/json' \
|
||||
-H 'Authorization: Bearer {api_token}' \
|
||||
|
||||
HTTP/1.1 204
|
||||
```
|
||||
@@ -1,363 +0,0 @@
|
||||
---
|
||||
title: Users
|
||||
sidebar_position: 2
|
||||
toc_max_heading_level: 4
|
||||
---
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
This endpoint allows an administrator to manage Users.
|
||||
|
||||
## Auto-Create Users from OpenID or SAML providers
|
||||
|
||||
You can set Configuration option `auto_create_users` to `true` to automatically create users
|
||||
from OpenID or SAML providers. Use it with care as anyone with access to the provider will be
|
||||
able to log-in to Firezone.
|
||||
|
||||
If `auto_create_users` is `false`, then you need to provision users with `password` attribute,
|
||||
otherwise they will have no means to log in.
|
||||
|
||||
## Disabling users
|
||||
|
||||
Even though API returns `disabled_at` attribute, currently, it's not possible to disable users via API,
|
||||
since this field is only for internal use by automatic user disabling mechanism on OIDC/SAML errors.
|
||||
|
||||
## API Documentation
|
||||
### List all Users [`GET /v0/users`]
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
#### Example
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
$ curl -i \
|
||||
-X GET "https://{firezone_host}/v0/users" \
|
||||
-H 'Content-Type: application/json' \
|
||||
-H 'Authorization: Bearer {api_token}' \
|
||||
|
||||
HTTP/1.1 200
|
||||
Content-Type: application/json; charset=utf-8
|
||||
|
||||
{
|
||||
"data": [
|
||||
{
|
||||
"disabled_at": null,
|
||||
"email": "test-5094@test",
|
||||
"id": "4963a5f0-dbb5-424a-8859-8032209eeaef",
|
||||
"inserted_at": "2023-03-29T15:11:47.363517Z",
|
||||
"last_signed_in_at": null,
|
||||
"last_signed_in_method": null,
|
||||
"role": "admin",
|
||||
"updated_at": "2023-03-29T15:11:47.363517Z"
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"disabled_at": null,
|
||||
"email": "test-5634@test",
|
||||
"id": "e904d9ae-c358-4ab4-9bfd-44b4bf942a15",
|
||||
"inserted_at": "2023-03-29T15:11:47.364938Z",
|
||||
"last_signed_in_at": null,
|
||||
"last_signed_in_method": null,
|
||||
"role": "admin",
|
||||
"updated_at": "2023-03-29T15:11:47.364938Z"
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"disabled_at": null,
|
||||
"email": "test-5666@test",
|
||||
"id": "e7decf88-4abb-45df-9dd0-35e3587dfb59",
|
||||
"inserted_at": "2023-03-29T15:11:47.366068Z",
|
||||
"last_signed_in_at": null,
|
||||
"last_signed_in_method": null,
|
||||
"role": "admin",
|
||||
"updated_at": "2023-03-29T15:11:47.366068Z"
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"disabled_at": null,
|
||||
"email": "test-5190@test",
|
||||
"id": "457aeee0-13aa-44b3-9057-181cc206edcb",
|
||||
"inserted_at": "2023-03-29T15:11:47.367568Z",
|
||||
"last_signed_in_at": null,
|
||||
"last_signed_in_method": null,
|
||||
"role": "admin",
|
||||
"updated_at": "2023-03-29T15:11:47.367568Z"
|
||||
}
|
||||
]
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
### Create a User [`POST /v0/users`]
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
Create a new User.
|
||||
|
||||
This endpoint is useful in two cases:
|
||||
|
||||
1. When [Local Authentication](/docs/authenticate/local-auth/) is enabled (discouraged in
|
||||
production deployments), it allows an administrator to provision users with their passwords;
|
||||
2. When `auto_create_users` in the associated OpenID or SAML configuration is disabled,
|
||||
it allows an administrator to provision users with their emails beforehand, effectively
|
||||
whitelisting specific users for authentication.
|
||||
|
||||
If `auto_create_users` is `true` in the associated OpenID or SAML configuration, there is no need
|
||||
to provision users; they will be created automatically when they log in for the first time using
|
||||
the associated OpenID or SAML provider.
|
||||
|
||||
#### User Attributes
|
||||
|
||||
| Attribute | Type | Required | Description |
|
||||
| --------- | ---- | -------- | ----------- |
|
||||
| `role` | `admin` or `unprivileged` (default) | No | User role. |
|
||||
| `email` | `string` | Yes | Email which will be used to identify the user. |
|
||||
| `password` | `string` | No | A password that can be used for login-password authentication. |
|
||||
| `password_confirmation` | `string` | -> | Is required when the `password` is set. |
|
||||
|
||||
#### Example
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
$ curl -i \
|
||||
-X POST "https://{firezone_host}/v0/users" \
|
||||
-H 'Content-Type: application/json' \
|
||||
-H 'Authorization: Bearer {api_token}' \
|
||||
--data-binary @- << EOF
|
||||
{
|
||||
"user": {
|
||||
"email": "new-user@test",
|
||||
"password": "test1234test",
|
||||
"password_confirmation": "test1234test",
|
||||
"role": "unprivileged"
|
||||
}
|
||||
}'
|
||||
EOF
|
||||
|
||||
HTTP/1.1 201
|
||||
Content-Type: application/json; charset=utf-8
|
||||
Location: /v0/users/2b7128fb-4a30-472d-9f45-d2a5063ba5db
|
||||
|
||||
{
|
||||
"data": {
|
||||
"disabled_at": null,
|
||||
"email": "new-user@test",
|
||||
"id": "2b7128fb-4a30-472d-9f45-d2a5063ba5db",
|
||||
"inserted_at": "2023-03-29T15:11:47.178709Z",
|
||||
"last_signed_in_at": null,
|
||||
"last_signed_in_method": null,
|
||||
"role": "unprivileged",
|
||||
"updated_at": "2023-03-29T15:11:47.178709Z"
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
#### Provision an unprivileged OpenID User
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
$ curl -i \
|
||||
-X POST "https://{firezone_host}/v0/users" \
|
||||
-H 'Content-Type: application/json' \
|
||||
-H 'Authorization: Bearer {api_token}' \
|
||||
--data-binary @- << EOF
|
||||
{
|
||||
"user": {
|
||||
"email": "new-user@test",
|
||||
"role": "unprivileged"
|
||||
}
|
||||
}'
|
||||
EOF
|
||||
|
||||
HTTP/1.1 201
|
||||
Content-Type: application/json; charset=utf-8
|
||||
Location: /v0/users/e4796108-f4d8-4a11-9860-d07b92b08d93
|
||||
|
||||
{
|
||||
"data": {
|
||||
"disabled_at": null,
|
||||
"email": "new-user@test",
|
||||
"id": "e4796108-f4d8-4a11-9860-d07b92b08d93",
|
||||
"inserted_at": "2023-03-29T15:11:47.192265Z",
|
||||
"last_signed_in_at": null,
|
||||
"last_signed_in_method": null,
|
||||
"role": "unprivileged",
|
||||
"updated_at": "2023-03-29T15:11:47.192265Z"
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
#### Provision an admin OpenID User
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
$ curl -i \
|
||||
-X POST "https://{firezone_host}/v0/users" \
|
||||
-H 'Content-Type: application/json' \
|
||||
-H 'Authorization: Bearer {api_token}' \
|
||||
--data-binary @- << EOF
|
||||
{
|
||||
"user": {
|
||||
"email": "new-user@test",
|
||||
"role": "admin"
|
||||
}
|
||||
}'
|
||||
EOF
|
||||
|
||||
HTTP/1.1 201
|
||||
Content-Type: application/json; charset=utf-8
|
||||
Location: /v0/users/479ed1cb-1657-4c82-bc32-2200f6cc82e9
|
||||
|
||||
{
|
||||
"data": {
|
||||
"disabled_at": null,
|
||||
"email": "new-user@test",
|
||||
"id": "479ed1cb-1657-4c82-bc32-2200f6cc82e9",
|
||||
"inserted_at": "2023-03-29T15:11:47.460359Z",
|
||||
"last_signed_in_at": null,
|
||||
"last_signed_in_method": null,
|
||||
"role": "admin",
|
||||
"updated_at": "2023-03-29T15:11:47.460359Z"
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
#### Error due to invalid parameters
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
$ curl -i \
|
||||
-X POST "https://{firezone_host}/v0/users" \
|
||||
-H 'Content-Type: application/json' \
|
||||
-H 'Authorization: Bearer {api_token}' \
|
||||
--data-binary @- << EOF
|
||||
{
|
||||
"user": {
|
||||
"email": "test@test.com",
|
||||
"password": "test1234"
|
||||
}
|
||||
}'
|
||||
EOF
|
||||
|
||||
HTTP/1.1 422
|
||||
Content-Type: application/json; charset=utf-8
|
||||
|
||||
{
|
||||
"errors": {
|
||||
"password": [
|
||||
"should be at least 12 character(s)"
|
||||
],
|
||||
"password_confirmation": [
|
||||
"can't be blank"
|
||||
]
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
### GET /v0/users/{id}
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
#### An email can be used instead of ID.
|
||||
**URI Parameters:**
|
||||
|
||||
- `id`: `test-905@test`
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
$ curl -i \
|
||||
-X GET "https://{firezone_host}/v0/users/{id}" \
|
||||
-H 'Content-Type: application/json' \
|
||||
-H 'Authorization: Bearer {api_token}' \
|
||||
|
||||
HTTP/1.1 200
|
||||
Content-Type: application/json; charset=utf-8
|
||||
|
||||
{
|
||||
"data": {
|
||||
"disabled_at": null,
|
||||
"email": "test-905@test",
|
||||
"id": "d43dae29-0687-456c-a3a4-a461eb744cf5",
|
||||
"inserted_at": "2023-03-29T15:11:47.340583Z",
|
||||
"last_signed_in_at": null,
|
||||
"last_signed_in_method": null,
|
||||
"role": "admin",
|
||||
"updated_at": "2023-03-29T15:11:47.340583Z"
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
### Update a User [`PATCH /v0/users/{id}`]
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
For details please see [Create a User](#create-a-user-post-v0users) section.
|
||||
|
||||
#### Update by email
|
||||
**URI Parameters:**
|
||||
|
||||
- `id`: `test-1960@test`
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
$ curl -i \
|
||||
-X PUT "https://{firezone_host}/v0/users/{id}" \
|
||||
-H 'Content-Type: application/json' \
|
||||
-H 'Authorization: Bearer {api_token}' \
|
||||
--data-binary @- << EOF
|
||||
{
|
||||
"user": {}
|
||||
}'
|
||||
EOF
|
||||
|
||||
HTTP/1.1 200
|
||||
Content-Type: application/json; charset=utf-8
|
||||
|
||||
{
|
||||
"data": {
|
||||
"disabled_at": null,
|
||||
"email": "test-1960@test",
|
||||
"id": "8830b359-2368-4f55-9879-1cb04ee0cbbf",
|
||||
"inserted_at": "2023-03-29T15:11:47.391921Z",
|
||||
"last_signed_in_at": null,
|
||||
"last_signed_in_method": null,
|
||||
"role": "unprivileged",
|
||||
"updated_at": "2023-03-29T15:11:47.391921Z"
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
#### Update by ID
|
||||
**URI Parameters:**
|
||||
|
||||
- `id`: `d542e1bc-25b2-453d-ae14-41f8f81605ee`
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
$ curl -i \
|
||||
-X PUT "https://{firezone_host}/v0/users/{id}" \
|
||||
-H 'Content-Type: application/json' \
|
||||
-H 'Authorization: Bearer {api_token}' \
|
||||
--data-binary @- << EOF
|
||||
{
|
||||
"user": {}
|
||||
}'
|
||||
EOF
|
||||
|
||||
HTTP/1.1 200
|
||||
Content-Type: application/json; charset=utf-8
|
||||
|
||||
{
|
||||
"data": {
|
||||
"disabled_at": null,
|
||||
"email": "test-1513@test",
|
||||
"id": "d542e1bc-25b2-453d-ae14-41f8f81605ee",
|
||||
"inserted_at": "2023-03-29T15:11:47.475440Z",
|
||||
"last_signed_in_at": null,
|
||||
"last_signed_in_method": null,
|
||||
"role": "unprivileged",
|
||||
"updated_at": "2023-03-29T15:11:47.475440Z"
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
### DELETE /v0/users/{id}
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
#### Example
|
||||
**URI Parameters:**
|
||||
|
||||
- `id`: `31156bf6-73de-4d9b-aa1e-2e419a45dd25`
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
$ curl -i \
|
||||
-X DELETE "https://{firezone_host}/v0/users/{id}" \
|
||||
-H 'Content-Type: application/json' \
|
||||
-H 'Authorization: Bearer {api_token}' \
|
||||
|
||||
HTTP/1.1 204
|
||||
Content-Type: application/json; charset=utf-8
|
||||
```
|
||||
#### An email can be used instead of ID.
|
||||
**URI Parameters:**
|
||||
|
||||
- `id`: `test-4996@test`
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
$ curl -i \
|
||||
-X DELETE "https://{firezone_host}/v0/users/{id}" \
|
||||
-H 'Content-Type: application/json' \
|
||||
-H 'Authorization: Bearer {api_token}' \
|
||||
|
||||
HTTP/1.1 204
|
||||
Content-Type: application/json; charset=utf-8
|
||||
```
|
||||
@@ -1,11 +0,0 @@
|
||||
---
|
||||
title: Reverse Proxy Templates
|
||||
sidebar_position: 8
|
||||
---
|
||||
|
||||
```mdx-code-block
|
||||
import DocCardList from '@theme/DocCardList';
|
||||
import {useCurrentSidebarCategory} from '@docusaurus/theme-common';
|
||||
|
||||
<DocCardList items={useCurrentSidebarCategory().items}/>
|
||||
```
|
||||
@@ -1,66 +0,0 @@
|
||||
---
|
||||
title: Apache
|
||||
sidebar_position: 1
|
||||
---
|
||||
|
||||
The following are example [apache](https://httpd.apache.org/) configurations
|
||||
with and without SSL termination.
|
||||
|
||||
These expect the apache to be running on the same host as Firezone and
|
||||
`default['firezone']['phoenix']['port']` to be `13000`.
|
||||
|
||||
## Without SSL termination
|
||||
|
||||
Since Firezone requires HTTPS for the web portal, please bear in mind a
|
||||
downstream proxy will need to terminate SSL connections in this scenario.
|
||||
|
||||
`<server-name>` needs to be replaced with your domain name.
|
||||
|
||||
This configuration needs to be placed in
|
||||
`/etc/sites-available/<server-name>.conf`
|
||||
|
||||
and activated with `a2ensite <server-name>`
|
||||
|
||||
```conf
|
||||
LoadModule rewrite_module /usr/lib/apache2/modules/mod_rewrite.so
|
||||
LoadModule proxy_module /usr/lib/apache2/modules/mod_proxy.so
|
||||
LoadModule proxy_http_module /usr/lib/apache2/modules/mod_proxy_http.so
|
||||
LoadModule proxy_wstunnel_module /usr/lib/apache2/modules/mod_proxy_wstunnel.so
|
||||
<VirtualHost *:80>
|
||||
ServerName <server-name>
|
||||
ProxyPassReverse "/" "http://127.0.0.1:13000/"
|
||||
ProxyPass "/" "http://127.0.0.1:13000/"
|
||||
RewriteEngine on
|
||||
RewriteCond %{HTTP:Upgrade} websocket [NC]
|
||||
RewriteCond %{HTTP:Connection} upgrade [NC]
|
||||
RewriteRule ^/?(.*) "ws://127.0.0.1:13000/$1" [P,L]
|
||||
</VirtualHost>
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
## With SSL termination
|
||||
|
||||
This configuration builds on the one above and uses Firezone's auto-generated
|
||||
self-signed certificates.
|
||||
|
||||
```conf
|
||||
LoadModule rewrite_module /usr/lib/apache2/modules/mod_rewrite.so
|
||||
LoadModule proxy_module /usr/lib/apache2/modules/mod_proxy.so
|
||||
LoadModule proxy_http_module /usr/lib/apache2/modules/mod_proxy_http.so
|
||||
LoadModule proxy_wstunnel_module /usr/lib/apache2/modules/mod_proxy_wstunnel.so
|
||||
LoadModule ssl_module /usr/lib/apache2/modules/mod_ssl.so
|
||||
LoadModule headers_module /usr/lib/apache2/modules/mod_headers.so
|
||||
Listen 443
|
||||
<VirtualHost *:443>
|
||||
ServerName <server-name>
|
||||
RequestHeader set X-Forwarded-Proto "https"
|
||||
ProxyPassReverse "/" "http://127.0.0.1:13000/"
|
||||
ProxyPass "/" "http://127.0.0.1:13000/"
|
||||
RewriteEngine on
|
||||
RewriteCond %{HTTP:Upgrade} websocket [NC]
|
||||
RewriteCond %{HTTP:Connection} upgrade [NC]
|
||||
RewriteRule ^/?(.*) "ws://127.0.0.1:13000/$1" [P,L]
|
||||
SSLEngine On
|
||||
SSLCertificateFile "/var/opt/firezone/ssl/ca/acme-test.firez.one.crt"
|
||||
SSLCertificateKeyFile "/var/opt/firezone/ssl/ca/acme-test.firez.one.key"
|
||||
</VirtualHost>
|
||||
```
|
||||
@@ -1,32 +0,0 @@
|
||||
---
|
||||
title: HAProxy
|
||||
sidebar_position: 3
|
||||
---
|
||||
|
||||
The following is an example reverse proxy configuration for [HAProxy](
|
||||
https://www.haproxy.org/) proxy. We assume
|
||||
`default['firezone']['phoenix']['port']` to be `13000` and the proxy running on
|
||||
the same host as the Firezone app.
|
||||
|
||||
Since Firezone requires HTTPS for the web portal, please bear in mind a
|
||||
downstream proxy will need to terminate SSL connections in this scenario.
|
||||
|
||||
You can also configure HAProxy to handle the SSL termination as explained
|
||||
[here](https://www.haproxy.com/blog/haproxy-ssl-termination/) but take into
|
||||
account that the `pem` file expected by `ssl crt` option needs to contain
|
||||
both the `crt` and `key` file.
|
||||
|
||||
`/etc/haproxy/haproxy.cfg`:
|
||||
|
||||
```conf
|
||||
defaults
|
||||
mode http
|
||||
|
||||
frontend app1
|
||||
bind *:80
|
||||
option forwardfor
|
||||
default_backend backend_app1
|
||||
|
||||
backend backend_app1
|
||||
server mybackendserver 127.0.0.1:13000
|
||||
```
|
||||
@@ -1,275 +0,0 @@
|
||||
---
|
||||
title: Traefik
|
||||
sidebar_position: 2
|
||||
---
|
||||
|
||||
The following are examples for configuring the [Traefik](https://traefik.io/)
|
||||
proxy as a reverse proxy for Firezone.
|
||||
|
||||
In these examples, we assume Traefik is deployed using Docker on the same host
|
||||
as Firezone. For this to work, you'll need to make sure
|
||||
`PHOENIX_EXTERNAL_TRUSTED_PROXIES` is set to include the Docker address of the
|
||||
Traefik service.
|
||||
|
||||
## Without SSL termination
|
||||
|
||||
Since Firezone requires HTTPS for the web portal, please bear in mind a
|
||||
downstream proxy will need to terminate SSL connections in this scenario.
|
||||
|
||||
Use the following `docker-compose.yml` and `rules.yml` files as a starting point
|
||||
for your own Firezone config:
|
||||
|
||||
### `docker-compose.yml`
|
||||
|
||||
```yaml
|
||||
version: '3'
|
||||
|
||||
x-deploy: &default-deploy
|
||||
restart_policy:
|
||||
condition: on-failure
|
||||
delay: 5s
|
||||
max_attempts: 3
|
||||
window: 120s
|
||||
update_config:
|
||||
order: start-first
|
||||
|
||||
networks:
|
||||
firezone-network:
|
||||
enable_ipv6: true
|
||||
ipam:
|
||||
config:
|
||||
- subnet: 172.25.0.0/16
|
||||
- subnet: 2001:3990:3990::/64
|
||||
|
||||
services:
|
||||
traefik:
|
||||
deploy:
|
||||
<<: *default-deploy
|
||||
# The official v2 Traefik docker image
|
||||
image: traefik:v2.8
|
||||
# Enables the web UI and tells Traefik to listen to docker
|
||||
command:
|
||||
- "--providers.docker"
|
||||
- "--providers.file.filename=rules.yml"
|
||||
- "--entrypoints.web.address=:80"
|
||||
- "--entrypoints.web.forwardedHeaders.insecure"
|
||||
- "--log.level=DEBUG"
|
||||
extra_hosts:
|
||||
- "host.docker.internal:host-gateway"
|
||||
ports:
|
||||
# The HTTP port
|
||||
- "80:80"
|
||||
volumes:
|
||||
# So that Traefik can listen to the Docker events
|
||||
- /var/run/docker.sock:/var/run/docker.sock
|
||||
- ./rules.yml:/rules.yml
|
||||
# make the IP of this service deterministic
|
||||
networks:
|
||||
firezone-network:
|
||||
ipv4_address: 172.25.0.99
|
||||
ipv6_address: 2001:3990:3990::99
|
||||
|
||||
firezone:
|
||||
image: firezone/firezone
|
||||
ports:
|
||||
- 51820:51820/udp
|
||||
env_file:
|
||||
# This should contain a list of env vars for configuring Firezone.
|
||||
# See https://www.firezone.dev/docs/reference/env-vars for more info.
|
||||
- ${FZ_INSTALL_DIR:-.}/.env
|
||||
volumes:
|
||||
# IMPORTANT: Persists WireGuard private key and other data. If
|
||||
# /var/firezone/private_key exists when Firezone starts, it is
|
||||
# used as the WireGuard private. Otherwise, one is generated.
|
||||
- ${FZ_INSTALL_DIR:-.}/firezone:/var/firezone
|
||||
cap_add:
|
||||
# Needed for WireGuard and firewall support.
|
||||
- NET_ADMIN
|
||||
- SYS_MODULE
|
||||
sysctls:
|
||||
# Needed for masquerading and NAT.
|
||||
- net.ipv6.conf.all.disable_ipv6=0
|
||||
- net.ipv4.ip_forward=1
|
||||
- net.ipv6.conf.all.forwarding=1
|
||||
depends_on:
|
||||
- postgres
|
||||
networks:
|
||||
firezone-network:
|
||||
ipv4_address: 172.25.0.100
|
||||
deploy:
|
||||
<<: *default-deploy
|
||||
|
||||
postgres:
|
||||
image: postgres:15
|
||||
volumes:
|
||||
- postgres-data:/var/lib/postgresql/data
|
||||
environment:
|
||||
POSTGRES_DB: ${DATABASE_NAME:-firezone}
|
||||
POSTGRES_USER: ${DATABASE_USER:-postgres}
|
||||
POSTGRES_PASSWORD: ${DATABASE_PASSWORD:?err}
|
||||
networks:
|
||||
- firezone-network
|
||||
deploy:
|
||||
<<: *default-deploy
|
||||
update_config:
|
||||
order: stop-first
|
||||
|
||||
# Postgres needs a named volume to prevent perms issues on non-linux platforms
|
||||
volumes:
|
||||
postgres-data:
|
||||
|
||||
networks:
|
||||
firezone-network:
|
||||
driver: bridge
|
||||
ipam:
|
||||
config:
|
||||
- subnet: 172.25.0.0/16
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
### `rules.yml`
|
||||
|
||||
```yaml
|
||||
http:
|
||||
routers:
|
||||
test:
|
||||
entryPoints:
|
||||
- "web"
|
||||
service: test
|
||||
rule: "Host(`44.200.42.78`)"
|
||||
services:
|
||||
test:
|
||||
loadBalancer:
|
||||
servers:
|
||||
- url: "http://firezone:13000"
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Now you should be able to start the Traefik proxy with `docker compose up`.
|
||||
|
||||
## With SSL termination
|
||||
|
||||
This configuration uses Firezone's auto-generated self-signed certificates.
|
||||
|
||||
### SSL `docker-compose.yml`
|
||||
|
||||
```yaml
|
||||
version: "3"
|
||||
|
||||
x-deploy: &default-deploy
|
||||
restart_policy:
|
||||
condition: on-failure
|
||||
delay: 5s
|
||||
max_attempts: 3
|
||||
window: 120s
|
||||
update_config:
|
||||
order: start-first
|
||||
|
||||
networks:
|
||||
app:
|
||||
enable_ipv6: true
|
||||
ipam:
|
||||
config:
|
||||
- subnet: 172.28.0.0/16
|
||||
- subnet: 2001:3990:3990::/64
|
||||
|
||||
services:
|
||||
firezone:
|
||||
image: firezone/firezone
|
||||
ports:
|
||||
- 51820:51820/udp
|
||||
volumes:
|
||||
# IMPORTANT: Persists WireGuard private key and other data. If
|
||||
# /var/firezone/private_key exists when Firezone starts, it is
|
||||
# used as the WireGuard private. Otherwise, one is generated.
|
||||
- ${HOME}/.firezone/firezone:/var/firezone
|
||||
environment:
|
||||
EXTERNAL_URL: ${EXTERNAL_URL:?err}
|
||||
DEFAULT_ADMIN_EMAIL: ${DEFAULT_ADMIN_EMAIL:?err}
|
||||
DEFAULT_ADMIN_PASSWORD: ${DEFAULT_ADMIN_PASSWORD:?err}
|
||||
GUARDIAN_SECRET_KEY: ${GUARDIAN_SECRET_KEY:?err}
|
||||
SECRET_KEY_BASE: ${SECRET_KEY_BASE:?err}
|
||||
LIVE_VIEW_SIGNING_SALT: ${LIVE_VIEW_SIGNING_SALT:?err}
|
||||
COOKIE_SIGNING_SALT: ${COOKIE_SIGNING_SALT:?err}
|
||||
COOKIE_ENCRYPTION_SALT: ${COOKIE_ENCRYPTION_SALT:?err}
|
||||
DATABASE_ENCRYPTION_KEY: ${DATABASE_ENCRYPTION_KEY:?err}
|
||||
|
||||
# Ensure this includes the traefik service IP.
|
||||
PHOENIX_EXTERNAL_TRUSTED_PROXIES: [""]
|
||||
networks:
|
||||
- app
|
||||
cap_add:
|
||||
- NET_ADMIN
|
||||
- SYS_MODULE
|
||||
sysctls:
|
||||
- net.ipv6.conf.all.disable_ipv6=0
|
||||
- net.ipv4.ip_forward=1
|
||||
- net.ipv6.conf.all.forwarding=1
|
||||
depends_on:
|
||||
- postgres
|
||||
traefik:
|
||||
deploy:
|
||||
<<: *default-deploy
|
||||
# The official v2 Traefik docker image
|
||||
image: traefik:v2.8
|
||||
# Enables the web UI and tells Traefik to listen to docker
|
||||
command:
|
||||
- "--providers.docker"
|
||||
- "--providers.file.filename=rules.yml"
|
||||
- "--entrypoints.web.address=:443"
|
||||
- "--entrypoints.web.forwardedHeaders.insecure"
|
||||
- "--log.level=DEBUG"
|
||||
extra_hosts:
|
||||
- "host.docker.internal:host-gateway"
|
||||
ports:
|
||||
# The HTTP port
|
||||
- "443:443"
|
||||
volumes:
|
||||
# So that Traefik can listen to the Docker events
|
||||
- /var/run/docker.sock:/var/run/docker.sock
|
||||
- ./rules.yml:/rules.yml
|
||||
# make the IP of this service deterministic
|
||||
networks:
|
||||
app:
|
||||
ipv4_address: 172.28.0.99
|
||||
ipv6_address: 2001:3990:3990::99
|
||||
postgres:
|
||||
image: postgres:15
|
||||
volumes:
|
||||
- postgres-data:/var/lib/postgresql/data
|
||||
environment:
|
||||
# same value as ## DB section above
|
||||
POSTGRES_DB: ${DATABASE_NAME:-firezone}
|
||||
POSTGRES_USER: ${DATABASE_USER:-postgres}
|
||||
POSTGRES_PASSWORD: ${DATABASE_PASSWORD:?err}
|
||||
deploy:
|
||||
<<: *default-deploy
|
||||
update_config:
|
||||
order: stop-first
|
||||
|
||||
# Postgres needs a named volume to prevent perms issues on non-linux platforms
|
||||
volumes:
|
||||
postgres-data:
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
### SSL `rules.yml`
|
||||
|
||||
```yaml
|
||||
http:
|
||||
routers:
|
||||
test:
|
||||
entryPoints:
|
||||
- "web"
|
||||
service: test
|
||||
rule: "Host(`44.200.42.78`)"
|
||||
tls: {}
|
||||
services:
|
||||
test:
|
||||
loadBalancer:
|
||||
servers:
|
||||
- url: "http://firezone:13000"
|
||||
tls:
|
||||
stores:
|
||||
default:
|
||||
defaultCertificate:
|
||||
certFile: /path/to/your/cert.crt
|
||||
keyFile: /path/to/your/key.key
|
||||
```
|
||||
@@ -1,65 +0,0 @@
|
||||
---
|
||||
title: Security Controls
|
||||
sidebar_position: 10
|
||||
---
|
||||
|
||||
Firezone employs a few different security controls to keep data secure in
|
||||
transit and at rest.
|
||||
|
||||
## Overview of Cryptography Used
|
||||
|
||||
Below is a table of cryptography used and to which contexts they apply.
|
||||
|
||||
| Cryptography | Context | Notes |
|
||||
| --- | --- | --- |
|
||||
| AES-GCM | Data at rest | Used to encrypt sensitive database fields such as device preshared keys and multi-factor authentication secrets. |
|
||||
| Argon2 | Data at rest | Used to hash user passwords for the local authentication method. |
|
||||
| TLSv1.2/TLSv1.3 | Data in transit | Used by the Caddy server to encrypt HTTP connections to the portal. Read more at https://caddyserver.com/docs/caddyfile/directives/tls. SSL certificates are provisioned automatically with the ACME protocol by Let's Encrypt by default. |
|
||||
| ChaCha20, Poly1305, Curve25519, BLAKE2s, SipHash24, HKDF | Data in transit | Used by WireGuard® for VPN tunnels. Read more at https://wireguard.com/protocol. Firezone uses Linux kernel WireGuard without modification. |
|
||||
|
||||
## Security policy
|
||||
|
||||
We take security issues very seriously and strive to fix all security issues
|
||||
as soon as they're reported.
|
||||
|
||||
### Announcements
|
||||
|
||||
We'll announce major security issues on our security mailing list located at:
|
||||
|
||||
https://discourse.firez.one/?utm_source=docs.firezone.dev
|
||||
|
||||
### Supported Versions
|
||||
|
||||
We release security patches for supported versions of Firezone. We recommend
|
||||
running the latest version of Firezone at all times.
|
||||
|
||||
### Reporting a Vulnerability
|
||||
|
||||
Please **do not** open a Github Issue for security issues you encounter.
|
||||
Instead, please send an email to `security AT firezone.dev` describing the issue
|
||||
and we'll respond as soon as possible.
|
||||
|
||||
### PGP Key
|
||||
|
||||
You may use the public key below to encrypt emails to `security AT firezone.dev`.
|
||||
You can also find this key at:
|
||||
|
||||
https://pgp.mit.edu/pks/lookup?op=get&search=0x45113BA04AD83D8A
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
-----BEGIN PGP PUBLIC KEY BLOCK-----
|
||||
Version: SKS 1.1.6
|
||||
Comment: Hostname: pgp.mit.edu
|
||||
|
||||
mDMEYYwK5BYJKwYBBAHaRw8BAQdA4ooDpwDy3V0wHCftM/LHD5e713LSr0SQy49joUMgHoS0
|
||||
JkZpcmV6b25lIFNlY3VyaXR5IDxzZWN1cml0eUBmaXJlei5vbmU+iJoEExYKAEIWIQQlD4tW
|
||||
gEEHBC38anNFETugStg9igUCYYwK5AIbAwUJA8JnAAULCQgHAgMiAgEGFQoJCAsCBBYCAwEC
|
||||
HgcCF4AACgkQRRE7oErYPYoORwEAiYi3arrcR2e5OfqsoAbCN0O6M0HWeo1K/ZoFWH2jLy0B
|
||||
AMsWk58vepKqNhUKhuDb8bSjK8TOr/IxB63lSkQaz9MIuDgEYYwK5BIKKwYBBAGXVQEFAQEH
|
||||
QPLzia/me7FOsFfAJKWm0X1qC5byv2GWn6LZPV013AdoAwEIB4h+BBgWCgAmFiEEJQ+LVoBB
|
||||
BwQt/GpzRRE7oErYPYoFAmGMCuQCGwwFCQPCZwAACgkQRRE7oErYPYr0ZQEAig86wu+zrNiT
|
||||
B4t3dk3psHRj+Kdn4uURLjUBZqYNvXoA+QEBUPtP7hNjum+1FrzYmHUFdCBA/cszz7x7PQ36
|
||||
5gcE
|
||||
=0gEr
|
||||
-----END PGP PUBLIC KEY BLOCK-----
|
||||
```
|
||||
@@ -1,90 +0,0 @@
|
||||
---
|
||||
title: Telemetry
|
||||
sidebar_position: 4
|
||||
---
|
||||
|
||||
This document presents an overview of the telemetry Firezone collects from your
|
||||
self-hosted instance and how to disable it.
|
||||
|
||||
## Why Firezone collects telemetry
|
||||
|
||||
We _rely_ on telemetry to prioritize our roadmap and optimize the engineering
|
||||
resources we have to make Firezone better for everyone.
|
||||
|
||||
The telemetry we collect aims to answer the following questions:
|
||||
|
||||
- How many people install, use, and stop using Firezone?
|
||||
- What features are most valuable, and which ones don’t see any use?
|
||||
- What functionality needs the most improvement?
|
||||
- When something breaks, why did it break, and how can we prevent it from happening
|
||||
in the future?
|
||||
|
||||
## How we collect telemetry
|
||||
|
||||
There are three main places where telemetry is collected in Firezone:
|
||||
|
||||
1. Package telemetry. Includes events such as install, uninstall, and upgrade.
|
||||
2. CLI telemetry from `firezone-ctl` commands.
|
||||
3. Product telemetry associated with the Web portal.
|
||||
|
||||
In each of these three contexts, we capture the minimum amount of data necessary
|
||||
to answer the questions in the section above.
|
||||
|
||||
Admin emails are collected **only if** you explicitly opt-in to product updates.
|
||||
Otherwise, personally-identifiable information is **_never_** collected.
|
||||
|
||||
We store telemetry in [PostHog](https://posthog.com) only accessible by the Firezone team.
|
||||
Here is an example of a telemetry event that is sent from your instance of
|
||||
Firezone to our telemetry server:
|
||||
|
||||
```json
|
||||
{
|
||||
"id": "0182272d-0b88-0000-d419-7b9a413713f1",
|
||||
"timestamp": "2022-07-22T18:30:39.748000+00:00",
|
||||
"event": "fz_http_started",
|
||||
"distinct_id": "1ec2e794-1c3e-43fc-a78f-1db6d1a37f54",
|
||||
"properties": {
|
||||
"$geoip_city_name": "Ashburn",
|
||||
"$geoip_continent_code": "NA",
|
||||
"$geoip_continent_name": "North America",
|
||||
"$geoip_country_code": "US",
|
||||
"$geoip_country_name": "United States",
|
||||
"$geoip_latitude": 39.0469,
|
||||
"$geoip_longitude": -77.4903,
|
||||
"$geoip_postal_code": "20149",
|
||||
"$geoip_subdivision_1_code": "VA",
|
||||
"$geoip_subdivision_1_name": "Virginia",
|
||||
"$geoip_time_zone": "America/New_York",
|
||||
"$ip": "52.200.241.107",
|
||||
"$plugins_deferred": [],
|
||||
"$plugins_failed": [],
|
||||
"$plugins_succeeded": ["GeoIP (3)"],
|
||||
"distinct_id": "1zc2e794-1c3e-43fc-a78f-1db6d1a37f54",
|
||||
"fqdn": "awsdemo.firezone.dev",
|
||||
"kernel_version": "linux 5.13.0",
|
||||
"version": "0.4.6"
|
||||
},
|
||||
"elements_chain": ""
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
## How to disable telemetry
|
||||
|
||||
:::note
|
||||
We _rely_ on product analytics to make Firezone better for everyone.
|
||||
Leaving telemetry enabled is the **single most valuable contribution** you can
|
||||
make to Firezone’s development. That said, we understand some users have higher
|
||||
privacy or security requirements and would prefer to disable telemetry altogether.
|
||||
If that’s you, keep reading.
|
||||
:::
|
||||
|
||||
Telemetry is enabled by default. To completely disable product telemetry:
|
||||
|
||||
<Tabs>
|
||||
<TabItem value="docker" label="Docker" default>
|
||||
|
||||
Set the `TELEMETRY_ENABLED` environment variable to `false` and
|
||||
restart the `firezone` container.
|
||||
|
||||
</TabItem>
|
||||
</Tabs>
|
||||
@@ -1,11 +0,0 @@
|
||||
---
|
||||
title: User Guides
|
||||
sidebar_position: 5
|
||||
---
|
||||
|
||||
```mdx-code-block
|
||||
import DocCardList from '@theme/DocCardList';
|
||||
import {useCurrentSidebarCategory} from '@docusaurus/theme-common';
|
||||
|
||||
<DocCardList items={useCurrentSidebarCategory().items}/>
|
||||
```
|
||||
@@ -1,32 +0,0 @@
|
||||
---
|
||||
title: Add Devices
|
||||
sidebar_position: 2
|
||||
---
|
||||
|
||||
# Add or remove devices
|
||||
|
||||
When a device is created, Firezone generates the WireGuard private key
|
||||
ephemerally in the user's browser. This key is **never saved**, and cannot
|
||||
be shown again once it is no longer displayed.
|
||||
|
||||
**We recommend asking end users to generate their own device configs so the
|
||||
WireGuard private key is not exposed.** Users can follow instructions
|
||||
on the [Client Instructions](/docs/user-guides/client-instructions/) page to
|
||||
generate their own WireGuard configs.
|
||||
|
||||
## Admin device config generation
|
||||
|
||||
Firezone admins can generate device configs for all users. This can be done by
|
||||
clicking the "Add Device" button on the user profile page found in `/users`.
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
Once the device profile is created, the admin can download and send the
|
||||
WireGuard configuration file to the user over a secure channel.
|
||||
|
||||
See [Add Users](/docs/user-guides/add-users/) for more information on how to add a
|
||||
user.
|
||||
|
||||
## Related guides
|
||||
|
||||
- [Client Instructions](/docs/user-guides/client-instructions/)
|
||||
@@ -1,24 +0,0 @@
|
||||
---
|
||||
title: Add Users
|
||||
sidebar_position: 1
|
||||
---
|
||||
|
||||
# Add or remove users
|
||||
|
||||
Once you have successfully installed Firezone you'll need to add users to grant
|
||||
them access to your network. This can be done through the Web UI or the
|
||||
[REST API](/docs/reference/rest-api/users).
|
||||
|
||||
## Web UI
|
||||
|
||||
Add a user by clicking the "Add User" button under `/users`. You will be asked
|
||||
to specify an email and a password for the user. Firezone can also integrate and
|
||||
sync with an identity provider to automatically grant access to users in your
|
||||
organization. See [Authenticate](/docs/authenticate/) for more
|
||||
information.
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
## Related guides
|
||||
|
||||
- [Authenticate](/docs/authenticate/)
|
||||
@@ -1,185 +0,0 @@
|
||||
---
|
||||
title: Client Instructions
|
||||
sidebar_position: 4
|
||||
description:
|
||||
Set up your client app to connect to your organization's private
|
||||
networks and resources. Download the open-source WireGuard® app
|
||||
for your operating system (Windows, MacOS, iOS, Android, Linux) to
|
||||
get started.
|
||||
---
|
||||
|
||||
# End-user client instructions
|
||||
|
||||
Follow these instructions if you're an end-user trying to set up your WireGuard client to work with Firezone.
|
||||
|
||||
## Install and setup
|
||||
|
||||
Follow this guide to establish a VPN session
|
||||
through the WireGuard native client.
|
||||
|
||||
### Step 1: Install the native WireGuard client
|
||||
|
||||
Firezone is compatible with the official WireGuard clients found here:
|
||||
|
||||
* [macOS](https://itunes.apple.com/us/app/wireguard/id1451685025)
|
||||
* [Windows](https://download.wireguard.com/windows-client/wireguard-installer.exe)
|
||||
* [iOS](https://itunes.apple.com/us/app/wireguard/id1441195209)
|
||||
* [Android](https://play.google.com/store/apps/details?id=com.wireguard.android)
|
||||
|
||||
For operating systems not listed above see the Official WireGuard site: [
|
||||
https://www.wireguard.com/install/](https://www.wireguard.com/install/).
|
||||
|
||||
### Step 2: Download the device config file
|
||||
|
||||
The device config file can either be obtained from your Firezone administrator
|
||||
or self-generated via the Firezone portal.
|
||||
|
||||
To self generate a device config file, visit the domain provided by your Firezone
|
||||
administrator. This URL will be specific to your company
|
||||
(in this example it is `https://firezone.example.com`)
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
### Step 3 (optional): Enable on boot
|
||||
|
||||
Open the WireGuard client and import the `.conf` file.
|
||||
Activate the VPN session by toggling the `Activate` switch.
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
## Re-authenticating your session
|
||||
|
||||
If your network admin has required periodic authentication to maintain your VPN session,
|
||||
follow the steps below. You will need:
|
||||
|
||||
* **URL of the Firezone portal**: Ask your Network Admin for the link.
|
||||
* **Credentials**: Your username and password should be provided by your Network
|
||||
Admin. If your company is using a Single Sign On provider (like Google or Okta),
|
||||
the Firezone portal will prompt you to authenticate via that provider.
|
||||
|
||||
### Step 1: Deactivate VPN session
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
### Step 2: Re-authenticate
|
||||
|
||||
Visit the URL of your Firezone portal and sign in using credentials provided by your
|
||||
network admin. If you are already logged into the portal,
|
||||
click the `Reauthenticate` button, then sign in again.
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
### Step 3: Activate VPN session
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
## Linux: Network Manager
|
||||
|
||||
The following steps can be used on Linux devices to import the WireGuard
|
||||
configuration profile using Network Manager CLI (`nmcli`).
|
||||
|
||||
:::note
|
||||
Importing the configuration file using the Network Manager GUI may fail
|
||||
with the following error if the profile has IPv6 support enabled:
|
||||
|
||||
```text
|
||||
ipv6.method: method "auto" is not supported for WireGuard
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
:::
|
||||
|
||||
### Step 1: Install the WireGuard tools
|
||||
|
||||
The WireGuard userspace tools need to be installed. For most Linux
|
||||
distributions this will be a package named `wireguard` or `wireguard-tools`.
|
||||
|
||||
For Debian/Ubuntu:
|
||||
|
||||
```shell
|
||||
sudo apt install wireguard
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
For Fedora:
|
||||
|
||||
```shell
|
||||
sudo dnf install wireguard-tools
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
For Arch Linux:
|
||||
|
||||
```shell
|
||||
sudo pacman -S wireguard-tools
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
For distributions not listed above see the Official WireGuard site: [
|
||||
https://www.wireguard.com/install/](https://www.wireguard.com/install/).
|
||||
|
||||
### Step 2: Download configuration
|
||||
|
||||
The device config file can either be obtained from your Firezone administrator
|
||||
or self-generated via the Firezone portal.
|
||||
|
||||
To self generate a device config file, visit the domain provided by your Firezone
|
||||
administrator. This URL will be specific to your company
|
||||
(in this example it is `https://firezone.example.com`)
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
### Step 3: Import configuration
|
||||
|
||||
Using `nmcli`, import the downloaded configuration file:
|
||||
|
||||
```shell
|
||||
sudo nmcli connection import type wireguard file /path/to/configuration.conf
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
:::note
|
||||
The WireGuard connection/interface will match the name of the configuration
|
||||
file. If required, the connection can be renamed after import:
|
||||
|
||||
```shell
|
||||
nmcli connection modify [old name] connection.id [new name]
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
:::
|
||||
|
||||
### Step 4: Connect/disconnect
|
||||
|
||||
To connect to the VPN via the command line:
|
||||
|
||||
```shell
|
||||
nmcli connection up [vpn name]
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
To disconnect:
|
||||
|
||||
```shell
|
||||
nmcli connection down [vpn name]
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
If using a GUI, the relevant Network Manager applet can also be used to control
|
||||
the connection.
|
||||
|
||||
### Auto connection
|
||||
|
||||
The VPN connection can be set to automatically connect by setting the `autoconnect`
|
||||
option to `yes`:
|
||||
|
||||
```shell
|
||||
nmcli connection modify [vpn name] connection.autoconnect yes
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
To disable the automatic connection set it back to `no`:
|
||||
|
||||
```shell
|
||||
nmcli connection modify [vpn name] connection.autoconnect no
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
## Enable multi-factor authentication
|
||||
|
||||
To enable MFA navigate to `/user_account/register_mfa` in the Firezone portal.
|
||||
After generating the QR code, scan using your authenticator app and
|
||||
input the 6 digit code.
|
||||
|
||||
If you lose your authenticator app, contact your Admin to reset
|
||||
access to your account.
|
||||
@@ -1,18 +0,0 @@
|
||||
---
|
||||
title: Egress Rules
|
||||
sidebar_position: 3
|
||||
description:
|
||||
Define access policies with egress filtering rules using
|
||||
Firezone's WireGuard®-based secure access platform.
|
||||
---
|
||||
|
||||
# Network access control
|
||||
|
||||
Firezone supports egress filtering controls to explicitly DROP or ACCEPT packets
|
||||
via the kernel's netfilter system. By default, all traffic is allowed.
|
||||
|
||||
The Allowlist and Denylist support both IPv4 and IPv6 CIDRs and IP addresses.
|
||||
When adding a rule, you may optionally scope it to a user which applies the
|
||||
rule to all their devices.
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
@@ -1,11 +0,0 @@
|
||||
---
|
||||
title: Common Use Cases
|
||||
sidebar_position: 10
|
||||
---
|
||||
|
||||
```mdx-code-block
|
||||
import DocCardList from '@theme/DocCardList';
|
||||
import {useCurrentSidebarCategory} from '@docusaurus/theme-common';
|
||||
|
||||
<DocCardList items={useCurrentSidebarCategory().items}/>
|
||||
```
|
||||
@@ -1,71 +0,0 @@
|
||||
---
|
||||
title: NAT Gateway
|
||||
sidebar_position: 3
|
||||
description: Set a static IP for egress traffic with Firezone's WireGuard®-based secure access platform.
|
||||
---
|
||||
|
||||
# Static egress IP with a NAT gateway
|
||||
|
||||
Firezone can be used as NAT gateway in order to provide a single,
|
||||
static egress IP for all of your team's traffic to flow out of.
|
||||
This is commonly used in the following scenarios:
|
||||
|
||||
- Consulting engagements: Ask your client to whitelist a single static
|
||||
IP address associated with your engagement instead of your employees'
|
||||
individual device IPs.
|
||||
- Masking your device IP or proxying your source IP for privacy or
|
||||
security reasons.
|
||||
|
||||
This guide will walk through a simple example restricting access for a
|
||||
self-hosted web app to a single whitelisted static IP running Firezone.
|
||||
|
||||
This is commonly done in place of maintaining an IP whitelist for
|
||||
multiple team members, which becomes impossible to manage as the
|
||||
access list grows and team members' IP addresses change.
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
## AWS example
|
||||
|
||||
Our goal is to configure VPN traffic to the restricted resource to be routed
|
||||
through a Firezone server on an EC2 instance. In this case Firezone is acting as
|
||||
a network proxy or NAT gateway to provide a single public egress IP for all the
|
||||
devices connected to it.
|
||||
|
||||
In this example the protected resource and Firezone are in separate VPC regions.
|
||||
|
||||
### Step 1: Deploy Firezone server
|
||||
|
||||
In this example, a Firezone instance has been set up on a `tc2.micro`
|
||||
EC2 instance. See the
|
||||
[Deployment Guide](/docs/deploy/)
|
||||
for details on deploying Firezone. Specific to AWS, ensure:
|
||||
|
||||
1. The security group of the Firezone EC2 instance allows outbound traffic to the
|
||||
IP of the protected resource.
|
||||
1. An Elastic IP is associated with the Firezone instance. This will be the
|
||||
source IP address of traffic routed through the Firezone instance to external destinations.
|
||||
In this case, the IP is `52.202.88.54`.
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
### Step 2: Restrict access to the protected resource
|
||||
|
||||
In this example, the protected resource is a self-hosted web app. Access to the
|
||||
web app is restricted to only requests from `52.202.88.54`.
|
||||
Depending on the resource, inbound traffic on different ports and traffic types
|
||||
may need to be allowed. This is outside the scope of this guide.
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
If the protected resource is controlled by a 3rd party, please inform the 3rd
|
||||
party to allow traffic from the static IP set in Step 1 (in this case `52.202.88.54`).
|
||||
|
||||
### Step 3: Route traffic to the protected resource through the VPN server
|
||||
|
||||
By default, all traffic from team members will be routed through Firezone
|
||||
and will originate from the static IP set in Step 1 (in this case `52.202.88.54`).
|
||||
However, if
|
||||
[split tunneling](/docs/user-guides/use-cases/split-tunnel/)
|
||||
has been enabled, configuration may be required to ensure the destination IP of
|
||||
the protected resource is included in the `Allowed IPs`.
|
||||
@@ -1,89 +0,0 @@
|
||||
---
|
||||
title: Restrict SSO to Firezone Users
|
||||
sidebar_position: 1
|
||||
description: Configure your identity provider to whitelist traffic from Firezone's WireGuard®-based secure access platform.
|
||||
---
|
||||
<!--
|
||||
XXX: This document is in draft status. Remove this notice when it's published.
|
||||
-->
|
||||
# Restrict application authentication to VPN users
|
||||
|
||||
Some identity providers support restricting SSO functionality
|
||||
Some identity providers support restricting SSO access to a predefined CIDR range or list of IP addresses. You can set this to the IP address of
|
||||
your Firezone gateway to restrict SSO to users connected to Firezone.
|
||||
|
||||
This adds an additional layer of security to any service that uses
|
||||
your identity provider for SSO.
|
||||
|
||||
We have identified a few common providers that support this
|
||||
feature and included basic instructions below on how you can set
|
||||
this up. The pre-requisites to this guide are a deployed Firezone
|
||||
server with a static IP
|
||||
([see NAT Gateway](.../nat-gateway))
|
||||
and ensuring traffic to the identity provider's SSO services are
|
||||
routed from client devices through the Firezone gateway
|
||||
([see Split Tunnel](.../split-tunnel)).
|
||||
|
||||
## Okta
|
||||
|
||||
Okta supports restricting SSO authentication to a "network zone" on
|
||||
a per application basis.
|
||||
|
||||
:::note
|
||||
If you have split tunneling enabled, ensure the AllowedIPs are
|
||||
correctly configured to direct traffic to
|
||||
[Okta's IPs](https://help.okta.com/en-us/Content/Topics/Security/ip-address-allow-listing.htm)
|
||||
through the Firezone gateway.
|
||||
:::
|
||||
|
||||
:::caution
|
||||
Sign-on policies are assigned on an application level. We advise
|
||||
excluding the Firezone application from the IP restriction policy above if Okta
|
||||
is being used for Firezone authentication.
|
||||
|
||||
With
|
||||
[periodic authentication](../../authenticate#enforce-periodic-re-authentication)
|
||||
enabled, you may be locked out of Okta entirely when your VPN session
|
||||
expires.
|
||||
:::
|
||||
|
||||
### Create the network zone
|
||||
|
||||
_This section is based on Okta's
|
||||
[documentation](https://help.okta.com/oie/en-us/Content/Topics/Security/network/create-ip-zone.htm)._
|
||||
|
||||
Navigate to **Security > Networks**. Add an **IP Zone** with the
|
||||
static IP of the Firezone Gateway in **Gateway IPs**.
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
### Create a sign-on policy
|
||||
|
||||
_This section is based on Okta's
|
||||
[documentation](https://help.okta.com/oie/en-us/Content/Topics/Security/network/add-network-zone-signon-policy.htm)._
|
||||
|
||||
Navigate to **Security > Authentication policies**. Create a new
|
||||
policy that denies access when a user
|
||||
is **NOT** on the network zone defined above.
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
### Associate sign-on policy to application
|
||||
|
||||
Under the **Sign On** tab, set the **Authentication policy** to the
|
||||
policy defined above. Do this for applications where authentication
|
||||
should be restricted only to users on the VPN.
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
### Configure VPN notification (optional)
|
||||
|
||||
_This section is based on Okta's
|
||||
[documentation](https://help.okta.com/oie/en-us/Content/Topics/Security/network/vpn-notification.htm)._
|
||||
|
||||
Optionally configure a notification to alert users why
|
||||
their access was denied.
|
||||
On the details page of your Okta application, configure the
|
||||
**General > VPN Notification** section.
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -1,83 +0,0 @@
|
||||
---
|
||||
title: Reverse Tunnel
|
||||
sidebar_position: 2
|
||||
description: Configure Firezone as a relay to connect two or more devices.
|
||||
---
|
||||
|
||||
This guide will walk through using Firezone as a relay to connect
|
||||
two devices. A typical use case for this configuration is to enable an
|
||||
administrator to access a server, container, or machine that is normally
|
||||
behind a NAT or firewall.
|
||||
|
||||
## General case: node to node
|
||||
|
||||
This example demonstrates a simple scenario where a tunnel is established
|
||||
between Device A and Device B.
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
Start by creating Device A and Device B by navigating to `/users/[user_id]/new_device`.
|
||||
In the settings for each device, ensure the following parameters are set to the
|
||||
values listed below. You can set device settings when creating the device config
|
||||
(see [Add Devices](/docs/user-guides/add-devices/)).
|
||||
If you need to update settings on an existing device, you can do so by generating
|
||||
a new device config.
|
||||
|
||||
Note `PersistentKeepalive` can also be set in on the
|
||||
`/settings/defaults` page for all devices.
|
||||
|
||||
Device A
|
||||
|
||||
- `AllowedIPs = 10.3.2.3/32`: This is the IP or range of IPs of Device B
|
||||
- `PersistentKeepalive = 25` If the device is behind a NAT, this ensures the
|
||||
device is able to keep the tunnel alive and continue to receive packets from
|
||||
the WireGuard interface. Usually a value of `25` is sufficient, but you may
|
||||
need to decrease this value depending on your environment.
|
||||
|
||||
Device B
|
||||
|
||||
- `AllowedIPs = 10.3.2.2/32`: This is the IP or range of IPs of Device A
|
||||
- `PersistentKeepalive = 25`
|
||||
|
||||
## Admin case: one to many nodes
|
||||
|
||||
This example demonstrates a scenario where Device A can communicate
|
||||
bi-directionally with Devices B through D. This configuration could represent an
|
||||
administrator or engineer accessing multiple resources
|
||||
(servers, containers, or machines) in different networks.
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
In the settings for each device, ensure the following parameters are set to the
|
||||
values listed below. You can set device settings when creating the device config
|
||||
(see [Add Devices](/docs/user-guides/add-devices/)).
|
||||
If you need to update settings on an existing device, you can do so by generating
|
||||
a new device config.
|
||||
|
||||
Device A (Administrator Node)
|
||||
|
||||
- `AllowedIPs = 10.3.2.3/32, 10.3.2.4/32, 10.3.2.5/32`: This is the IP of
|
||||
devices B through D. Optionally you could set a range of IPs as long as it
|
||||
includes the IPs of Devices B through D.
|
||||
- `PersistentKeepalive = 25` If the device is behind a NAT, this ensures the
|
||||
device is able to keep the tunnel alive and continue to receive packets from
|
||||
the WireGuard interface. Usually a value of `25` is sufficient, but you may
|
||||
need to decrease this value depending on your environment.
|
||||
|
||||
Device B
|
||||
|
||||
- `AllowedIPs = 10.3.2.2/32`: This is the IP or range of IPs of Device A
|
||||
- `PersistentKeepalive = 25`
|
||||
|
||||
Device C
|
||||
|
||||
- `AllowedIPs = 10.3.2.2/32`: This is the IP or range of IPs of Device A
|
||||
- `PersistentKeepalive = 25`
|
||||
|
||||
Device D
|
||||
|
||||
- `AllowedIPs = 10.3.2.2/32`: This is the IP or range of IPs of Device A
|
||||
- `PersistentKeepalive = 25`
|
||||
|
||||
## Related guides
|
||||
|
||||
- [NAT Gateway](/docs/user-guides/use-cases/nat-gateway/)
|
||||
@@ -1,61 +0,0 @@
|
||||
---
|
||||
title: Split Tunnel VPN
|
||||
sidebar_position: 1
|
||||
description: Configure Firezone for split tunneling. Route some network traffic
|
||||
from end users through the encrypted WireGuard® tunnel.
|
||||
---
|
||||
|
||||
# Set up IP-based split tunneling with Firezone
|
||||
|
||||
This guide will describe the steps required to enable split tunneling with
|
||||
WireGuard using Firezone so only traffic to defined IP ranges will be routed
|
||||
through the VPN.
|
||||
|
||||
Firezone sets the `Allowed IPs` field so traffic destined for
|
||||
specific IPs are encrypted and routed through the gateway.
|
||||
|
||||
## Step 1: Set AllowedIPs
|
||||
|
||||
AllowedIPs can be set globally on the `/settings/default` page or individually
|
||||
for each device during creation. Changes will only apply to new WireGuard
|
||||
tunnel configurations generated by Firezone.
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
Some examples of values in this field are:
|
||||
|
||||
- `0.0.0.0/0, ::/0` - all network traffic will be routed to the VPN server.
|
||||
- `192.0.2.3/32` - only traffic to a single IP address
|
||||
will be routed to the VPN server.
|
||||
- `3.5.140.0/22` - only traffic to IPs in the `3.5.140.1 - 3.5.143.254` range
|
||||
will be routed to the VPN server.
|
||||
In this example, the CIDR range for the `ap-northeast-2` AWS region was used.
|
||||
|
||||
:::note
|
||||
When deciding where to route a packet, Firezone chooses the egress
|
||||
interface corresponding to the most specific route first.
|
||||
:::
|
||||
|
||||
## Step 2 (optional): Set the DNS server(s)
|
||||
|
||||
You can define the DNS server(s) used by devices when the WireGuard tunnel
|
||||
is active. By default, it uses Cloudflare's DNS servers (`1.1.1.1, 1.0.0.1`).
|
||||
Visit the `/settings/default` page to override this value.
|
||||
|
||||
For split tunneling, this may be desired if you run a DNS server that
|
||||
resolves internal hosts to private IPs reachable via Firezone.
|
||||
|
||||
:::note
|
||||
If you wish to resolve DNS queries
|
||||
over the encrypted VPN tunnel (recommended), ensure the DNS IPs are included in `AllowedIPs`.
|
||||
:::
|
||||
|
||||
## Step 3: Regenerate the device configurations
|
||||
|
||||
Changes made to global settings in the **Defaults** tab are only applied to
|
||||
future device configurations generated by Firezone.
|
||||
|
||||
Users need to regenerate device configurations to update existing devices
|
||||
for the updated configuration changes to `AllowedIPs`, `DNS`, `PersistentKeepalive`, `MTU`, and `Endpoint`.
|
||||
|
||||
See [add device](/docs/user-guides/add-devices/) for instructions.
|
||||
@@ -1,199 +0,0 @@
|
||||
// @ts-check
|
||||
// Note: type annotations allow type checking and IDEs autocompletion
|
||||
|
||||
const lightCodeTheme = require("prism-react-renderer/themes/github");
|
||||
const darkCodeTheme = require("prism-react-renderer/themes/dracula");
|
||||
|
||||
/** @type {import('@docusaurus/types').Config} */
|
||||
const config = {
|
||||
title: "firezone",
|
||||
tagline: "Open-source secure remote access built on WireGuard®",
|
||||
url: "https://www.firezone.dev",
|
||||
baseUrl: "/",
|
||||
onBrokenLinks: "throw",
|
||||
onBrokenMarkdownLinks: "warn",
|
||||
trailingSlash: true,
|
||||
favicon: "img/favicon.ico",
|
||||
|
||||
// GitHub pages deployment config.
|
||||
// If you aren't using GitHub pages, you don't need these.
|
||||
organizationName: "firezone", // Usually your GitHub org/user name.
|
||||
projectName: "firezone", // Usually your repo name.
|
||||
|
||||
// Even if you don't use internalization, you can use this field to set useful
|
||||
// metadata like html lang. For example, if your site is Chinese, you may want
|
||||
// to replace 'en' with 'zh-Hans'.
|
||||
i18n: {
|
||||
defaultLocale: "en",
|
||||
locales: ["en"],
|
||||
},
|
||||
|
||||
// An array of scripts to load. The values can be either strings or plain
|
||||
// objects of attribute-value maps. The <script> tags will be inserted in the
|
||||
// HTML <head>. If you use a plain object, the only required attribute is src,
|
||||
// and any other attributes are permitted (each one should have boolean/string
|
||||
// values).
|
||||
//
|
||||
// Note that <script> added here are render-blocking, so you might want to
|
||||
// add async: true/defer: true to the objects.
|
||||
scripts: [
|
||||
{
|
||||
src: "/js/posthog.js",
|
||||
async: true,
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
src: "//js.hs-scripts.com/23723443.js",
|
||||
async: true,
|
||||
defer: true,
|
||||
},
|
||||
],
|
||||
|
||||
plugins: [],
|
||||
|
||||
themes: [],
|
||||
|
||||
presets: [
|
||||
[
|
||||
"classic",
|
||||
/** @type {import('@docusaurus/preset-classic').Options} */
|
||||
({
|
||||
pages: {
|
||||
routeBasePath: "/",
|
||||
},
|
||||
docs: {
|
||||
routeBasePath: "/docs",
|
||||
sidebarPath: require.resolve("./sidebars.js"),
|
||||
editUrl: "https://github.com/firezone/firezone/blob/master/www/",
|
||||
docLayoutComponent: "@theme/DocPage",
|
||||
},
|
||||
blog: {
|
||||
routeBasePath: "/blog",
|
||||
blogSidebarTitle: "All posts",
|
||||
blogSidebarCount: "ALL",
|
||||
showReadingTime: true,
|
||||
},
|
||||
theme: {
|
||||
customCss: require.resolve("./src/css/custom.css"),
|
||||
},
|
||||
}),
|
||||
],
|
||||
],
|
||||
|
||||
themeConfig:
|
||||
/** @type {import('@docusaurus/preset-classic').ThemeConfig} */
|
||||
({
|
||||
navbar: {
|
||||
title: "firezone",
|
||||
logo: {
|
||||
alt: "Firezone Logo",
|
||||
src: "img/logo.svg",
|
||||
},
|
||||
items: [
|
||||
{
|
||||
href: "/docs",
|
||||
label: "Documentation",
|
||||
position: "left",
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
href: "/blog",
|
||||
label: "Blog",
|
||||
position: "left",
|
||||
},
|
||||
// {
|
||||
// href: "/pricing",
|
||||
// label: "Pricing",
|
||||
// position: "left",
|
||||
// },
|
||||
{
|
||||
href: "/contact/support",
|
||||
label: "Contact support",
|
||||
position: "right",
|
||||
"aria-label": "Contact support",
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
html: '<img alt="GitHub Repo stars" src="https://img.shields.io/github/stars/firezone/firezone?label=Stars&style=social" style="margin-top: 6px;" height="24">',
|
||||
href: "https://github.com/firezone/firezone",
|
||||
position: "right",
|
||||
"aria-label": "GitHub repository",
|
||||
},
|
||||
],
|
||||
},
|
||||
footer: {
|
||||
style: "light",
|
||||
links: [
|
||||
{
|
||||
title: "Company",
|
||||
items: [
|
||||
{
|
||||
label: "Home",
|
||||
href: "/",
|
||||
},
|
||||
// {
|
||||
// label: "Pricing",
|
||||
// href: "/pricing",
|
||||
// },
|
||||
],
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
title: "Community",
|
||||
items: [
|
||||
{
|
||||
label: "Support Forums",
|
||||
href: "https://discourse.firez.one/?utm_source=docs.firezone.dev",
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
label: "Slack",
|
||||
href: "https://join.slack.com/t/firezone-users/shared_invite/zt-19jd956j4-rWcCqiKMh~ikPGsUFbvZiA",
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
label: "Github",
|
||||
href: "https://github.com/firezone/firezone?utm_source=docs.firezone.dev",
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
label: "Twitter",
|
||||
href: "https://twitter.com/firezonehq?utm_source=docs.firezone.dev",
|
||||
},
|
||||
],
|
||||
},
|
||||
],
|
||||
copyright: `Copyright © ${new Date().getFullYear()} Firezone, Inc.`,
|
||||
},
|
||||
prism: {
|
||||
theme: lightCodeTheme,
|
||||
darkTheme: darkCodeTheme,
|
||||
additionalLanguages: ["ruby", "elixir"],
|
||||
},
|
||||
algolia: {
|
||||
// The application ID provided by Algolia
|
||||
appId: "XXPZ9QVGFB",
|
||||
|
||||
start_urls: ["https://www.firezone.dev/docs"],
|
||||
|
||||
sitemap_urls: ["https://www.firezone.dev/sitemap.xml"],
|
||||
|
||||
// Public API key: it is safe to commit it
|
||||
apiKey: "66664e8765e1645ea0b500acebb0b0c2",
|
||||
|
||||
indexName: "firezone",
|
||||
|
||||
// Optional: see doc section below
|
||||
// Requires more configuration and setup to work, so disabling. See
|
||||
// https://discourse.algolia.com/t/algolia-searchbar-is-not-working-with-docusaurus-v2/14659/2
|
||||
contextualSearch: true,
|
||||
|
||||
// Optional: path for search page that enabled by default (`false` to disable it)
|
||||
searchPagePath: "search",
|
||||
|
||||
//... other Algolia params
|
||||
},
|
||||
metadata: [
|
||||
{
|
||||
name: "keywords",
|
||||
content:
|
||||
"wireguard, vpn, firewall, remote access, network, documentation",
|
||||
},
|
||||
],
|
||||
}),
|
||||
};
|
||||
|
||||
module.exports = config;
|
||||
@@ -1,54 +0,0 @@
|
||||
{
|
||||
"name": "firezone-docs",
|
||||
"version": "0.0.0",
|
||||
"private": true,
|
||||
"scripts": {
|
||||
"docusaurus": "docusaurus",
|
||||
"start": "docusaurus start",
|
||||
"build": "docusaurus build",
|
||||
"swizzle": "docusaurus swizzle",
|
||||
"deploy": "docusaurus deploy",
|
||||
"clear": "docusaurus clear",
|
||||
"serve": "docusaurus serve",
|
||||
"write-translations": "docusaurus write-translations",
|
||||
"write-heading-ids": "docusaurus write-heading-ids",
|
||||
"typecheck": "tsc"
|
||||
},
|
||||
"dependencies": {
|
||||
"@docusaurus/core": "^2.1.0",
|
||||
"@docusaurus/preset-classic": "^2.1.0",
|
||||
"@docusaurus/theme-search-algolia": "^2.1.0",
|
||||
"@mdx-js/react": "^1.6.22",
|
||||
"clsx": "^1.1.1",
|
||||
"markdownlint-cli": "^0.31.1",
|
||||
"prism-react-renderer": "^1.3.3",
|
||||
"react": "^17.0.2",
|
||||
"react-dom": "^17.0.2"
|
||||
},
|
||||
"devDependencies": {
|
||||
"@docusaurus/module-type-aliases": "2.1.0",
|
||||
"@tsconfig/docusaurus": "^1.0.5",
|
||||
"asciinema-player": "^3.0.1",
|
||||
"css-minimizer-webpack-plugin": "4.1.0",
|
||||
"remark-cli": "^11.0.0",
|
||||
"remark-lint": "^9.1.1",
|
||||
"remark-lint-list-item-indent": "^3.1.1",
|
||||
"remark-mdx": "^2.1.5",
|
||||
"remark-preset-lint-consistent": "^5.1.1",
|
||||
"remark-preset-lint-markdown-style-guide": "^5.1.2",
|
||||
"remark-preset-lint-recommended": "^6.1.2",
|
||||
"typescript": "^4.7.4"
|
||||
},
|
||||
"browserslist": {
|
||||
"production": [
|
||||
">0.5%",
|
||||
"not dead",
|
||||
"not op_mini all"
|
||||
],
|
||||
"development": [
|
||||
"last 1 chrome version",
|
||||
"last 1 firefox version",
|
||||
"last 1 safari version"
|
||||
]
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
@@ -1,31 +0,0 @@
|
||||
/**
|
||||
* Creating a sidebar enables you to:
|
||||
- create an ordered group of docs
|
||||
- render a sidebar for each doc of that group
|
||||
- provide next/previous navigation
|
||||
|
||||
The sidebars can be generated from the filesystem, or explicitly defined here.
|
||||
|
||||
Create as many sidebars as you want.
|
||||
*/
|
||||
|
||||
// @ts-check
|
||||
|
||||
/** @type {import('@docusaurus/plugin-content-docs').SidebarsConfig} */
|
||||
const sidebars = {
|
||||
// By default, Docusaurus generates a sidebar from the docs folder structure
|
||||
tutorialSidebar: [{ type: "autogenerated", dirName: "." }],
|
||||
|
||||
// But you can create a sidebar manually
|
||||
/*
|
||||
tutorialSidebar: [
|
||||
{
|
||||
type: 'category',
|
||||
label: 'Tutorial',
|
||||
items: ['hello'],
|
||||
},
|
||||
],
|
||||
*/
|
||||
};
|
||||
|
||||
module.exports = sidebars;
|
||||
@@ -1,50 +0,0 @@
|
||||
import React from "react";
|
||||
import styles from "./styles.module.css";
|
||||
|
||||
const AccentBlock = ({
|
||||
title,
|
||||
description,
|
||||
buttonOneText,
|
||||
buttonOneLink,
|
||||
buttonTwoText,
|
||||
buttonTwoLink,
|
||||
imageSrc,
|
||||
imageAlt,
|
||||
imageHeight,
|
||||
}) => {
|
||||
return (
|
||||
<div className={styles.accentBlock}>
|
||||
<div className={styles.contentBlock}>
|
||||
<div>
|
||||
<h1>{title ? title : "Please Add Title"}</h1>
|
||||
<p>{description ? description : "Please Add Description"}</p>
|
||||
</div>
|
||||
<div className={styles.btnWrapper}>
|
||||
{buttonOneText && buttonOneLink && (
|
||||
<button
|
||||
onClick={() => window.open(buttonOneLink)}
|
||||
className={styles.btnPrimary}>
|
||||
{buttonOneText}
|
||||
</button>
|
||||
)}
|
||||
{buttonTwoText && buttonTwoLink && (
|
||||
<button
|
||||
onClick={() => window.open(buttonTwoLink)}
|
||||
className={styles.btn}>
|
||||
{buttonTwoText}
|
||||
</button>
|
||||
)}
|
||||
</div>
|
||||
</div>
|
||||
{imageSrc && (
|
||||
<img
|
||||
alt={imageAlt}
|
||||
src={imageSrc}
|
||||
height={imageHeight}
|
||||
className={styles.sideImage}></img>
|
||||
)}
|
||||
</div>
|
||||
);
|
||||
};
|
||||
|
||||
export default AccentBlock;
|
||||
@@ -1,75 +0,0 @@
|
||||
.accentBlock {
|
||||
width: 100%;
|
||||
background-color: #f8f7f7;
|
||||
border-radius: 12px;
|
||||
padding: 20px;
|
||||
margin-top: 40px;
|
||||
display: flex;
|
||||
justify-content: space-between;
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
[data-theme="dark"] .accentBlock {
|
||||
background-color: #1b140e;
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
.contentBlock {
|
||||
width: 60%;
|
||||
height: inherit;
|
||||
display: flex;
|
||||
flex-direction: column;
|
||||
justify-content: space-between;
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
.accentBlock h1 {
|
||||
margin: 0 !important;
|
||||
font-size: 2rem;
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
.accentBlock p {
|
||||
font-size: 1rem;
|
||||
margin-top: 5px;
|
||||
margin-bottom: 0px;
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
.btnWrapper {
|
||||
margin-top: 10px;
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
.btnWrapper button {
|
||||
padding: 15px 25px;
|
||||
margin: 5px;
|
||||
border-radius: 6px;
|
||||
font-size: 1rem;
|
||||
cursor: pointer;
|
||||
transition: all 0.2s ease-out;
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
.btnWrapper button:first-child {
|
||||
margin-left: 0px;
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
.btnPrimary {
|
||||
background-color: #1b140e;
|
||||
color: #fcfcfc;
|
||||
border: none;
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
[data-theme="dark"] .btnPrimary {
|
||||
background-color: #4c3e33;
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
.btnPrimary:hover {
|
||||
transform: scale(1.05);
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
.btn {
|
||||
background: transparent;
|
||||
border: none;
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
.sideImage {
|
||||
padding: 10px;
|
||||
width: 40%;
|
||||
object-fit: cover;
|
||||
border: none;
|
||||
}
|
||||
@@ -1,44 +0,0 @@
|
||||
import React, { useEffect, useRef } from 'react';
|
||||
import BrowserOnly from '@docusaurus/BrowserOnly';
|
||||
|
||||
type AsciinemaPlayerProps = {
|
||||
src: string;
|
||||
// START asciinemaOptions
|
||||
cols: string;
|
||||
rows: string;
|
||||
autoPlay: boolean
|
||||
preload: boolean;
|
||||
loop: boolean | number;
|
||||
startAt: number | string;
|
||||
speed: number;
|
||||
idleTimeLimit: number;
|
||||
theme: string;
|
||||
poster: string;
|
||||
fit: string;
|
||||
fontSize: string;
|
||||
// END asciinemaOptions
|
||||
};
|
||||
|
||||
const AsciinemaPlayer: React.FC<AsciinemaPlayerProps> = ({
|
||||
src,
|
||||
...asciinemaOptions
|
||||
}) => {
|
||||
const ref = useRef<HTMLDivElement>(null);
|
||||
|
||||
return (
|
||||
<BrowserOnly fallback={<div>Loading...</div>}>
|
||||
{() => {
|
||||
const AsciinemaPlayerLibrary = require('asciinema-player');
|
||||
|
||||
useEffect(() => {
|
||||
const currentRef = ref.current;
|
||||
AsciinemaPlayerLibrary.create(src, currentRef, asciinemaOptions);
|
||||
}, [src]);
|
||||
|
||||
return <div ref={ref} />
|
||||
}}
|
||||
</BrowserOnly>
|
||||
);
|
||||
};
|
||||
|
||||
export default AsciinemaPlayer;
|
||||
@@ -1,46 +0,0 @@
|
||||
import React, { useState } from "react";
|
||||
import styles from "./styles.module.css";
|
||||
|
||||
const Feedback = () => {
|
||||
const [showFeedbackAction, setShowFeedbackAction] = useState(false);
|
||||
return (
|
||||
<div className={styles.feedbackWrapper}>
|
||||
<h1>
|
||||
{showFeedbackAction
|
||||
? "Thanks for the feedback"
|
||||
: "Was this page useful?"}
|
||||
</h1>
|
||||
{!showFeedbackAction ? (
|
||||
<div className={styles.voteWrapper}>
|
||||
<button onClick={() => setShowFeedbackAction(true)}>
|
||||
<img src="img/like.svg"></img> Like
|
||||
</button>
|
||||
<button onClick={() => setShowFeedbackAction(true)}>
|
||||
<img src="img/dislike.svg"></img> Dislike
|
||||
</button>
|
||||
</div>
|
||||
) : (
|
||||
<div>
|
||||
<p>
|
||||
If you need help on any of the above, feel free to create an issue
|
||||
on{" "}
|
||||
<a href="https://github.com/firezone/firezone" target="_blank">
|
||||
our repo
|
||||
</a>
|
||||
, or{" "}
|
||||
<a
|
||||
href="https://join.slack.com/t/firezone-users/shared_invite/zt-19jd956j4-rWcCqiKMh~ikPGsUFbvZiA"
|
||||
target="_blank">
|
||||
join our Slack
|
||||
</a>{" "}
|
||||
where a member of our team can assist you! Chances are that if you
|
||||
have a problem or question, someone else does too - so please don't
|
||||
hesitate to create a new issue or ask us a question.
|
||||
</p>
|
||||
</div>
|
||||
)}
|
||||
</div>
|
||||
);
|
||||
};
|
||||
|
||||
export default Feedback;
|
||||
@@ -1,58 +0,0 @@
|
||||
.feedbackWrapper {
|
||||
width: 100%;
|
||||
height: 200px;
|
||||
margin: 10px 0px;
|
||||
padding: 0px;
|
||||
background-color: transparent;
|
||||
border-radius: 12px;
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
.feedbackWrapper h1 {
|
||||
margin: 0 !important;
|
||||
font-size: 1.2rem;
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
.feedbackWrapper p {
|
||||
font-size: 1rem;
|
||||
margin-top: 10px;
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
.voteWrapper {
|
||||
margin-top: 10px;
|
||||
display: flex;
|
||||
}
|
||||
.voteWrapper button {
|
||||
padding: 15px 20px;
|
||||
border: none;
|
||||
cursor: pointer;
|
||||
display: flex;
|
||||
align-items: center;
|
||||
justify-content: center;
|
||||
border-radius: 6px;
|
||||
font-size: 1rem;
|
||||
margin: 10px;
|
||||
background-color: transparent;
|
||||
border: 1px solid rgba(0, 0, 0, 0.5);
|
||||
transition: all 0.2s ease-out;
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
[data-theme="dark"] .voteWrapper button {
|
||||
border: 1px solid rgba(255, 255, 255, 0.5);
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
.voteWrapper button:first-child {
|
||||
margin-left: 0px;
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
.voteWrapper button:hover {
|
||||
border: 1px solid rgba(0, 0, 0, 1);
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
[data-theme="dark"] .voteWrapper button:hover {
|
||||
border: 1px solid rgba(255, 255, 255, 1);
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
.voteWrapper button img {
|
||||
height: 20px;
|
||||
margin-right: 10px;
|
||||
}
|
||||
@@ -1,70 +0,0 @@
|
||||
import React from 'react';
|
||||
import clsx from 'clsx';
|
||||
import styles from './styles.module.css';
|
||||
|
||||
type FeatureItem = {
|
||||
title: string;
|
||||
Svg: React.ComponentType<React.ComponentProps<'svg'>>;
|
||||
description: JSX.Element;
|
||||
};
|
||||
|
||||
const FeatureList: FeatureItem[] = [
|
||||
{
|
||||
title: 'Easy to Use',
|
||||
Svg: require('@site/static/img/undraw_docusaurus_mountain.svg').default,
|
||||
description: (
|
||||
<>
|
||||
Docusaurus was designed from the ground up to be easily installed and
|
||||
used to get your website up and running quickly.
|
||||
</>
|
||||
),
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
title: 'Focus on What Matters',
|
||||
Svg: require('@site/static/img/undraw_docusaurus_tree.svg').default,
|
||||
description: (
|
||||
<>
|
||||
Docusaurus lets you focus on your docs, and we'll do the chores. Go
|
||||
ahead and move your docs into the <code>docs</code> directory.
|
||||
</>
|
||||
),
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
title: 'Powered by React',
|
||||
Svg: require('@site/static/img/undraw_docusaurus_react.svg').default,
|
||||
description: (
|
||||
<>
|
||||
Extend or customize your website layout by reusing React. Docusaurus can
|
||||
be extended while reusing the same header and footer.
|
||||
</>
|
||||
),
|
||||
},
|
||||
];
|
||||
|
||||
function Feature({title, Svg, description}: FeatureItem) {
|
||||
return (
|
||||
<div className={clsx('col col--4')}>
|
||||
<div className="text--center">
|
||||
<Svg className={styles.featureSvg} role="img" />
|
||||
</div>
|
||||
<div className="text--center padding-horiz--md">
|
||||
<h3>{title}</h3>
|
||||
<p>{description}</p>
|
||||
</div>
|
||||
</div>
|
||||
);
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
export default function HomepageFeatures(): JSX.Element {
|
||||
return (
|
||||
<section className={styles.features}>
|
||||
<div className="container">
|
||||
<div className="row">
|
||||
{FeatureList.map((props, idx) => (
|
||||
<Feature key={idx} {...props} />
|
||||
))}
|
||||
</div>
|
||||
</div>
|
||||
</section>
|
||||
);
|
||||
}
|
||||
@@ -1,11 +0,0 @@
|
||||
.features {
|
||||
display: flex;
|
||||
align-items: center;
|
||||
padding: 2rem 0;
|
||||
width: 100%;
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
.featureSvg {
|
||||
height: 200px;
|
||||
width: 200px;
|
||||
}
|
||||
@@ -1,34 +0,0 @@
|
||||
import React from 'react';
|
||||
|
||||
class HubspotForm extends React.Component<{
|
||||
portalId: string;
|
||||
formId: string;
|
||||
region: string;
|
||||
}> {
|
||||
componentDidMount() {
|
||||
const script = document.createElement("script");
|
||||
script.src = "https://js.hsforms.net/forms/v2.js";
|
||||
document.body.appendChild(script);
|
||||
|
||||
script.addEventListener("load", () => {
|
||||
// @ts-ignore
|
||||
if (window.hbspt) {
|
||||
// @ts-ignore
|
||||
window.hbspt.forms.create({
|
||||
target: "#hubspot-form",
|
||||
...this.props,
|
||||
});
|
||||
}
|
||||
});
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
render() {
|
||||
return (
|
||||
<div>
|
||||
<div id="hubspot-form" />
|
||||
</div>
|
||||
);
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
export default HubspotForm;
|
||||
@@ -1,22 +0,0 @@
|
||||
import React from "react";
|
||||
import CodeBlock from '@theme/CodeBlock';
|
||||
import BrowserOnly from '@docusaurus/BrowserOnly';
|
||||
|
||||
export default function InstallBlock() {
|
||||
return (
|
||||
<BrowserOnly fallback={<div>Loading...</div>}>
|
||||
{() => {
|
||||
const distinct_id =
|
||||
(window.posthog && typeof window.posthog.get_distinct_id === "function")
|
||||
? window.posthog.get_distinct_id()
|
||||
: "posthog-blocked"
|
||||
|
||||
return (
|
||||
<CodeBlock language="bash">
|
||||
{`bash <(curl -fsSL https://github.com/firezone/firezone/raw/master/scripts/install.sh) ${distinct_id}`}
|
||||
</CodeBlock>
|
||||
)
|
||||
}}
|
||||
</BrowserOnly>
|
||||
)
|
||||
}
|
||||
@@ -1,24 +0,0 @@
|
||||
import React, { useState } from "react";
|
||||
import styles from "./styles.module.css";
|
||||
|
||||
const SignUp = () => {
|
||||
const [email, setEmail] = useState("");
|
||||
const [isInvalid, setIsInvalid] = useState("");
|
||||
|
||||
const onSubmit = () => {
|
||||
if (email.length > 1) {
|
||||
console.log(email);
|
||||
}
|
||||
};
|
||||
return (
|
||||
<div className={styles.signupWrapper}>
|
||||
<iframe
|
||||
height="100%"
|
||||
width="100%"
|
||||
src="https://cdn.forms-content.sg-form.com/ae95a755-f1b0-11ec-bae1-cec19e074e52"
|
||||
/>
|
||||
</div>
|
||||
);
|
||||
};
|
||||
|
||||
export default SignUp;
|
||||
@@ -1,10 +0,0 @@
|
||||
.signupWrapper {
|
||||
width: 100%;
|
||||
height: 500px;
|
||||
background-color: #f8f7f7;
|
||||
border-radius: 12px;
|
||||
display: flex;
|
||||
flex-direction: column;
|
||||
justify-content: space-between;
|
||||
margin: 20px 0px;
|
||||
}
|
||||
@@ -1,73 +0,0 @@
|
||||
/**
|
||||
* Any CSS included here will be global. The classic template
|
||||
* bundles Infima by default. Infima is a CSS framework designed to
|
||||
* work well for content-centric websites.
|
||||
*/
|
||||
|
||||
@import url('https://fonts.googleapis.com/css2?family=Fira+Sans:ital,wght@0,300;0,400;0,700;1,300;1,400;1,700&family=Open+Sans:ital,wght@0,300;0,400;0,700;1,300;1,400;1,700&display=swap');
|
||||
@import "asciinema-player/dist/bundle/asciinema-player.css";
|
||||
|
||||
/* You can override the default Infima variables here. */
|
||||
:root {
|
||||
--ifm-color-primary: #3400c2;
|
||||
--ifm-color-primary-dark: #766a60;
|
||||
--ifm-color-primary-darker: #4c3e33;
|
||||
--ifm-color-primary-darkest: #1b140e;
|
||||
--ifm-color-primary-light: #dfdedd;
|
||||
--ifm-color-primary-lighter: #ebebea;
|
||||
--ifm-color-primary-lightest: #f8f7f7;
|
||||
--ifm-code-font-size: 95%;
|
||||
--docusaurus-highlighted-code-line-bg: rgba(205, 153, 153, 0.2);
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
/* For readability concerns, you should choose a lighter palette in dark mode. */
|
||||
[data-theme="dark"] {
|
||||
--ifm-color-primary: #ff7300;
|
||||
--ifm-color-primary-dark: #c25700;
|
||||
--ifm-color-primary-darker: #7f3900;
|
||||
--ifm-color-primary-darkest: #5c2900;
|
||||
--ifm-color-primary-light: #ffbc85;
|
||||
--ifm-color-primary-lighter: #ffddc2;
|
||||
--ifm-color-primary-lightest: #fff1e5;
|
||||
--ifm-code-font-size: 95%;
|
||||
--docusaurus-highlighted-code-line-bg: rgba(0, 0, 0, 0.3);
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
body {
|
||||
font-family: 'Fira Sans', sans-serif;
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
h1,h2,h3,h4,h5,h6 {
|
||||
font-family: 'Open Sans', sans-serif;
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
table {
|
||||
display: table;
|
||||
width: 100%;
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
.header-github-link:hover {
|
||||
opacity: 0.6;
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
.header-github-link::before {
|
||||
content: '';
|
||||
width: 24px;
|
||||
height: 24px;
|
||||
display: flex;
|
||||
background: url(/img/github_light.svg) no-repeat;
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
[data-theme='dark'] .header-github-link::before {
|
||||
background: url(/img/github_dark.svg) no-repeat;
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
/* Show a border around Tab containers to make it more clear
|
||||
* where they end
|
||||
*/
|
||||
.tabs-container {
|
||||
background: rgba(100, 100, 100, 0.1);
|
||||
padding-bottom: 1.5rem;
|
||||
padding-left: 1.5rem;
|
||||
border-radius: 5px;
|
||||
}
|
||||
@@ -1,168 +0,0 @@
|
||||
---
|
||||
title: Firezone • Pricing
|
||||
description: Explore Firezone's pricing.
|
||||
---
|
||||
|
||||
<div className="hero shadow--lw">
|
||||
<div className="container">
|
||||
<h1 className="hero__title">Firezone pricing</h1>
|
||||
<p>
|
||||
Firezone works with teams of all sizes to deliver fast, low-latency access
|
||||
to private networks and resources.
|
||||
</p>
|
||||
</div>
|
||||
</div>
|
||||
|
||||
<h2 className="margin-vert--lg">Enterprise plan</h2>
|
||||
|
||||
<p>
|
||||
Direct support from the team that built Firezone and additional features built
|
||||
for larger teams.
|
||||
</p>
|
||||
|
||||
<ul>
|
||||
<li>
|
||||
Get immediate assistance from a <strong>dedicated support engineer</strong>{" "}
|
||||
through email and your own <strong>private Slack channel</strong>.
|
||||
</li>
|
||||
<li>
|
||||
Ensure business continuity and reduce risk with SLAs and{" "}
|
||||
<strong>expert guidance</strong> from the creators of Firezone.
|
||||
</li>
|
||||
<li>
|
||||
Maintain privacy and control by <strong>hosting on-prem</strong> in
|
||||
security-sensitive environments.
|
||||
</li>
|
||||
<li>
|
||||
Shape Firezone's future roadmap and <strong>accelerate development</strong>{" "}
|
||||
of the features you need.
|
||||
</li>
|
||||
</ul>
|
||||
|
||||
<div className="container">
|
||||
<div className="row margin-vert--lg">
|
||||
<div className="col col--12">
|
||||
<center>
|
||||
<h4>
|
||||
Hundreds of organizations trust Firezone to secure access for their
|
||||
team.
|
||||
</h4>
|
||||
</center>
|
||||
</div>
|
||||
</div>
|
||||
<div className="row margin-vert--lg">
|
||||
<div className="col col--2">
|
||||
<img
|
||||
alt="bunq logo"
|
||||
src="https://user-images.githubusercontent.com/167144/218763171-3b768826-eddf-499c-9b84-5ad365e8da6e.png"
|
||||
width="100px"
|
||||
height="55px"
|
||||
/>
|
||||
</div>
|
||||
<div className="col col--2">
|
||||
<img
|
||||
alt="tribe logo"
|
||||
src="https://user-images.githubusercontent.com/167144/218763181-61c8b4a7-4367-41a6-a790-0fa2b2a34461.png"
|
||||
width="100px"
|
||||
height="55px"
|
||||
/>
|
||||
</div>
|
||||
<div className="col col--2">
|
||||
<img
|
||||
alt="poughkeepsie logo"
|
||||
src="https://user-images.githubusercontent.com/167144/218763199-69def673-f37d-4e6b-aee9-13eac24ad93b.png"
|
||||
width="100px"
|
||||
height="55px"
|
||||
/>
|
||||
</div>
|
||||
<div className="col col--2">
|
||||
<img
|
||||
alt="rebank logo"
|
||||
src="https://user-images.githubusercontent.com/167144/218763213-265a562c-1ed0-4206-8a9f-6726aaaaeed4.png"
|
||||
width="100px"
|
||||
height="55px"
|
||||
/>
|
||||
</div>
|
||||
<div className="col col--2">
|
||||
<img
|
||||
alt="square1 logo"
|
||||
src="https://user-images.githubusercontent.com/167144/218763233-ac4fd4f2-c58b-4136-a3b1-ceeb09a4f954.png"
|
||||
width="100px"
|
||||
height="55px"
|
||||
/>
|
||||
</div>
|
||||
<div className="col col--2">
|
||||
<img
|
||||
alt="db11 logo"
|
||||
src="https://user-images.githubusercontent.com/167144/218763247-e75a2410-baa0-45f8-bd5f-aa33d5fd0898.png"
|
||||
width="100px"
|
||||
height="55px"
|
||||
/>
|
||||
</div>
|
||||
</div>
|
||||
<div className="row">
|
||||
<div className="col col--2 col--offset-10">
|
||||
<a className="button button--primary" href="/sales">
|
||||
Get in touch
|
||||
</a>
|
||||
</div>
|
||||
</div>
|
||||
</div>
|
||||
|
||||
<hr className="margin-bottom--xl" />
|
||||
|
||||
<div className="container">
|
||||
<div className="row">
|
||||
<div className="col col--1">
|
||||
<img src="/img/github_light.svg" />
|
||||
</div>
|
||||
<div className="col col--11">
|
||||
<h3>Looking for the free, open-source version of Firezone?</h3>
|
||||
<p>
|
||||
The Community Plan is perfect for individuals and small teams with basic
|
||||
secure access needs.
|
||||
</p>
|
||||
</div>
|
||||
</div>
|
||||
<div className="row">
|
||||
<div className="col col--2 col--offset-10">
|
||||
<a href="https://github.com/firezone/firezone">Visit GitHub ></a>
|
||||
</div>
|
||||
</div>
|
||||
</div>
|
||||
|
||||
<hr className="margin-bottom--xl" />
|
||||
|
||||
<center>
|
||||
<h1>Find the best plan for your organization</h1>
|
||||
<p>
|
||||
Have a feature request? Open an issue on{" "}
|
||||
<a href="https://github.com/firezone/firezone/issues">GitHub</a>, or{" "}
|
||||
<a href="/sales">get in touch</a> with our team.
|
||||
</p>
|
||||
</center>
|
||||
|
||||
| | Community | Enterprise |
|
||||
| ---------------------------------------- | -------------------------------------------------------------------- | -------------------------------------------------------------------- |
|
||||
| <strong>Management</strong> | | |
|
||||
| Users | Unlimited | Unlimited |
|
||||
| Devices | Unlimited | Unlimited |
|
||||
| Self-hosted | <span className="badge badge--success">✔</span> | <span className="badge badge--success">✔</span> |
|
||||
| | | |
|
||||
| <strong>Security and compliance</strong> | | |
|
||||
| User-scoped access rules | <span className="badge badge--success">✔</span> | <span className="badge badge--success">✔</span> |
|
||||
| Single sign-on | <span className="badge badge--success">✔</span> | <span className="badge badge--success">✔</span> |
|
||||
| Debug logs | <span className="badge badge--success">✔</span> | <span className="badge badge--success">✔</span> |
|
||||
| | | |
|
||||
| <strong>Support</strong> | | |
|
||||
| Community support | <span className="badge badge--success">✔</span> | <span className="badge badge--success">✔</span> |
|
||||
| Priority email support | | <span className="badge badge--success">✔</span> |
|
||||
| Dedicated Slack channel | | <span className="badge badge--success">✔</span> |
|
||||
| White-glove onboarding | | <span className="badge badge--success">✔</span> |
|
||||
| SLAs | | <span className="badge badge--success">✔</span> |
|
||||
| Assisted upgrades | | <span className="badge badge--success">✔</span> |
|
||||
| | | |
|
||||
| <strong>Custom development</strong> | | |
|
||||
| Custom integrations | | <span className="badge badge--success">✔</span> |
|
||||
| Roadmap acceleration | | <span className="badge badge--success">✔</span> |
|
||||
| | <a href="https://github.com/firezone/firezone">Visit GitHub ></a> | <a className="button button--primary" href="/sales">Get in touch</a> |
|
||||
@@ -1,48 +0,0 @@
|
||||
---
|
||||
title: Firezone • Open Source Remote Access
|
||||
description: Firezone • Contact us
|
||||
---
|
||||
|
||||
<div className="hero shadow--lw">
|
||||
<div className="container">
|
||||
<h1 className="hero__title">Talk to a Firezone expert</h1>
|
||||
<p>
|
||||
Ready to manage secure remote access for your organization? Learn how
|
||||
Firezone can help.
|
||||
</p>
|
||||
</div>
|
||||
</div>
|
||||
|
||||
<center>
|
||||
<h2 className="margin-vert--xl">Contact support</h2>
|
||||
</center>
|
||||
|
||||
<div className="container">
|
||||
<div className="row">
|
||||
<div className="col col--6">
|
||||
<h3>Ensure business continuity</h3>
|
||||
<ul>
|
||||
<li>Technical support with SLAs</li>
|
||||
<li>Private Slack channel</li>
|
||||
<li>White-glove onboarding</li>
|
||||
</ul>
|
||||
<h3>Built for privacy and compliance</h3>
|
||||
<ul>
|
||||
<li>Host on-prem in security sensitive environments</li>
|
||||
<li>Maintain full control of your data and network traffic</li>
|
||||
</ul>
|
||||
<h3>Simplify management for admins</h3>
|
||||
<ul>
|
||||
<li>Automatic de-provisioning with SCIM</li>
|
||||
<li>Deployment advice for complex use cases</li>
|
||||
</ul>
|
||||
</div>
|
||||
<div className="col col--6">
|
||||
<HubspotForm
|
||||
region="na1"
|
||||
portalId="23723443"
|
||||
formId="76637b95-cef7-4b94-8e7a-411aeec5fbb1"
|
||||
/>
|
||||
</div>
|
||||
</div>
|
||||
</div>
|
||||
@@ -1,404 +0,0 @@
|
||||
---
|
||||
title: Firezone • Open Source Remote Access
|
||||
description: Deploy in minutes to secure remote access to your private resources.
|
||||
---
|
||||
|
||||
<div className="hero">
|
||||
<div className="container">
|
||||
<h1 className="hero__title">Fast, effortless secure access</h1>
|
||||
<p>
|
||||
Firezone is an open-source remote access platform built on WireGuard®, a
|
||||
modern VPN protocol that's 4-6x faster than OpenVPN. Deploy on your
|
||||
infrastructure and start onboarding users in minutes.
|
||||
</p>
|
||||
<center>
|
||||
<a className="button button--primary" href="/docs/deploy">
|
||||
Deploy now
|
||||
</a>
|
||||
</center>
|
||||
</div>
|
||||
</div>
|
||||
|
||||
<div className="container">
|
||||
<img
|
||||
alt="Overview gif"
|
||||
src="https://user-images.githubusercontent.com/167144/218759566-acaffd2e-ef37-4b42-a014-bfaa8d33e655.gif"
|
||||
/>
|
||||
</div>
|
||||
|
||||
<hr className="margin-vert--xl" />
|
||||
|
||||
<center>
|
||||
<h2 className="margin-bottom--lg">Trusted by organizations like</h2>
|
||||
</center>
|
||||
|
||||
<div className="container">
|
||||
<div className="row">
|
||||
<div className="col col--2">
|
||||
<img
|
||||
alt="bunq logo"
|
||||
src="https://user-images.githubusercontent.com/167144/218763171-3b768826-eddf-499c-9b84-5ad365e8da6e.png"
|
||||
width="100px"
|
||||
height="55px"
|
||||
/>
|
||||
</div>
|
||||
<div className="col col--2">
|
||||
<img
|
||||
alt="tribe logo"
|
||||
src="https://user-images.githubusercontent.com/167144/218763181-61c8b4a7-4367-41a6-a790-0fa2b2a34461.png"
|
||||
width="100px"
|
||||
height="55px"
|
||||
/>
|
||||
</div>
|
||||
<div className="col col--2">
|
||||
<img
|
||||
alt="poughkeepsie logo"
|
||||
src="https://user-images.githubusercontent.com/167144/218763199-69def673-f37d-4e6b-aee9-13eac24ad93b.png"
|
||||
width="100px"
|
||||
height="55px"
|
||||
/>
|
||||
</div>
|
||||
<div className="col col--2">
|
||||
<img
|
||||
alt="rebank logo"
|
||||
src="https://user-images.githubusercontent.com/167144/218763213-265a562c-1ed0-4206-8a9f-6726aaaaeed4.png"
|
||||
width="100px"
|
||||
height="55px"
|
||||
/>
|
||||
</div>
|
||||
<div className="col col--2">
|
||||
<img
|
||||
alt="square1 logo"
|
||||
src="https://user-images.githubusercontent.com/167144/218763233-ac4fd4f2-c58b-4136-a3b1-ceeb09a4f954.png"
|
||||
width="100px"
|
||||
height="55px"
|
||||
/>
|
||||
</div>
|
||||
<div className="col col--2">
|
||||
<img
|
||||
alt="db11 logo"
|
||||
src="https://user-images.githubusercontent.com/167144/218763247-e75a2410-baa0-45f8-bd5f-aa33d5fd0898.png"
|
||||
width="100px"
|
||||
height="55px"
|
||||
/>
|
||||
</div>
|
||||
</div>
|
||||
</div>
|
||||
|
||||
<hr className="margin-vert--xl" />
|
||||
|
||||
<div className="hero">
|
||||
<div className="container">
|
||||
<h1 className="hero__title">An alternative to old VPNs</h1>
|
||||
</div>
|
||||
</div>
|
||||
|
||||
<!-- Feature 1 -->
|
||||
|
||||
<div className="container">
|
||||
<center>
|
||||
<h2 className="margin-bottom--lg">
|
||||
Streamline workflows. Reduce total cost of ownership.
|
||||
</h2>
|
||||
</center>
|
||||
</div>
|
||||
<div className="container">
|
||||
<div className="row">
|
||||
<div className="col col--6">
|
||||
<p>
|
||||
Legacy VPNs are cumbersome to manage and take weeks to configure
|
||||
correctly. Firezone takes minutes to deploy and the Web GUI makes
|
||||
managing secure access effortless for admins.
|
||||
</p>
|
||||
<ul>
|
||||
<li>Integrate any identity provider to enforce 2FA / MFA</li>
|
||||
<li>Define user-scoped access rules</li>
|
||||
<li>Manage users with a snappy admin dashboard</li>
|
||||
</ul>
|
||||
</div>
|
||||
<div className="col col--6">
|
||||
<img
|
||||
alt="Feature 1"
|
||||
src="https://user-images.githubusercontent.com/167144/218778243-37f22d1e-0bdf-4f3d-8859-4b81dd91878a.png"
|
||||
/>
|
||||
</div>
|
||||
</div>
|
||||
</div>
|
||||
|
||||
<hr className="margin-vert--xl" />
|
||||
|
||||
<!-- Feature 2 -->
|
||||
|
||||
<div className="container">
|
||||
<center>
|
||||
<h2 className="margin-bottom--lg">
|
||||
High throughput and low latency. Up to 4-6x faster than OpenVPN.
|
||||
</h2>
|
||||
</center>
|
||||
</div>
|
||||
<div className="container">
|
||||
<div className="row">
|
||||
<div className="col col--6">
|
||||
<img
|
||||
alt="Feature 2"
|
||||
src="https://user-images.githubusercontent.com/167144/218778241-c2baa6d1-499a-4da3-a9d3-7e0d4590f75f.png"
|
||||
/>
|
||||
<p>
|
||||
<a href="https://core.ac.uk/download/pdf/322886318.pdf">
|
||||
Performance comparison of VPN solutions (Osswald et al.)
|
||||
</a>
|
||||
</p>
|
||||
</div>
|
||||
<div className="col col--6">
|
||||
<p>
|
||||
Increase productivity and decrease connection issues for your remote
|
||||
team. Firezone uses kernel WireGuard® to be efficient, reliable, and
|
||||
performant in any environment.
|
||||
</p>
|
||||
<ul>
|
||||
<li>
|
||||
<a href="https://www.wireguard.com/protocol/">
|
||||
State-of-the-art cryptography
|
||||
</a>
|
||||
</li>
|
||||
<li>
|
||||
<a href="https://www.wireguard.com/formal-verification/">
|
||||
Auditable and formally verified
|
||||
</a>
|
||||
</li>
|
||||
<li>
|
||||
<a href="https://www.wireguard.com/performance/">Multi-threaded</a>
|
||||
</li>
|
||||
</ul>
|
||||
</div>
|
||||
</div>
|
||||
</div>
|
||||
|
||||
<hr className="margin-vert--xl" />
|
||||
|
||||
<!-- Feature 3 -->
|
||||
|
||||
<div className="container">
|
||||
<center>
|
||||
<h2 className="margin-bottom--lg">
|
||||
Firezone runs entirely on your infrastructure. No vendor lock-in.
|
||||
</h2>
|
||||
</center>
|
||||
</div>
|
||||
<div className="container">
|
||||
<div className="row">
|
||||
<div className="col col--6">
|
||||
Deploy Firezone on any platform that supports Docker. There's no need to
|
||||
risk breaches by sending data to third parties.
|
||||
<ul>
|
||||
<li>VPC, data center, or on-prem</li>
|
||||
<li>Auto-renewing SSL certs from Let's Encrypt via ACME</li>
|
||||
<li>Flexible and configurable</li>
|
||||
</ul>
|
||||
</div>
|
||||
<div className="col col--6">
|
||||
<img
|
||||
alt="Feature 3"
|
||||
src="https://user-images.githubusercontent.com/167144/218778234-b8150dcb-5af1-410a-8c16-95c660171d81.png"
|
||||
/>
|
||||
<a href="/docs/deploy">Explore the deployment documentation ></a>
|
||||
</div>
|
||||
</div>
|
||||
</div>
|
||||
|
||||
<hr className="margin-vert--xl" />
|
||||
|
||||
<div className="container">
|
||||
<center>
|
||||
<h2 className="margin-bottom--lg">
|
||||
Integrate your identity provider for SSO to enforce 2FA / MFA.
|
||||
</h2>
|
||||
</center>
|
||||
<p>
|
||||
Only allow connections from authenticated users and automatically disable
|
||||
access for employees who have left. Firezone integrates with any OIDC and
|
||||
SAML 2.0 compatible identity provider for single sign-on (SSO).
|
||||
</p>
|
||||
</div>
|
||||
|
||||
<div className="container">
|
||||
<div className="row">
|
||||
<div className="col col--2">
|
||||
<a href="/docs/authenticate/oidc/keycloak/">
|
||||
<img
|
||||
width="109px"
|
||||
height="41px"
|
||||
alt="keycloak logo"
|
||||
src="https://user-images.githubusercontent.com/167144/218770941-2d8cdf09-d1f4-48bb-9049-b8dc486d909a.png"
|
||||
/>
|
||||
</a>
|
||||
</div>
|
||||
<div className="col col--2">
|
||||
<a href="/docs/authenticate/oidc/google/">
|
||||
<img
|
||||
width="109px"
|
||||
height="41px"
|
||||
src="google logo"
|
||||
src="https://user-images.githubusercontent.com/167144/218770954-e41318d4-a8b1-40e5-ab4a-3343d63013a0.png"
|
||||
/>
|
||||
</a>
|
||||
</div>
|
||||
<div className="col col--2">
|
||||
<a href="/docs/authenticate/oidc/okta/">
|
||||
<img
|
||||
width="109px"
|
||||
height="41px"
|
||||
alt="okta logo"
|
||||
src="https://user-images.githubusercontent.com/167144/218770967-9615c64a-c948-448b-9019-0226c1e3e086.png"
|
||||
/>
|
||||
</a>
|
||||
</div>
|
||||
<div className="col col--2">
|
||||
<a href="/docs/authenticate/oidc/onelogin/">
|
||||
<img
|
||||
width="109px"
|
||||
height="41px"
|
||||
alt="onelogin logo"
|
||||
src="https://user-images.githubusercontent.com/167144/218770990-6959fb55-ebf3-417e-a75b-1981cf86bab0.png"
|
||||
/>
|
||||
</a>
|
||||
</div>
|
||||
<div className="col col--2">
|
||||
<a href="/docs/authenticate/oidc/azuread/">
|
||||
<img
|
||||
width="109px"
|
||||
height="41px"
|
||||
alt="azure logo"
|
||||
src="https://user-images.githubusercontent.com/167144/218771000-ff5616d7-f391-4c75-9806-09e5bf1a6a91.png"
|
||||
/>
|
||||
</a>
|
||||
</div>
|
||||
<div className="col col--2">
|
||||
<a href="/docs/authenticate/saml/jumpcloud/">
|
||||
<img
|
||||
width="109px"
|
||||
height="41px"
|
||||
alt="jumpcloud logo"
|
||||
src="https://user-images.githubusercontent.com/167144/218771019-fb525e97-ec0c-465e-8160-a547a54feab2.png"
|
||||
/>
|
||||
</a>
|
||||
</div>
|
||||
</div>
|
||||
</div>
|
||||
|
||||
<hr className="margin-vert--xl" />
|
||||
|
||||
<div className="container">
|
||||
<center>
|
||||
<h2 className="margin-bottom--lg">Who can benefit from Firezone?</h2>
|
||||
</center>
|
||||
<p>Easy to deploy and manage for individuals and organizations alike.</p>
|
||||
</div>
|
||||
|
||||
<div className="container margin-top--lg">
|
||||
<div className="row">
|
||||
<div className="col col--6">
|
||||
<div className="card">
|
||||
<div class="card__header">
|
||||
<h4>Individuals and home lab users</h4>
|
||||
</div>
|
||||
<div className="card__body">
|
||||
<p>
|
||||
Lightweight and fast. Access your home network securely when on the
|
||||
road.
|
||||
</p>
|
||||
<ul>
|
||||
<li>Effortless to deploy on any infrastructure</li>
|
||||
<li>Community plan supports unlimited devices</li>
|
||||
<li>Open-source and self-hosted</li>
|
||||
</ul>
|
||||
</div>
|
||||
<div class="card__footer">
|
||||
<a href="/docs">Access your personal project ></a>
|
||||
</div>
|
||||
</div>
|
||||
</div>
|
||||
<div className="col col--6">
|
||||
<div className="card">
|
||||
<div class="card__header">
|
||||
<h4>Growing businesses</h4>
|
||||
</div>
|
||||
<div className="card__body">
|
||||
<p>
|
||||
Keep up with increasing network and compliance demands as you scale
|
||||
your team and infrastructure.
|
||||
</p>
|
||||
<ul>
|
||||
<li>Integrate your identity provider</li>
|
||||
<li>Quickly onboard/offboard employees</li>
|
||||
<li>Segment access for contractors</li>
|
||||
<li>High performance, reduce bottlenecks</li>
|
||||
</ul>
|
||||
</div>
|
||||
<div className="card__footer">
|
||||
<a href="/docs">Scale your secure access ></a>
|
||||
</div>
|
||||
</div>
|
||||
</div>
|
||||
</div>
|
||||
<div className="row margin-top--md">
|
||||
<div className="col col--6">
|
||||
<div className="card">
|
||||
<div class="card__header">
|
||||
<h4>Remote organizations</h4>
|
||||
</div>
|
||||
<div className="card__body">
|
||||
<p>
|
||||
Transitioning to remote? Perfect timing to replace the legacy VPN.
|
||||
Improve your security posture and reduce support tickets.
|
||||
</p>
|
||||
<ul>
|
||||
<li>Require periodic re-authentication</li>
|
||||
<li>Enforce MFA / 2FA</li>
|
||||
<li>Self-serve user portal</li>
|
||||
<li>Export logs to your observability platform</li>
|
||||
</ul>
|
||||
</div>
|
||||
<div className="card__footer">
|
||||
<a href="/docs">Secure your remote workforce ></a>
|
||||
</div>
|
||||
</div>
|
||||
</div>
|
||||
<div className="col col--6">
|
||||
<div className="card">
|
||||
<div class="card__header">
|
||||
<h4>Technical IT teams</h4>
|
||||
</div>
|
||||
<div className="card__body">
|
||||
<p>
|
||||
Firezone runs on your infrastructure. Customize it to suit your
|
||||
needs and architecture.
|
||||
</p>
|
||||
<ul>
|
||||
<li>Built on WireGuard®</li>
|
||||
<li>No vendor lock-in</li>
|
||||
<li>Supports OIDC and SAML 2.0</li>
|
||||
<li>Flexible and configurable</li>
|
||||
</ul>
|
||||
</div>
|
||||
<div className="card__footer">
|
||||
<a href="/docs">Explore the documentation ></a>
|
||||
</div>
|
||||
</div>
|
||||
</div>
|
||||
</div>
|
||||
</div>
|
||||
|
||||
<hr className="margin-vert--xl" />
|
||||
|
||||
<center>
|
||||
<h2>Ready to get started?</h2>
|
||||
</center>
|
||||
|
||||
<p>
|
||||
Set up secure access and start onboarding users in minutes. Run the install
|
||||
script on a supported host to deploy Firezone with Docker. Copy the one-liner
|
||||
below to install Firezone in minutes.
|
||||
</p>
|
||||
|
||||
<InstallBlock />
|
||||
@@ -1,8 +0,0 @@
|
||||
## Need additional help?
|
||||
|
||||
Try asking on one of our community-powered support channels:
|
||||
|
||||
- [Discussion Forums](https://discourse.firez.one/?utm_source=docs.firezone.dev): Ask questions, report bugs,
|
||||
and suggest features.
|
||||
- [Public Slack Group](https://join.slack.com/t/firezone-users/shared_invite/zt-111043zus-j1lP_jP5ohv52FhAayzT6w):
|
||||
join discussions, meet other users, and meet the contributors
|
||||
@@ -1,25 +0,0 @@
|
||||
// Import the original mapper
|
||||
import MDXComponents from "@theme-original/MDXComponents";
|
||||
import AsciinemaPlayer from '@site/src/components/AsciinemaPlayer';
|
||||
import HubspotForm from '@site/src/components/HubspotForm';
|
||||
import InstallBlock from "@site/src/components/InstallBlock";
|
||||
import AccentBlock from "@site/src/components/AccentBlock";
|
||||
import Feedback from "@site/src/components/Feedback";
|
||||
import SignUp from "@site/src/components/SignUp";
|
||||
import Tabs from "@theme/Tabs";
|
||||
import TabItem from "@theme/TabItem";
|
||||
|
||||
export default {
|
||||
// Re-use the default mapping
|
||||
...MDXComponents,
|
||||
// Map the "highlight" tag to our <Highlight /> component!
|
||||
// `Highlight` will receive all props that were passed to `highlight` in MDX
|
||||
AsciinemaPlayer: AsciinemaPlayer,
|
||||
HubspotForm: HubspotForm,
|
||||
InstallBlock: InstallBlock,
|
||||
accentblock: AccentBlock,
|
||||
feedback: Feedback,
|
||||
newsletter: SignUp,
|
||||
Tabs: Tabs,
|
||||
TabItem: TabItem,
|
||||
};
|
||||
Binary file not shown.
|
Before Width: | Height: | Size: 15 KiB |
@@ -1 +0,0 @@
|
||||
<svg viewBox='0 0 24 24' xmlns='http://www.w3.org/2000/svg'><path fill='white' d='M12 .297c-6.63 0-12 5.373-12 12 0 5.303 3.438 9.8 8.205 11.385.6.113.82-.258.82-.577 0-.285-.01-1.04-.015-2.04-3.338.724-4.042-1.61-4.042-1.61C4.422 18.07 3.633 17.7 3.633 17.7c-1.087-.744.084-.729.084-.729 1.205.084 1.838 1.236 1.838 1.236 1.07 1.835 2.809 1.305 3.495.998.108-.776.417-1.305.76-1.605-2.665-.3-5.466-1.332-5.466-5.93 0-1.31.465-2.38 1.235-3.22-.135-.303-.54-1.523.105-3.176 0 0 1.005-.322 3.3 1.23.96-.267 1.98-.399 3-.405 1.02.006 2.04.138 3 .405 2.28-1.552 3.285-1.23 3.285-1.23.645 1.653.24 2.873.12 3.176.765.84 1.23 1.91 1.23 3.22 0 4.61-2.805 5.625-5.475 5.92.42.36.81 1.096.81 2.22 0 1.606-.015 2.896-.015 3.286 0 .315.21.69.825.57C20.565 22.092 24 17.592 24 12.297c0-6.627-5.373-12-12-12'/></svg>
|
||||
|
Before Width: | Height: | Size: 804 B |
@@ -1 +0,0 @@
|
||||
<svg viewBox='0 0 24 24' xmlns='http://www.w3.org/2000/svg'><path d='M12 .297c-6.63 0-12 5.373-12 12 0 5.303 3.438 9.8 8.205 11.385.6.113.82-.258.82-.577 0-.285-.01-1.04-.015-2.04-3.338.724-4.042-1.61-4.042-1.61C4.422 18.07 3.633 17.7 3.633 17.7c-1.087-.744.084-.729.084-.729 1.205.084 1.838 1.236 1.838 1.236 1.07 1.835 2.809 1.305 3.495.998.108-.776.417-1.305.76-1.605-2.665-.3-5.466-1.332-5.466-5.93 0-1.31.465-2.38 1.235-3.22-.135-.303-.54-1.523.105-3.176 0 0 1.005-.322 3.3 1.23.96-.267 1.98-.399 3-.405 1.02.006 2.04.138 3 .405 2.28-1.552 3.285-1.23 3.285-1.23.645 1.653.24 2.873.12 3.176.765.84 1.23 1.91 1.23 3.22 0 4.61-2.805 5.625-5.475 5.92.42.36.81 1.096.81 2.22 0 1.606-.015 2.896-.015 3.286 0 .315.21.69.825.57C20.565 22.092 24 17.592 24 12.297c0-6.627-5.373-12-12-12'/></svg>
|
||||
|
Before Width: | Height: | Size: 791 B |
@@ -1,5 +0,0 @@
|
||||
<svg width="228" height="184" viewBox="0 0 228 184" fill="none" xmlns="http://www.w3.org/2000/svg">
|
||||
<path fill-rule="evenodd" clip-rule="evenodd" d="M145.858 0C190.958 37.5635 144.268 120.815 160.744 154.43C126.887 105.847 173.016 64.0952 145.858 0Z" fill="#EF7A30"/>
|
||||
<path fill-rule="evenodd" clip-rule="evenodd" d="M170.867 72.3025C200.346 91.4569 164.96 136.337 183.798 147.825C202.876 159.46 200.717 111.106 227.059 123.51C199.632 114.179 211.01 171.748 177.025 164.087C138.134 155.319 186.501 93.4581 170.867 72.3025Z" fill="#7F3900"/>
|
||||
<path fill-rule="evenodd" clip-rule="evenodd" d="M0 137.888C56.1454 93.1552 132.622 164.939 168.711 169.425C215.123 175.192 202.76 121.53 225.99 123.53C204.585 126.111 217.433 182.233 169.576 183.967C117.459 185.856 65.4612 106.395 9.60305e-05 137.888H0Z" fill="#331700"/>
|
||||
</svg>
|
||||
|
Before Width: | Height: | Size: 821 B |
@@ -1,3 +0,0 @@
|
||||
<!-- Start of HubSpot Embed Code -->
|
||||
<script type="text/javascript" id="hs-script-loader" async defer src="//js.hs-scripts.com/23723443.js"></script>
|
||||
<!-- End of HubSpot Embed Code -->
|
||||
Some files were not shown because too many files have changed in this diff Show More
Reference in New Issue
Block a user